| Bridging larger gaps in peripheral nerves using neural prosthetics and physical therapeutic agents Muhammad Sana Ullah Sahar, Matthew Barton, Geoffrey Douglas Tansley Neural Regeneration Research 2019 14(7):1109-1115 Peripheral nerve injuries are relatively common and can be caused by a variety of traumatic events such as motor vehicle accidents. They can lead to long-term disability, pain, and financial burden, and contribute to poor quality of life. In this review, we systematically analyze the contemporary literature on peripheral nerve gap management using nerve prostheses in conjunction with physical therapeutic agents. The use of nerve prostheses to assist nerve regeneration across large gaps (> 30 mm) has revolutionized neural surgery. The materials used for nerve prostheses have been greatly refined, making them suitable for repairing large nerve gaps. However, research on peripheral nerve gap management using nerve prostheses reports inconsistent functional outcomes, especially when prostheses are integrated with physical therapeutic agents, and thus warrants careful investigation. This review explores the effectiveness of nerve prostheses for bridging large nerve gaps and then addresses their use in combination with physical therapeutic agents. |
| Magnesium: Pathophysiological mechanisms and potential therapeutic roles in intracerebral hemorrhage Jason J Chang, Rocco Armonda, Nitin Goyal, Adam S Arthur Neural Regeneration Research 2019 14(7):1116-1121 Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) remains the second-most common form of stroke with high morbidity and mortality. ICH can be divided into two pathophysiological stages: an acute primary phase, including hematoma volume expansion, and a subacute secondary phase consisting of blood-brain barrier disruption and perihematomal edema expansion. To date, all major trials for ICH have targeted the primary phase with therapies designed to reduce hematoma expansion through blood pressure control, surgical evacuation, and hemostasis. However, none of these trials has resulted in improved clinical outcomes. Magnesium is a ubiquitous element that also plays roles in vasodilation, hemostasis, and blood-brain barrier preservation. Animal models have highlighted potential therapeutic roles for magnesium in neurological diseases specifically targeting these pathophysiological mechanisms. Retrospective studies have also demonstrated inverse associations between admission magnesium levels and hematoma volume, hematoma expansion, and clinical outcome in patients with ICH. These associations, coupled with the multifactorial role of magnesium that targets both primary and secondary phases of ICH, suggest that magnesium may be a viable target of study in future ICH studies. |
| Network-centric medicine for peripheral nerve injury: Treating the whole to boost endogenous mechanisms of neuroprotection and regeneration David Romeo-Guitart, Caty Casas Neural Regeneration Research 2019 14(7):1122-1128 Peripheral nerve injuries caused by accidents may lead to paralysis, sensory disturbances, anaesthesia, and lack of autonomic functions. Functional recovery after disconnection of the motoneuronal soma from target tissue with proximal rupture of axons is determined by several factors: motoneuronal soma viability, proper axonal sprouting across inhibitory zones and elongation toward specific muscle, effective synapse contact rebuilding, and prevention of muscle atrophy. Therapies, such as adjuvant drugs with pleiotropic effects, that promote functional recovery after peripheral nerve injury are needed. Toward this aim, we designed a drug discovery workflow based on a network-centric molecular vision using unbiased proteomic data and neural artificial computational tools. Our focus is on boosting intrinsic capabilities of neurons for neuroprotection; this is in contrast to the common approach based on suppression of a pathobiological pathway known to be associated with disease condition. Using our workflow, we discovered neuroheal, a combination of two repurposed drugs that promotes motoneuronal soma neuroprotection, is anti-inflammatory, enhances axonal regeneration after axotomy, and reduces muscle atrophy. This drug discovery workflow has thus yielded a therapy that is close to its clinical application. |
| Exogenous neural stem cell transplantation for cerebral ischemia Ling-Yi Liao, Benson Wui-Man Lau, Dalinda Isabel Sánchez-Vidaña, Qiang Gao Neural Regeneration Research 2019 14(7):1129-1137 Cerebral ischemic injury is the main manifestation of stroke, and its incidence in stroke patients is 70–80%. Although ischemic stroke can be treated with tissue-type plasminogen activator, its time window of effectiveness is narrow. Therefore, the incidence of paralysis, hypoesthesia, aphasia, dysphagia, and cognitive impairment caused by cerebral ischemia is high. Nerve tissue regeneration can promote the recovery of the aforementioned dysfunction. Neural stem cells can participate in the reconstruction of the damaged nervous system and promote the recovery of nervous function during self-repair of damaged brain tissue. Neural stem cell transplantation for ischemic stroke has been a hot topic for more than 10 years. This review discusses the treatment of ischemic stroke with neural stem cells, as well as the mechanisms of their involvement in stroke treatment. |
| Potential therapeutic molecular targets for blood-brain barrier disruption after subarachnoid hemorrhage Hideki Kanamaru, Hidenori Suzuki Neural Regeneration Research 2019 14(7):1138-1143 Aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage remains serious hemorrhagic stroke with high morbidities and mortalities. Aneurysm rupture causes arterial bleeding-induced mechanical brain tissue injuries and elevated intracranial pressure, followed by global cerebral ischemia. Post-subarachnoid hemorrhage ischemia, tissue injuries as well as extravasated blood components and the breakdown products activate microglia, astrocytes and Toll-like receptor 4, and disrupt blood-brain barrier associated with the induction of many inflammatory and other cascades. Once blood-brain barrier is disrupted, brain tissues are directly exposed to harmful blood contents and immune cells, which aggravate brain injuries furthermore. Blood-brain barrier disruption after subarachnoid hemorrhage may be developed by a variety of mechanisms including endothelial cell apoptosis and disruption of tight junction proteins. Many molecules and pathways have been reported to disrupt the blood-brain barrier after subarachnoid hemorrhage, but the exact mechanisms remain unclear. Multiple independent and/or interconnected signaling pathways may be involved in blood-brain barrier disruption after subarachnoid hemorrhage. This review provides recent understandings of the mechanisms and the potential therapeutic targets of blood-brain barrier disruption after subarachnoid hemorrhage. |
| Choroid plexus tumor necrosis factor receptor 1: A new neuroinflammatory piece of the complex Alzheimer's disease puzzle Sophie Steeland, Roosmarijn E Vandenbroucke Neural Regeneration Research 2019 14(7):1144-1147 Due to the aging of the population and despite the enormous scientific effort, Alzheimer’s disease remains one of the biggest medical and pharmaceutical challenges in current medicine. Novel insights highlight the importance of neuroinflammation as an undeniable player in the onset and progression of Alzheimer’s disease. Tumor necrosis factor is a master inflammatory cytokine that signals via tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 and tumor necrosis factor receptor 2, but that also regulates several brain functions in health and disease. However, clinical trials investigating drugs that interfere with the tumor necrosis factor pathway in Alzheimer’s disease led to inconclusive results, partially because not only the pro-inflammatory tumor necrosis factor/tumor necrosis factor receptor 1, but also the beneficial tumor necrosis factor/tumor necrosis factor receptor 2 signaling was antagonized in these trials. We recently found that tumor necrosis factor is the main upregulated cytokine in the choroid plexus of Alzheimer’s disease patients, signaling via tumor necrosis factor receptor 1. In agreement with this, choroidal tumor necrosis factor/tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 signaling was also upregulated in different Alzheimer’s disease mouse models. Interestingly, both genetic and nanobody-based pharmacological blockage of tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 signaling was accompanied by favorable effects on Alzheimer’s disease-associated inflammation, choroidal morphology and cognitive functioning. Here, we briefly summarize the detrimental effects that can be mediated by tumor necrosis factor/tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 signaling in (early) Alzheimer’s disease, and the consequences this might have on the disease progression. As the main hypothesis in Alzheimer’s disease clinical trials is still based on the amyloid beta-cascade, the importance of Alzheimer’s disease-associated neuroinflammation urge the development of novel therapeutic strategies that might be effective in the early stages of Alzheimer’s disease and prevent the irreversible neurodegeneration and resulting memory decline. |
| Transcriptional dysregulation in neurodegenerative diseases: Who tipped the balance of Yin Yang 1 in the brain? Zhefan Stephen Chen, Ho Yin Edwin Chan Neural Regeneration Research 2019 14(7):1148-1151 Yin Yang 1 (YY1) is a multi-functional transcription factor that regulates gene expression in a range of cell types, including neurons. It controls neuronal differentiation, as well as neuronal specification and migration during the development of the mammalian nervous system. Besides, YY1 also mediates the transcription of genes that are required for neuronal survival. An impairment of the transcriptional function of YY1 causes neuronal death. This review summarizes recent research findings that unveil the dysfunction of YY1 in multiple neurodegenerative disorders. The expression of disease proteins perturbs the function of YY1 via distinct molecular mechanisms, including recruitment to protein aggregates, protein degradation and aberrant nuclear/cytoplasmic shuttling. Understanding the pathogenic roles of YY1 will further broaden our knowledge of the disease mechanisms in distinct neurodegenerative disorders. |
| Effects of Ginkgo biloba extract EGb761 on neural differentiation of stem cells offer new hope for neurological disease treatment Chao Ren, Yong-Qiang Ji, Hong Liu, Zhe Wang, Jia-Hui Wang, Cai-Yi Zhang, Li-Na Guan, Pei-Yuan Yin Neural Regeneration Research 2019 14(7):1152-1157 Stem cell transplantation has brought new hope for the treatment of neurological diseases. The key to stem cell therapy lies in inducing the specific differentiation of stem cells into nerve cells. Because the differentiation of stem cells in vitro and in vivo is affected by multiple factors, the final differentiation outcome is strongly associated with the microenvironment in which the stem cells are located. Accordingly, the optimal microenvironment for inducing stem cell differentiation is a hot topic. EGb761 is extracted from the leaves of the Ginkgo biloba tree. It is used worldwide and is becoming one of the focuses of stem cell research. Studies have shown that EGb761 can antagonize oxygen free radicals, stabilize cell membranes, promote neurogenesis and synaptogenesis, increase the level of brain-derived neurotrophic factors, and replicate the environment required during the differentiation of stem cells into nerve cells. This offers the possibility of using EGb761 to induce the differentiation of stem cells, facilitating stem cell transplantation. To provide a comprehensive reference for the future application of EGb761 in stem cell therapy, we reviewed studies investigating the influence of EGb761 on stem cells. These started with the composition and neuropharmacology of EGb761, and eventually led to the finding that EGb761 and some of its important components play important roles in the differentiation of stem cells and the protection of a beneficial microenvironment for stem cell transplantation. |
| Amelioration of Alzheimer's disease pathology and cognitive deficits by immunomodulatory agents in animal models of Alzheimer's disease Bridget Martinez, Philip V Peplow Neural Regeneration Research 2019 14(7):1158-1176 The most common age-related neurodegenerative disease is Alzheimer’s disease (AD) characterized by aggregated amyloid-β (Aβ) peptides in extracellular plaques and aggregated hyperphosphorylated tau protein in intraneuronal neurofibrillary tangles, together with loss of cholinergic neurons, synaptic alterations, and chronic inflammation within the brain. These lead to progressive impairment of cognitive function. There is evidence of innate immune activation in AD with microgliosis. Classically-activated microglia (M1 state) secrete inflammatory and neurotoxic mediators, and peripheral immune cells are recruited to inflammation sites in the brain. The few drugs approved by the US FDA for the treatment of AD improve symptoms but do not change the course of disease progression and may cause some undesirable effects. Translation of active and passive immunotherapy targeting Aβ in AD animal model trials had limited success in clinical trials. Treatment with immunomodulatory/anti-inflammatory agents early in the disease process, while not preventive, is able to inhibit the inflammatory consequences of both Aβ and tau aggregation. The studies described in this review have identified several agents with immunomodulatory properties that alleviated AD pathology and cognitive impairment in animal models of AD. The majority of the animal studies reviewed had used transgenic models of early-onset AD. More effort needs to be given to creat models of late-onset AD. The effects of a combinational therapy involving two or more of the tested pharmaceutical agents, or one of these agents given in conjunction with one of the cell-based therapies, in an aged animal model of AD would warrant investigation. |
| Precision medicine in pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration Mónica Alvarez-Cordoba, Marina Villanueva-Paz, Irene Villalón-García, Suleva Povea-Cabello, Juan M Suárez-Rivero, Marta Talaverón-Rey, Javier Abril-Jaramillo, Ana Belén Vintimilla-Tosi, José A Sánchez-Alcázar Neural Regeneration Research 2019 14(7):1177-1185 Neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation is a broad term that describes a heterogeneous group of progressive and invalidating neurologic disorders in which iron deposits in certain brain areas, mainly the basal ganglia. The predominant clinical symptoms include spasticity, progressive dystonia, Parkinson’s disease-like symptoms, neuropsychiatric alterations, and retinal degeneration. Among the neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation disorders, the most frequent subtype is pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration (PKAN) caused by defects in the gene encoding the enzyme pantothenate kinase 2 (PANK2) which catalyzed the first reaction of the coenzyme A biosynthesis pathway. Currently there is no effective treatment to prevent the inexorable course of these disorders. The aim of this review is to open up a discussion on the utility of using cellular models derived from patients as a valuable tool for the development of precision medicine in PKAN. Recently, we have described that dermal fibroblasts obtained from PKAN patients can manifest the main pathological changes of the disease such as intracellular iron accumulation accompanied by large amounts of lipofuscin granules, mitochondrial dysfunction and a pronounced increase of markers of oxidative stress. In addition, PKAN fibroblasts showed a morphological senescence-like phenotype. Interestingly, pantothenate supplementation, the substrate of the PANK2 enzyme, corrected all pathophysiological alterations in responder PKAN fibroblasts with low/residual PANK2 enzyme expression. However, pantothenate treatment had no favourable effect on PKAN fibroblasts harbouring mutations associated with the expression of a truncated/incomplete protein. The correction of pathological alterations by pantothenate in individual mutations was also verified in induced neurons obtained by direct reprograming of PKAN fibroblasts. Our observations indicate that pantothenate supplementation can increase/stabilize the expression levels of PANK2 in specific mutations. Fibroblasts and induced neurons derived from patients can provide a useful tool for recognizing PKAN patients who can respond to pantothenate treatment. The presence of low but significant PANK2 expression which can be increased in particular mutations gives valuable information which can support the treatment with high dose of pantothenate. The evaluation of personalized treatments in vitro of fibroblasts and neuronal cells derived from PKAN patients with a wide range of pharmacological options currently available, and monitoring its effect on the pathophysiological changes, can help for a better therapeutic strategy. In addition, these cell models will be also useful for testing the efficacy of new therapeutic options developed in the future. |
Medicine by Alexandros G. Sfakianakis,Anapafseos 5 Agios Nikolaos 72100 Crete Greece,00302841026182,00306932607174,alsfakia@gmail.com,
Αρχειοθήκη ιστολογίου
-
►
2023
(272)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (141)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (131)
-
►
2022
(2066)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (80)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (170)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (190)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (203)
-
►
2021
(7399)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (186)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (472)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (851)
-
►
2020
(2517)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (792)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (21)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (28)
-
▼
2019
(12076)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (19)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (54)
-
▼
Φεβρουαρίου
(4765)
-
▼
Φεβ 25
(156)
- Neural Regeneration Research (Neural Regen Res)
- Mediterranean diet, alkaline water may be as effec...
- US climate and oceans agency hit by leadership sha...
- US climate and oceans agency hit by leadership sha...
- Dentin hypersensitivity monitored by cold air quan...
- Progression of Albuminuria Among Patients with Typ...
- Interview: Students have embraced the VR program a...
- Influenza Diagnostic Methods: RT-PCR vs. RIDTs
- Medtronic revises IN.PACT post-market study data d...
- Handles VG-05
- Positive two-year results for Kardiozis EVAR devic...
- Researchers are working on a pill that could cure ...
- SPOTTED: Stirring Water Bath
- Handle Series AE “Clean Line / Medical Line”
- IDS 2019 Cologne Germany
- Comparative Efficacy of Therapies for Treatment of...
- Health Care in 2030: Will Artificial Intelligence ...
- Comparing the Effectiveness of Depression Treatmen...
- Performance Characteristics of Fecal Immunochemica...
- ASCENDing to New Heights in Our Understanding of t...
- Predicting Bleeding Risk to Guide Aspirin Use for ...
- Are We There Yet? Another Milepost in the Journey ...
- Bloodletting to Treat Severe Hypertriglyceridemia
- Why What You May Not Know About Fecal Immunochemic...
- A quest for silver sparked epic voyages by an anci...
- Clouds' cooling effect could vanish in a warmer world
- The humble wild plant that made the strawberry suc...
- [ASAP] Amino Acid-Assisted Construction of Single-...
- [ASAP] Two Non-p-Conjugated Deep-UV Nonlinear Opti...
- [ASAP] Ruthenium(II)-Catalyzed Enantioselective ?-...
- The humble wild plant that made the strawberry suc...
- Clouds' cooling effect could vanish in a warmer world
- A quest for silver sparked epic voyages by an anci...
- Are there benefits from using bone-borne maxillary...
- Satisfaction and Awareness of Systemic Psoriasis T...
- Satisfaction and Awareness of Systemic Psoriasis T...
- Supply-Side Climate Policy: On the Role of Explora...
- Pesticide use and incident hyperthyroidism in farm...
- Environmental asbestos exposure in childhood and r...
- Response to: 'Are children more vulnerable to meso...
- Long-term transportation noise exposure and incide...
- Performance of specific immunoglobulin E tests for...
- Evidence for moiré excitons in van der Waals heter...
- The skeleton articulated
- Wanted: climate leadership for the World Bank
- Signatures of moiré-trapped valley excitons in MoS...
- Observation of moiré excitons in WSe2/WS2 heterost...
- The IFN-γ–p38, ERK kinase axis exacerbates neutrop...
- [ASAP] Mitigation of Hydrophobicity-Induced Immuno...
- Referees in 2018
- Evidence for moiré excitons in van der Waals heter...
- Signatures of moiré-trapped valley excitons in MoS...
- Observation of moiré excitons in WSe2/WS2 heterost...
- Prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus among hepat...
- Evaluation of the effect of insulin sensitivity-en...
- WOMEN's Knowledge of Obstetric Danger signs in Eth...
- Screening for periodontal diseases by non-dental h...
- Gender-based violence among female youths in educa...
- Successful Defibrillation of Four Hypothermic Pati...
- Wanted: climate leadership for the World Bank
- Bioengineering of microbial transglutaminase for b...
- [ASAP] K Atom Promotion of O2 Chemisorption on Au(...
- The IFN-γ–p38, ERK kinase axis exacerbates neutrop...
- The skeleton articulated
- The race for enzymatic DNA synthesis heats up
- Influence of the fat/carbohydrate component of sna...
- Hypersynchronicity in the default mode-like networ...
- High-fructose diet initiated during adolescence do...
- Construction of a 6/5/9-membered tricyclic structu...
- Feasibility of quantitative MR-perfusion imaging t...
- New satellite-based estimates show significant tre...
- Peptide-oligourea hybrids analogue of GLP-1 with i...
- Author Correction: Growth hormone regulates neuroe...
- Hybridization is a recurrent evolutionary stimulus...
- Publisher Correction: A meiosis-specific BRCA2 bin...
- Author Correction: Planar and van der Waals hetero...
- Assembly and functionality of the ribosome with te...
- A molecular mechanism for transthyretin amyloidoge...
- Dynamic network coding of working-memory domains a...
- The race for enzymatic DNA synthesis heats up
- Timing of Parathyroidectomy Does Not Influence Ren...
- The Use of Prophylactic Somatostatin Therapy Foll...
- Performance and emission characteristics analysis ...
- Stability and uptake of methylphenidate and ritali...
- Antioxidant and cytoprotective effects of N -acety...
- Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Arising in Mucinous Cyst...
- Changes in Clostridium ( Clostridioides ) difficil...
- When Jump Height is not a Good Indicator of Lower ...
- Comment on: “Effects of Carbohydrate Mouth Rinse o...
- Reply to Li et al.: Comment on “Effects of Carbohy...
- Current Anti-Doping Crisis: The Limits of Medical ...
- Electroclinical insights into autoimmune epilepsy.
- Co-medication and potential drug interactions amon...
- From adagio to allegretto: The changing tempo of t...
- Volume-Staged CyberKnife Stereotactic Radiosurgery...
- Risk Factors for Development of and Progression of...
- Re-assessment of the high-grade serous ovarian can...
- Incidence of brain metastasis in lung adenocarcino...
- Volume-Staged CyberKnife Stereotactic Radiosurgery...
- Nucleus Accumbens (NAc) DBS for obsessive compulsi...
-
▼
Φεβ 25
(156)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (5155)
-
►
2018
(3144)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (3144)
Ετικέτες
Πληροφορίες
Δευτέρα 25 Φεβρουαρίου 2019
Neural Regeneration Research (Neural Regen Res)
Mediterranean diet, alkaline water may be as effective as PPIs for laryngopharyngeal reflux
US climate and oceans agency hit by leadership shake-up
US climate and oceans agency hit by leadership shake-up
US climate and oceans agency hit by leadership shake-up, Published online: 26 February 2019; doi:10.1038/d41586-019-00702-z
Former industry scientist Neil Jacobs takes over as acting chief of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, in sudden switch.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2U6QkEQ
US climate and oceans agency hit by leadership shake-up
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2T4egMN
Dentin hypersensitivity monitored by cold air quantitative sensory testing
Abstract
Background
Quantification of dentin hypersensitivity (DH) is challenging and requires standardized, graded stimulation by natural‐like stimuli.
Objective
The present study aimed at identifying DH subjects and longitudinally monitoring their pain thresholds by cold air quantitative sensory testing (QST).
Methods
Subject recruitment started with an online DH questionnaire. Respondents were screened by dental air stimulation. Sensitizing and habituating subjects were excluded. A recently developed stimulation device was employed for cold air QST. Single tooth DH was verified by applying an equi‐intense stimulus to a control tooth. Descriptive statistics were applied for subject characteristics. Mean values were calculated for the stimulation parameters temperature and air flow. Reliability of temperatures for detecting pain and for evoking moderate pain over multiple time points within a three weeks period were analyzed by two‐way random single and average measures intra‐class correlation coefficients.
Results
353 persons completed the online DH questionnaire of which 117 were screened. 44 passed the screening, yet 15 were excluded for various reasons. 29 subjects were monitored by QST across three weeks. Results revealed a high intra‐individual stability of the temperature inducing moderate to strong pain intensity (MPI) (single measures ICC of TMPI 0.83, p < 0.001). Mean TMPI was ‐13.69 °C, yet it highly varied among the 29 subjects (SD±10.04 °C).
Conclusions
Using a novel approach, namely dental QST based on cold air stimuli, we present evidence for temporally stable DH perceptions over a three weeks period. The method fulfills international guideline requirements and is recommendable for obtaining valid results when testing various interventions for DH management.
This article is protected by copyright. All rights reserved.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2NtYc0C
Progression of Albuminuria Among Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Long Term Observational Follow-up Study

Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes
DOI: 10.1055/a-0848-8076
Background The purpose of the present study was to determine whether patients with DM1 have shown improvement, stabilization or deterioration of their urine albumin excretion levels during a close follow-up. Patients and Methods A cohort of 84 patients, 18–76 years of age, a median duration of diabetes of 24 years (1–50 years) and a median follow-up duration of 12 years (1–37 years) were included in the study. Results Among the 84 patients for whom we had UAE levels at the beginning and by the end of the study, mean glycosylated hemoglobin was statistically significantly decreased during the follow-up period, from 8.02±2.04–7.06±1.05% (p=0.036). Normoalbuminuria was present in 66 patients and remained so in 56 patients while 9 patients progressed to microalbuminuria and one patient to macroalbuminuria by the end of the study. Microalbuminuria was present in 15 patients: regression was observed in 8 patients, and progression in one patient. Regression of macroalbuminuria to microalbuminuria was noted in one patient and to normoalbuminuria was noted in one participant, too. Conclusions Improvement of glycemic control with close monitoring of DM1 patients together with the appropriate use ACE or AT2 inhibitors and statins, seems to exert nephron-protective potential and to delay or even reverse the presence of micro/macroalbuminuria. This long term follow-up study has demonstrated a statistically significant increase in serum HDLcholesterol levels. The study also revealed that intensively treated diabetes patients may show reductions in serum ALP levels. Whether this finding is related to diabetic nephropathy, NAFLD, or diabetic hepatosclerosis remains to be assessed in future trials.
[...]
© Georg Thieme Verlag KG Stuttgart · New York
Article in Thieme eJournals:
Table of contents | Abstract | Full text
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2EaSZqi
Interview: Students have embraced the VR program as part of their dental anaesthetic education
How does your VR anaesthesia simulation work? Practically speaking, the student puts the VR headgear on, holds the hand controllers and interacts with the particular program he or she is working with. It requires the student to select and move the syringe, identify the injection site, position the syringe at the correct angulation, penetrate the mucosa at the correct depth, position the needle tip adjacent to the apex of the tooth and deposit the correct amount of anaesthetic solution at the...
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2StJ3Ny
Influenza Diagnostic Methods: RT-PCR vs. RIDTs
The 2017-2018 flu season in the U.S. was the worst recorded since 1976. There were an estimated 80,000 deaths and a record 900,000 hospitalizations for influenza and its complications. Rapid and accurate diagnosis of influenza can save lives by facilitating early treatment, save money by preventing inappropriate treatment, and prevent epidemics by minimizing viral transmission. For accurate diagnosis, reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR) is considered the gold standard. Rapid influenza diag...
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2XnGCQt
Medtronic revises IN.PACT post-market study data due to programming error, but conclusions remain the same
Medtronic has issued the following statement regarding revised clinical study data: Recently, Medtronic became aware of a programming error in the clinical data reporting isolated to the two- and three-year follow-up periods in our IN.PACT Global post-market study, part of the IN.PACT Admiral clinical programme for the treatment of femoropopliteal artery disease. Preliminary results of this study were first released at the Leipzig Interventional Course (LINC) and Medtronic issued a press r...
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2SrwlyN
Handles VG-05
Material and surface: Round stainless steel; material no. 1.4404; ground and brushed with dull bright finish. Design advantages: The connecting bow is arrested to the handle shank by a stainless steel grub screw M8. Scope of supply: Including hexagon head screws M10x20 DIN 933 and stainless steelwashers DIN 125. Note: Any desired handle lengths on request. Stress resistance: min. 1000 N.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2XnOvVZ
Positive two-year results for Kardiozis EVAR device using fibre embolisation
The results were presented at the Controversies And Updates in Vascular Surgery congress (CACVS; 7–9 February, Paris, France) by principal investigator Dominique Fabre. Study contributors include Frederic Cochennec, Claude Angel, Eric Allaire, Philippe Brenot, Riyad Bourkaib Jean-Yves Riou, Pascal Desgranges, Benoit Gerardin, Delphine Mitilian, Carlos Garcia Alonzo, Sarah Hamdi, Jean-Pierre Becquemin and Stéphan Haulon. The SCOPE 1 clinical trial began in 2013 under the lead of Dominique F...
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2SqkbGL
Researchers are working on a pill that could cure loneliness
Loneliness can negatively affect your health Whether we live in the countryside or in the cities, loneliness can affect everyone. However feeling lonely can also be harmful to our health as it weakens our immune system and cognitive capacities. In 2018, a Danish study stated that loneliness can also weaken the heart and can double the risk of death from a cardiovascular disease. In China, work was carried out to try and find a remedy for loneliness among the elderly. In 2017, 230 million ...
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2XnewF0
SPOTTED: Stirring Water Bath
Our Stirring Water Bath has been featured in the research of 'Insight into lmiquimod Skin Permeation and Increased delivery using microneedle pre-treatment. To view the research paper please copy and paste the following link into your search bar: https://ift.tt/2XnGv7v. Our stirring water baths are a powerful magnetic stirring mechanism combined with high wattage heating, which allows the water bath to maintain temperatures to a maximum of 9...
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2SqIm7K
Handle Series AE “Clean Line / Medical Line”
Material and surface: Profiled aluminium AlMgSi 0.5; vibratory ground and powder coated in RAL 9002 grey white or with antibacterial coating in RAL 9003. Note: Other dimensions on request. Stress resistance: min. 500 N.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2Sr5qDA
IDS 2019 Cologne Germany
Visit us at IDS 2019 Cologne Germany from 12 March to 16 March 2019. IDS-2019 Koelnmesse Hall 3.2 Aisle No: E 058.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2XnKkJW
Comparative Efficacy of Therapies for Treatment of Depression for Patients Undergoing Maintenance Hemodialysis A Randomized Clinical Trial
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2BTpbhz
Health Care in 2030: Will Artificial Intelligence Replace Physicians?
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2U3YyNL
Comparing the Effectiveness of Depression Treatments for Patients Undergoing Maintenance Hemodialysis
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2BSXmpE
Performance Characteristics of Fecal Immunochemical Tests for Colorectal Cancer and Advanced Adenomatous Polyps A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2U9dBWv
ASCENDing to New Heights in Our Understanding of the Treatment of Depression Among Individuals Receiving Hemodialysis
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2BMUSJp
Predicting Bleeding Risk to Guide Aspirin Use for the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease A Cohort Study
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2U4ch7y
Are We There Yet? Another Milepost in the Journey to Identify Appropriate Candidates for Aspirin Primary Prevention
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2BSEzut
Bloodletting to Treat Severe Hypertriglyceridemia
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2U4cyY8
Why What You May Not Know About Fecal Immunochemical Testing Matters
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2BVpw3o
A quest for silver sparked epic voyages by an ancient people
A quest for silver sparked epic voyages by an ancient people
A quest for silver sparked epic voyages by an ancient people , Published online: 25 February 2019; doi:10.1038/d41586-019-00686-w
Chemical evidence suggests that the Phoenicians had spread to the Iberian Peninsula by the ninth century bc.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2BUhSGn
Clouds' cooling effect could vanish in a warmer world
Clouds' cooling effect could vanish in a warmer world
Clouds' cooling effect could vanish in a warmer world, Published online: 25 February 2019; doi:10.1038/d41586-019-00685-x
High concentrations of atmospheric carbon dioxide can result in the dispersal of cloud banks that reflect about 30% of Earth's sunlight.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2U8P04f
The humble wild plant that made the strawberry succulent
The humble wild plant that made the strawberry succulent
The humble wild plant that made the strawberry succulent, Published online: 25 February 2019; doi:10.1038/d41586-019-00657-1
Beloved fruit has a tangled family tree — but owes much of its fragrance and sweetness to just one ancestor.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2EbnNqT
[ASAP] Amino Acid-Assisted Construction of Single-Crystalline Hierarchical Nanozeolites via Oriented-Aggregation and Intraparticle Ripening

from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2TbCN1D
[ASAP] Two Non-p-Conjugated Deep-UV Nonlinear Optical Sulfates

from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2ICT63c
[ASAP] Ruthenium(II)-Catalyzed Enantioselective ?-Lactams Formation by Intramolecular C–H Amidation of 1,4,2-Dioxazol-5-ones

from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2TeJkZq
The humble wild plant that made the strawberry succulent
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2TbxoYp
Clouds' cooling effect could vanish in a warmer world
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2IxmNTk
A quest for silver sparked epic voyages by an ancient people
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2TbxiQx
Are there benefits from using bone-borne maxillary expansion instead of tooth-borne maxillary expansion? A systematic review with meta-analysis
The aim of the current systematic review was to compare the clinical effects of bone-borne or hybrid tooth-bone-borne rapid maxillary expansion (RME) with conventional tooth-borne RME in the treatment of maxil...
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2U8MWt1
Satisfaction and Awareness of Systemic Psoriasis Treatments: A National Survey Comparing Biologic and Nonbiologic Users
Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery, Ahead of Print.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2GL1Hiu
Satisfaction and Awareness of Systemic Psoriasis Treatments: A National Survey Comparing Biologic and Nonbiologic Users
Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery, Ahead of Print.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2GL1Hiu
Supply-Side Climate Policy: On the Role of Exploration and Asymmetric Information
Abstract
In the world economy with interdependent markets for fossil fuel deposits and extracted fossil fuel, a coalition of countries may fight climate change by purchasing fossil fuel deposits for preservation. Harstad (J Polit Econ 120:77–115, 2012) has shown that the coalition's supply-side climate policy implements the first-best. The present paper focuses on the role exploration and asymmetric information with respect to climate damage plays for the efficiency of unilateral supply-side climate policy. Under the assumption of non-strategic exploration and truthful reporting of climate damage, the deposit policy turns out to be efficient. If exploration is used strategically or the coalition misreports its climate damage, however, the deposit policy becomes inefficient.
from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2TdC0gB
Pesticide use and incident hyperthyroidism in farmers in the Agricultural Health Study
Background
Few studies have evaluated associations between pesticides and hyperthyroidism.
ObjectiveWe evaluated associations between specific pesticides and incident hyperthyroidism in private pesticide applicators in the Agricultural Health Study.
MethodsWe used Cox proportional hazards models to estimate HRs and 95% CIs for associations between pesticide use at enrolment and hyperthyroidism (n=271) in 35 150 applicators (mostly men), adjusting for potential confounders.
ResultsEver use of several pesticides (organophosphate insecticide malathion, fungicide maneb/mancozeb, herbicides dicamba, metolachlor, and atrazine in overall sample and chlorimuron ethyl among those ≤62 years) was associated with reduced hyperthyroidism risk, with HRs ranging from 0.50 (95% CI 0.30 to 0.83) for maneb/mancozeb to 0.77 (95% CI 0.59 to 1.00) for atrazine. Hyperthyroidism risk was lowest among those with higher intensity-weighted lifetime days of using carbofuran and chlorpyrifos (ptrend ≤0.05).
ConclusionsObserved associations between pesticides and decreased risk of hyperthyroidism warrant further investigation.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2Eby6v2
Environmental asbestos exposure in childhood and risk of mesothelioma later in life: a long-term follow-up register-based cohort study
Objective
To examine the risk of malignant mesothelioma (MM) in former pupils who attended primary school near an asbestos cement plant.
MethodsA cohort of 12 111 former pupils, born 1940–1970, was established from individual historical records from four primary schools located at a distance of 100–750 m in the prevailing wind direction from an asbestos cement plant operating from 1928 to 1984 in Aalborg, Denmark. The school cohort and a comparison cohort consisting of 108 987 gender and 5-year frequency-matched subjects were followed up (2015) for MM in the Danish Cancer Registry. Using Cox regression, HRs were estimated for the incidence of MM. Adjustments for occupational and familial asbestos exposure were made with a job exposure matrix. An SIR analysis including latency periods testing the cancer incidence rate was performed with the comparison cohort as the reference rate.
ResultsThe median person-years of follow-up were 62.5 years in the school cohort and 62.2 years in the comparison cohort. There were 32 males and 6 females of the former pupils who developed MM during the follow-up: HRmale 7.01 (95% CI 4.24 to 11.57), HRfemale 7.43 (95% CI 2.50 to 22.13). Those who attended school 250 m north of the plant had the highest HR for MM, 10.65 (95% Cl 5.82 to 19.48). No significant trend between school distance and risk of MM was established (p=0.35).
ConclusionOur results suggest that boys and girls who attended schools and lived in the neighbourhood of an asbestos cement plant later in life have a significantly increased risk of MM.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2E9OSdV
Response to: 'Are children more vulnerable to mesothelioma than adults? A comparison of mesothelioma risk among children and adults exposed non-occupationally to blue asbestos at Wittenoom by Reid et al
Dear Sir,
We read with interest the paper published by Reid and colleagues.1 The authors aimed at comparing the risk of mesothelioma among those first exposed to asbestos as children with those first exposed as adults. In a cohort of 4704 people living near an asbestos mine and mill, they observed higher rates of mesothelioma among residents first exposed after the age of 15 years compared with those exposed during the childhood. We have a couple of concerns regarding the interpretation and the validity of the findings from Reid et al.1
The authors noted that 'The mesothelioma rate was lower among children than adults by categories of time since first exposure for all periods, although CIs overlapped (table 3)'. Moreover, the estimates reported in their table 3 are not adjusted by age (and gender). It is likely that the age distributions of those aged less than 5 years...
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2T3qQff
Long-term transportation noise exposure and incidence of ischaemic heart disease and stroke: a cohort study
Background
There is limited evidence from longitudinal studies on transportation noise from different sources and development of ischaemic heart disease (IHD) and stroke.
ObjectivesThis cohort study assessed associations between exposure to noise from road traffic, railway or aircraft and incidence of IHD and stroke.
MethodsIn a cohort of 20 012 individuals from Stockholm County, we estimated long-term residential exposure to road traffic, railway and aircraft noise. National Patient and Cause-of-Death Registers were used to identify IHD and stroke events. Information on risk factors was obtained from questionnaires and registers. Adjusted HR for cardiovascular outcomes related to source-specific noise exposure were computed using Cox proportional hazards regression.
ResultsNo clear or consistent associations were observed between transportation noise and incidence of IHD or stroke. However, noise exposure from road traffic and aircraft was related to IHD incidence in women, with HR of 1.11 (95% CI 1.00 to 1.22) and 1.25 (95% CI 1.09 to 1.44) per 10 dB Lden, respectively. For both sexes taken together, we observed a particularly high risk of IHD in those exposed to all three transportation noise sources at≥45 dB Lden, with a HR of 1.57 (95% CI 1.06 to 2.32), and a similar tendency for stroke (HR 1.42; 95% CI 0.87 to 2.32).
ConclusionNo overall associations were observed between transportation noise exposure and incidence of IHD or stroke. However, there appeared to be an increased risk of IHD in women exposed to road traffic or aircraft noise as well as in those exposed to multiple sources of transportation noise.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2SYu8QF
Performance of specific immunoglobulin E tests for diagnosing occupational asthma: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Objectives
To determine the test performance parameters for the retrievable range of high-molecular-weight (HMW) and low-molecular-weight (LMW) occupational allergens and to evaluate the impact of allergenic components and the implementation of measures for test validation.
MethodsA protocol with predefined objectives and inclusion criteria was the basis of an electronic literature search of MEDLINE and EMBASE (time period 1967–2016). The specific inhalation challenge and serial peak flow measurements were the reference standards for the specific IgE (sIgE) test parameters. All of the review procedures were reported according to Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses.
ResultsSeventy-one studies were selected, and 62 entered meta-analysis. Pooled pairs analysis indicated a sensitivity of 0.74(95% CI 0.66 to 0.80) and specificity of 0.71(95% CI 0.63 to 0.77) for HMW allergens and a sensitivity of 0.28(95% CI 0.18 to 0.40) and specificity of 0.89(95% CI 0.77 to 0.95) for LMW allergens. Component-specific analysis improved the test parameters for some allergens. Test validation was handled heterogeneously among studies.
ConclusionsIgE test performance is rather satisfactory for a wide range of HMW allergens with the potential for component-specific approaches, whereas sensitivity for LMW allergens is considerably lower, indicating methodological complications and/or divergent pathomechanisms. A common standard for test validation is needed.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2Eby0DG
Evidence for moiré excitons in van der Waals heterostructures
Evidence for moiré excitons in van der Waals heterostructures
Evidence for moiré excitons in van der Waals heterostructures, Published online: 25 February 2019; doi:10.1038/s41586-019-0975-z
Multiple interlayer exciton resonances in a MoSe2/WSe2 heterobilayer with a small twist angle are attributed to excitonic ground and excited states confined within the moiré potential.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2IA3dpq
The skeleton articulated
The skeleton articulated
The skeleton articulated, Published online: 25 February 2019; doi:10.1038/d41586-019-00679-9
Jan Zalasiewicz enjoys Brian Switek's exploration of how the human scaffold — and our ideas about it — evolved.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2tA3rmp
Wanted: climate leadership for the World Bank
Wanted: climate leadership for the World Bank
Wanted: climate leadership for the World Bank, Published online: 25 February 2019; doi:10.1038/d41586-019-00661-5
US President Donald Trump's candidate to lead the global institution could undermine its efforts to get greener. Nations need the courage to challenge the nomination.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2SlJuJW
Signatures of moiré-trapped valley excitons in MoSe2/WSe2 heterobilayers
Signatures of moiré-trapped valley excitons in MoSe2/WSe2 heterobilayers
Signatures of moiré-trapped valley excitons in MoSe<sub>2</sub>/WSe<sub>2</sub> heterobilayers, Published online: 25 February 2019; doi:10.1038/s41586-019-0957-1
The trapping of interlayer valley excitons in a moiré potential formed by a molybdenum diselenide/tungsten diselenide heterobilayer with twist angle control is reported.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2TmfAdf
Observation of moiré excitons in WSe2/WS2 heterostructure superlattices
Observation of moiré excitons in WSe2/WS2 heterostructure superlattices
Observation of moiré excitons in WSe<sub>2</sub>/WS<sub>2</sub> heterostructure superlattices, Published online: 25 February 2019; doi:10.1038/s41586-019-0976-y
Moiré superlattice exciton states are observed in WSe2/WS2 heterostructures with closely aligned layers.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2IBTBKT
The IFN-γ–p38, ERK kinase axis exacerbates neutrophilic chronic rhinosinusitis by inducing the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
The IFN-γ–p38, ERK kinase axis exacerbates neutrophilic chronic rhinosinusitis by inducing the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
The IFN-γ–p38, ERK kinase axis exacerbates neutrophilic chronic rhinosinusitis by inducing the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, Published online: 25 February 2019; doi:10.1038/s41385-019-0149-1
The IFN-γ–p38, ERK kinase axis exacerbates neutrophilic chronic rhinosinusitis by inducing the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transitionfrom A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2ILiuno
[ASAP] Mitigation of Hydrophobicity-Induced Immunotoxicity by Sugar Poly(orthoesters)

from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2tBl6Ka
Evidence for moiré excitons in van der Waals heterostructures
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2SokYba
Signatures of moiré-trapped valley excitons in MoSe2/WSe2 heterobilayers
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2XplE3u
Observation of moiré excitons in WSe2/WS2 heterostructure superlattices
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2Sqdfck
Prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus among hepatitis C virus-infected patients: a protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis
The ever-increasing global hepatitis C infection is fueling the burden of diabetes mellitus, which exaggerates various complications and may be a cause of death for millions. Several studies have reported that...
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2tFqrA8
Evaluation of the effect of insulin sensitivity-enhancing lifestyle- and dietary-related adjuncts on antidepressant treatment response: protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis
Depression is the leading cause of disability worldwide and is known to be associated with insulin resistance (IR). Insulin resistance worsens the symptoms of depression and reduces the effectiveness of antide...
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2H21uqL
WOMEN's Knowledge of Obstetric Danger signs in Ethiopia (WOMEN's KODE):a systematic review and meta-analysis
According to the 2015 World Health Organization report, globally, an estimated 10.7 million mothers died from 1990 to 2015 due to obstetric complications. This report showed that almost all global maternal dea...
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2tCN8oX
Screening for periodontal diseases by non-dental health professionals: a protocol for a systematic review and overview of reviews
Periodontal diseases are responsible for a vast burden of disease globally and are associated with other severe illnesses such as cardiovascular diseases or diabetes. Tests for early diagnosis of periodontal d...
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2H21mHN
Gender-based violence among female youths in educational institutions of Sub-Saharan Africa: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Gender-based violence is a public health issue. The prevalence of gender-based violence is high in Sub-Saharan Africa. Therefore, this study aims to produce an overall summary estimate on the prevalence of gen...
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2tCN5JN
Successful Defibrillation of Four Hypothermic Patients with Witnessed Cardiac Arrest
High Altitude Medicine &Biology, Ahead of Print.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2IAj3R5
Wanted: climate leadership for the World Bank
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2Vm3G0d
Bioengineering of microbial transglutaminase for biomedical applications
Abstract
Microbial transglutaminase (mTGase) is commonly known in the food industry as meat glue due to its incredible ability to "glue" meat proteins together. Aside from being widely exploited in the meat processing industries, mTGase is also widely applied in other food and textile industries by catalysing the formation of isopeptide bonds between peptides or protein substrates. The advancement of technology has opened up new avenues for mTGase in the field of biomedical engineering. Efforts have been made to study the structural properties of mTGase in order to gain an in-depth understanding of the structure-function relationship. This review highlights the developments in mTGase engineering together with its role in biomedical applications including biomaterial fabrication for tissue engineering and biotherapeutics.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2SXouyo
[ASAP] K Atom Promotion of O2 Chemisorption on Au(111) Surface

from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2tBWuRC
The IFN-γ–p38, ERK kinase axis exacerbates neutrophilic chronic rhinosinusitis by inducing the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2VjfyzQ
The race for enzymatic DNA synthesis heats up
The race for enzymatic DNA synthesis heats up
The race for enzymatic DNA synthesis heats up, Published online: 25 February 2019; doi:10.1038/d41586-019-00682-0
An alternative to chemical oligonucleotide synthesis inches closer to reality.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2IBpKSP
Influence of the fat/carbohydrate component of snack food on energy intake pattern and reinforcing properties in rodents
Publication date: Available online 23 February 2019
Source: Behavioural Brain Research
Author(s): Andreas Hess, Stefanie Kress, Stefan Rakete, Gerald Muench, Johannes Kornhuber, Monika Pischetsrieder, Christian P. Müller
Abstract
Hedonic intake of strongly rewarding foods is independent from biological needs and, thus, a common cause of obesity. The effect of potato chips on energy intake in a snacking model could be explained by their fat/carbohydrate content (FCHc). The present study investigated if the FCHc shapes energy intake patterns and reward processing of satiated rodents. Modulation of energy intake patterns was studied in an established snacking model offering FCHc rich food for 3 × 10 min/day to satiated rats. Reward processing was analyzed by a previously established conditioned place preference tests in satiated mice. The limited access to FCHc rich food led to higher daily energy intake compared to days without access (110 ± 10 vs. 96 ± 5 kcal/day) indicating that fat/carbohydrate intake was not fully compensated by reducing standard chow intake during the rest of the day. Furthermore, fat/carbohydrate snacking led to binge eating episodes with up to 55% of the daily energy intake consumed during limited access. Forced withdrawal from fat/carbohydrate snacking opportunities for six weeks increased the total daily energy intake and the relative amount of energy consumed by FCHc after reintroducing fat/carbohydrate snacking. Snack food and fat/carbohydrate food were powerful food reinforcers in satiated mice in contrast to standard chow. Altogether, these data suggest that the FCHc of snack food has strong reinforcing properties, which are probably responsible for the significant modulation of the amount and pattern of food intake in ad libitum fed animals.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2U5KBiA
Hypersynchronicity in the default mode-like network in a neurodevelopmental animal model with relevance for schizophrenia
Publication date: Available online 23 February 2019
Source: Behavioural Brain Research
Author(s): Stephan Missault, Cynthia Anckaerts, Soumaya Ahmadoun, Ines Blockx, Michaël Barbier, Kenny Bielen, Disha Shah, Samir Kumar-Singh, Winnok H. De Vos, Annemie Van der Linden, Stefanie Dedeurwaerdere, Marleen Verhoye
Abstract
Background
Immune activation during pregnancy is an important risk factor for schizophrenia. Brain dysconnectivity and NMDA receptor (NMDAR) hypofunction have been postulated to be central to schizophrenia pathophysiology. The aim of this study was to investigate resting-state functional connectivity (resting-state functional MRI-rsfMRI), microstructure (diffusion tension imaging-DTI) and response to NMDAR antagonist (pharmacological fMRI-phMRI) using multimodal MRI in offspring of pregnant dams exposed to immune challenge (maternal immune activation-MIA model), and determine whether these neuroimaging readouts correlate with schizophrenia-related behaviour.
Methods
Pregnant rats were injected with Poly I:C or saline on gestational day 15. The maternal weight response was assessed. Since previous research has shown behavioural deficits can differ between MIA offspring dependent on the maternal response to immune stimulus, offspring were divided into three groups: controls (saline, n = 11), offspring of dams that gained weight (Poly I:C WG, n = 12) and offspring of dams that lost weight post-MIA (Poly I:C WL, n = 16). Male adult offspring were subjected to rsfMRI, DTI, phMRI with NMDAR antagonist, behavioural testing and histological assessment.
Results
Poly I:C WL offspring exhibited increased functional connectivity in default mode-like network (DMN). Poly I:C WG offspring showed the most pronounced attenuation in NMDAR antagonist response versus controls. DTI revealed no differences in Poly I:C offspring versus controls. Poly I:C offspring exhibited anxiety.
Conclusions
MIA offspring displayed a differential pathophysiology depending on the maternal response to immune challenge. While Poly I:C WL offspring displayed hypersynchronicity in the DMN, altered NMDAR antagonist response was most pronounced in Poly I:C WG offspring.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2BPWwtE
High-fructose diet initiated during adolescence does not affect basolateral amygdala excitability or affective-like behavior in Sprague Dawley rats
Publication date: Available online 23 February 2019
Source: Behavioural Brain Research
Author(s): Brendan O'Flaherty, Gretchen N. Neigh, Donald Rainnie
Abstract
Patients with type-2 diabetes, obesity, and metabolic syndrome have a significantly increased risk of developing depression. Dysregulated metabolism may contribute to the etiology of depression by affecting neuronal activity in key limbic areas. The basolateral amygdala (BLA) acts as a critical emotional valence detector in the brain's limbic circuit, and shows hyperactivity and abnormal glucose metabolism in depressed patients. Furthermore, administering a periadolescent high-fructose diet (HFrD; a model of metabolic syndrome) to male Wistar rats increases anxiety- and depressive-like behavior. Repeated shock stress in Sprague Dawley rats similarly increases anxiety-like behavior and increases BLA excitability. We therefore investigated whether a metabolic stressor (HFrD) would have similar effects as shock stress on BLA excitability in Sprague Dawley rats. We found that a HFrD did not affect the intrinsic excitability of BLA neurons. Fructose-fed Sprague Dawley rats had elevated body fat mass, but did not show increases in metabolic efficiency and fasting blood glucose relative to control. Finally unlike Wistar rats, fructose-fed Sprague Dawley rats did not show increased anxiety- and depressive-like behavior. These results suggest that genetic differences between rat strains may affect susceptibility to a metabolic insult. Collectively, these data show that a periadolescent HFrD disrupts metabolism, but does not change affective behavior or BLA excitability in Sprague Dawley rats.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2U1YXjU
Construction of a 6/5/9-membered tricyclic structure of cladiellins via radical-polar crossover reaction
Construction of a 6/5/9-membered tricyclic structure of cladiellins via radical-polar crossover reaction
Construction of a 6/5/9-membered tricyclic structure of cladiellins via radical-polar crossover reaction, Published online: 25 February 2019; doi:10.1038/s41429-019-0150-7
Construction of a 6/5/9-membered tricyclic structure of cladiellins via radical-polar crossover reactionfrom A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2SnHLnu
Feasibility of quantitative MR-perfusion imaging to monitor treatment response after uterine artery embolization (UAE) in symptomatic uterus fibroids
Publication date: Available online 23 February 2019
Source: Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Author(s): Maliha Sadick, Jakob Richers, Benjamin Tuschy, Lothar R. Schad, Stefan O. Schoenberg, Frank G. Zöllner
Abstract
Introduction
In 25% of women, symptomatic uterus myomas are diagnosed with clinical and functional impairment ranging from abdominal and pelvic pain to dys- and hypermenorrhea, dyspareunia, pollakiuria and infertility. Women undergoing a treatment increasingly prefer nowadays minimal invasive, uterus preserving therapies like uterine artery embolization (UAE) over surgical hysterectomy, nowadays. To emphasize the efficacy of UAE as a uterus preserving treatment with targeted therapy of myomas only, analysis of tissue perfusion pre and post embolization is required. The purpose of this study was to assess treatment response in UAE in females with symptomatic uterus myomas by quantitative magnetic resonance perfusion imaging.
Methods
Seven females scheduled for uterus myoma embolization underwent three MRI examinations (pre, post, follow-up) including morphological and dynamic contrast enhanced perfusion imaging at 3 T. To measure tumor volume, regions-of-interest covering the tumor and the uterus were drawn by two readers in consensus. Blood flow, blood volume, and mean transit time were calculated by a pixel-by-pixel deconvolution approach. Kruskal-Wallis/Friedman test was employed to test whether the group medians differ significantly with correction for multiple comparisons using Bonferroni method.
Results
Change of volume could be observed in all patients after embolization but was significantly different only between pre/post and follow-up time point. Measured differences in all perfusion parameters were significant between pre-intervention and post-intervention/follow-up in the myomas, no significant differences could be detected for the uterus tissue.
Conclusions
Our results demonstrate devascularization of symptomatic myomas which correlates with cessation of hypermenorrhea in all treated patients without affecting healthy uterus tissue. Supplementing UAE with perfusion imaging to monitor early treatment response is feasible and might provide valuable information for the follow-up of patients and contribute to providing confidence for the patients in treatment success.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2BQASWq
New satellite-based estimates show significant trends in spring phenology and complex sensitivities to temperature and precipitation at northern European latitudes
Abstract
Recent climate warming has altered plant phenology at northern European latitudes, but conclusions regarding the spatial patterns of phenological change and relationships with climate are still challenging as quantitative estimates are strongly diverging. To generate consistent estimates of broad-scale spatially continuous spring plant phenology at northern European latitudes (> 50° N) from 2000 to 2016, we used a novel vegetation index, the plant phenology index (PPI), derived from MODerate-resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) data. To obtain realistic and strong estimates, the phenology trends and their relationships with temperature and precipitation over the past 17 years were analyzed using a panel data method. We found that in the studied region the start of the growing season (SOS) has on average advanced by 0.30 day year−1. The SOS showed an overall advancement rate of 2.47 day °C−1 to spring warming, and 0.18 day cm−1 to decreasing precipitation in spring. The previous winter and summer temperature had important effects on the SOS but were spatially heterogeneous. Overall, the onset of SOS was delayed 0.66 day °C−1 by winter warming and 0.56 day °C−1 by preceding summer warming. The precipitation in winter and summer influenced the SOS in a relatively weak and complex manner. The findings indicate rapid recent phenological changes driven by combined seasonal climates in northern Europe. Previously unknown spatial patterns of phenological change and relationships with climate drivers are presented that improve our capacity to understand and foresee future climate effects on vegetation.
from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2H0Jhd6
Peptide-oligourea hybrids analogue of GLP-1 with improved action in vivo
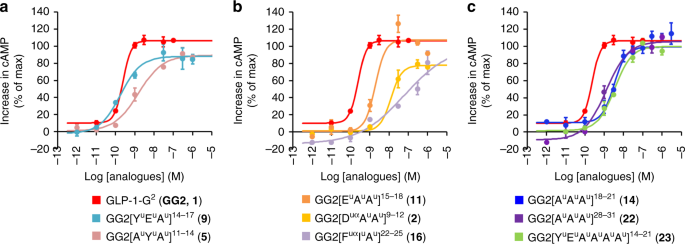
Peptide-oligourea hybrids analogue of GLP-1 with improved action in vivo
Peptide-oligourea hybrids analogue of GLP-1 with improved action in vivo, Published online: 25 February 2019; doi:10.1038/s41467-019-08793-y
The peptide hormone GLP-1 has the potential to be a remedy for diabetes type II, yet is unstable. Here, the authors synthesized α-peptide-oligourea hybrid analogues of GLP-1 some of which showing significantly prolonged activity in vivo.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2TeacbN
Author Correction: Growth hormone regulates neuroendocrine responses to weight loss via AgRP neurons
Author Correction: Growth hormone regulates neuroendocrine responses to weight loss via AgRP neurons
Author Correction: Growth hormone regulates neuroendocrine responses to weight loss via AgRP neurons, Published online: 25 February 2019; doi:10.1038/s41467-019-09022-2
Author Correction: Growth hormone regulates neuroendocrine responses to weight loss via AgRP neuronsfrom A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2T7SxCP
Hybridization is a recurrent evolutionary stimulus in wild yeast speciation
Hybridization is a recurrent evolutionary stimulus in wild yeast speciation
Hybridization is a recurrent evolutionary stimulus in wild yeast speciation, Published online: 25 February 2019; doi:10.1038/s41467-019-08809-7
Hybridization can contribute to diversity from the genomic to the species level. Here, Eberlein, Hénault et al. investigate genomic, transcriptomic and phenotypic variation among wild lineages of the yeast Saccharomyces paradoxus and suggest that an incipient species has formed by recurrent hybridization.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2TgfhjU
Publisher Correction: A meiosis-specific BRCA2 binding protein recruits recombinases to DNA double-strand breaks to ensure homologous recombination
Publisher Correction: A meiosis-specific BRCA2 binding protein recruits recombinases to DNA double-strand breaks to ensure homologous recombination
Publisher Correction: A meiosis-specific BRCA2 binding protein recruits recombinases to DNA double-strand breaks to ensure homologous recombination, Published online: 25 February 2019; doi:10.1038/s41467-019-08995-4
Publisher Correction: A meiosis-specific BRCA2 binding protein recruits recombinases to DNA double-strand breaks to ensure homologous recombinationfrom A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2IyP5gd
Author Correction: Planar and van der Waals heterostructures for vertical tunnelling single electron transistors
Author Correction: Planar and van der Waals heterostructures for vertical tunnelling single electron transistors
Author Correction: Planar and van der Waals heterostructures for vertical tunnelling single electron transistors, Published online: 25 February 2019; doi:10.1038/s41467-019-08910-x
Author Correction: Planar and van der Waals heterostructures for vertical tunnelling single electron transistorsfrom A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2IBi7vT
Assembly and functionality of the ribosome with tethered subunits
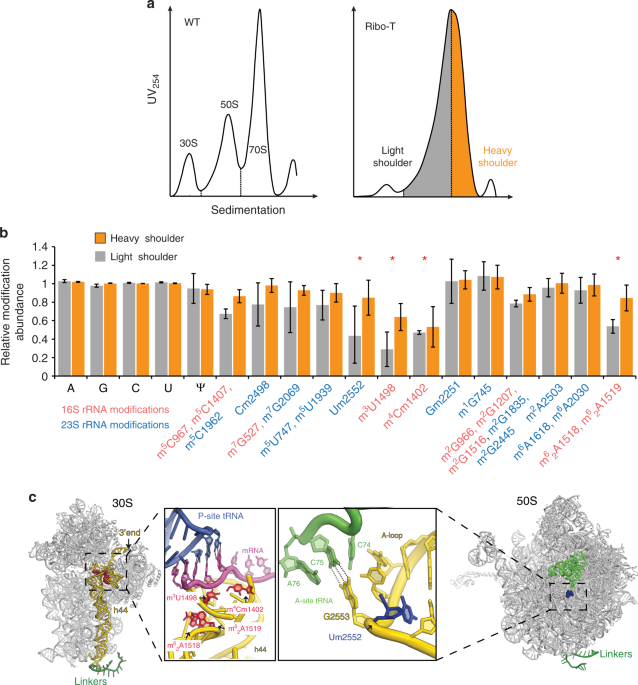
Assembly and functionality of the ribosome with tethered subunits
Assembly and functionality of the ribosome with tethered subunits, Published online: 25 February 2019; doi:10.1038/s41467-019-08892-w
The tethered ribosome system Ribo-T supports cell proliferation though at a reduced rate. Here the authors show this is due to slower ribosome assembly instead of reduced functionality.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2IAZYye
A molecular mechanism for transthyretin amyloidogenesis
A molecular mechanism for transthyretin amyloidogenesis
A molecular mechanism for transthyretin amyloidogenesis, Published online: 25 February 2019; doi:10.1038/s41467-019-08609-z
A number of disease-causing human transthyretin (TTR) mutations are known to lead to amyloid formation. Here the authors combine neutron crystallography, native mass spectrometry and modelling studies to characterize the T119M and S52P-TTR mutants, providing mechanistic insights into TTR amyloidosis.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2Tlqa4c
Dynamic network coding of working-memory domains and working-memory processes
Dynamic network coding of working-memory domains and working-memory processes
Dynamic network coding of working-memory domains and working-memory processes, Published online: 25 February 2019; doi:10.1038/s41467-019-08840-8
Early neuropsychological studies suggested that different aspects of working memory (WM) are exclusively associated with specific brain areas. Here, the authors show, using machine-learning analysis of fMRI, how WM processes are dynamically coded by large-scale overlapping networks in the human brain.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2IAIv9c
The race for enzymatic DNA synthesis heats up
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2GZwLdP
Timing of Parathyroidectomy Does Not Influence Renal Function After Kidney Transplantation.
| Related Articles |
Timing of Parathyroidectomy Does Not Influence Renal Function After Kidney Transplantation.
World J Surg. 2019 Feb 24;:
Authors: van der Plas WY, El Moumni M, von Forstner PJ, Koh EY, Dulfer RR, van Ginhoven TM, Rotmans JI, Appelman-Dijkstra NM, Schepers A, Hoorn EJ, Plukker JTM, Vogt L, Engelsman AF, Nieveen van Dijkum EJM, Kruijff S, Pol RA, de Borst MH, Dutch Hyperparathyroidism Study Group
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Parathyroidectomy (PTx) is the treatment of choice for end-stage renal disease (ESRD) patients with therapy-resistant hyperparathyroidism (HPT). The optimal timing of PTx for ESRD-related HPT-before or after kidney transplantation (KTx)-is subject of debate.
METHODS: Patients with ESRD-related HPT who underwent both PTx and KTx between 1994 and 2015 were included in a multicenter retrospective study in four university hospitals. Two groups were formed according to treatment sequence: PTx before KTx (PTxKTx) and PTx after KTx (KTxPTx). Primary endpoint was renal function (eGFR, CKD-EPI) between both groups at several time points post-transplantation. Correlation between the timing of PTx and KTx and the course of eGFR was assessed using generalized estimating equations (GEE).
RESULTS: The PTxKTx group consisted of 102 (55.1%) and the KTxPTx group of 83 (44.9%) patients. Recipient age, donor type, PTx type, and pre-KTx PTH levels were significantly different between groups. At 5 years after transplantation, eGFR was similar in the PTxKTx group (eGFR 44.5 ± 4.0 ml/min/1.73 m2) and KTxPTx group (40.0 ± 6.4 ml/min/1.73 m2, p = 0.43). The unadjusted GEE model showed that timing of PTx was not correlated with graft function over time (mean difference -1.0 ml/min/1.73 m2, 95% confidence interval -8.4 to 6.4, p = 0.79). Adjustment for potential confounders including recipient age and sex, various donor characteristics, PTx type, and PTH levels did not materially influence the results.
CONCLUSIONS: In this multicenter cohort study, timing of PTx before or after KTx does not independently impact graft function over time.
PMID: 30798418 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher]
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2GGO2t7
The Use of Prophylactic Somatostatin Therapy Following Pancreaticoduodenectomy: A Meta-analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials.
| Related Articles |
The Use of Prophylactic Somatostatin Therapy Following Pancreaticoduodenectomy: A Meta-analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials.
World J Surg. 2019 Feb 23;:
Authors: Adiamah A, Arif Z, Berti F, Singh S, Laskar N, Gomez D
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Prophylactic administration of somatostatin analogues (SA) to reduce the incidence of post-operative pancreatic fistula (POPF) remains contentious. This meta-analysis evaluated its impact on outcomes following pancreaticoduodenectomy (PD).
METHODS: The EMBASE, MEDLINE and Cochrane databases were searched for randomised controlled trials (RCTs) investigating prophylactic SA following PD. Comparative effects were summarised as odds ratio and weighted mean difference based on an intention to treat. Quantitative pooling of the effect sizes was derived using the random-effects model.
MAIN RESULTS: Twelve RCTs were included involving 1615 patients [SA-treated group (n = 820) and control group (n = 795)]. The SA used included somatostatin-14, pasireotide, vapreotide and octreotide. Pooling of the data showed no significant benefit of its use for the primary outcome measure of all grades of POPF, odds ratio (OR) 0.73 [95% confidence interval (CI), 0.51-1.05, p = 0.09] and clinically relevant POPF, OR 0.48 [95% CI, 0.22-1.06, p = 0.07]. There were no benefits in the secondary outcome measures of delayed gastric emptying, OR 0.98 [95% CI, 0.57-1.69, p = 0.94]; infected abdominal collections, OR 0.80 [95% CI, 0.44-1.43, p = 0.80]; reoperation rates, OR 1.24 [95% CI, 0.73-2.13, p = 0.42]; duration of hospital stay, - 0.23 [95% CI - .59 to 1.13, p = 0.74]; and mortality, 1.78 [95% CI, 0.94-3.39, p = 0.08].
CONCLUSION: SA did not improve the post-operative outcomes following PD, including reducing the incidence of POPF. The routine administration of SA cannot be recommended following PD.
PMID: 30798417 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher]
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2NrTv7A
Performance and emission characteristics analysis of thermal barrier coated diesel engine using palm biodiesel
Abstract
Various research works are being undertaken around the world on the subject of thermal efficiency improvisation and emission reduction from diesel engines. This research work analyzes the performance and emission characteristics of a thermal barrier coated diesel engine which used palm biodiesel. The piston and cylinder liners were coated with equal percentages of alumina (Al2O3) and yittria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ) powder using plasma spraying coating method. The piston was coated with 100 μm thickness and the two cylinder liners were coated with 150 and 200 μm thicknesses and were used to analyze the performance and emission characteristics. Test results of the thermal barrier coated engine using palm biodiesel were compared with the results derived from the base engine. The tests revealed an increase of 3.8% specific fuel consumption (SFC) as an average when neat palm biodiesel was used in the base engine. Interestingly, the palm biodiesel used in the 150- and 200-μm thick thermal barrier coated engine was responsible for a significant decrease of the SFC by an average of 4.18% and 8.05% respectively. The brake thermal efficiency was found to decrease on an average of 1.02% when tests were run using the neat palm biodiesel in the base engine. But an average proportionate increase of 0.72% and 2.19% was visible when palm biodiesel was used in the tests conducted on the 150- and 200-μm thick thermal barrier coated engine. There was also an understandable brake specific reduction of 0.991 g/kWh carbon monoxide (CO) emission and 0.025 g/kWh unburned hydrocarbon (HC) levels. The nitrogen oxide (NOx) emission was observed as 14.06 g/kWh in the 200-μm thick thermal barrier coated engine which was slightly higher when the results were compared with that of the uncoated engine. The novelty of this research investigation is based on the usage of yttrium-stabilized zirconia and alumina thermal barrier coating on the cylinder liner and piston head of engine. This is justified due to the fact that most of the previous investigations undertaken focused on the thermal barrier coating in the piston, valve, and cylinder head alone. The utility factor of the palm biodiesel (B 100) in the low heat rejection engine has also proved to be another significant and novel factor in the present investigation outlined in this paper. This is mainly due to the fact that the ongoing investigations in this realm concentrated only on blends of 20 to 30% of palm biodiesel with diesel fuel in the low heat rejection diesel engine.
from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2E9w8LL
Stability and uptake of methylphenidate and ritalinic acid in nine-spine stickleback ( Pungitius pungitius ) and water louse ( Asellus aquaticus )
Abstract
The presence of human pharmaceuticals in the environment has garnered significant research attention because these compounds may exert therapeutic effects on exposed wildlife. Yet, for many compounds, there is still little research documenting their stability in the water column and uptake in organism tissues. Here, we measured the uptake and stability of methylphenidate (Ritalin®, a frequently prescribed central nervous system stimulant) and its primary metabolite, ritalinic acid, in (1) water only or (2) with nine-spine stickleback and water louse. Methylphenidate degraded to ritalinic acid in both studies faster at a higher temperature (20 °C versus 10 °C), with concentrations of ritalinic acid surpassing methylphenidate after 48–100 h, depending on temperature. The concentration of methylphenidate in stickleback was highest at the first sampling point (60 min), while the concentration in water louse tissues reached comparatively higher levels and peaked after ~ 6 days. Neither stickleback nor water louse took up ritalinic acid in tissues despite being present in the water column. Our findings provide valuable data for use in future risk assessment of methylphenidate and will aid in the design of studies aimed at measuring any ecotoxicological effects on, for example, the behaviour or physiology of aquatic organisms.
from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2T2IBvb
Antioxidant and cytoprotective effects of N -acetylcysteine against subchronic oral glyphosate-based herbicide-induced oxidative stress in rats
Abstract
It is claimed that oxidative stress has a prominent role in the mechanism of toxic effects formed by glyphosate-based herbicide (GBH) in living systems. A strong thiol compound, N-acetylcysteine (NAC), has antioxidative and cytoprotective properties. The objective in this subchronic toxicity study was to identify the prophylactic effect of NAC over histopathological changes and oxidative stress induced by GBH in blood, renal, liver, cardiac, and brain tissues. A sum of 28 male Wistar rats were divided into four equal groups, each containing 7 rats. During the study, group I (control group) was supplied with normal rodent bait and tap water ad libitum. The applied agents were 160 mg/kg NAC to group II, 375 mg/kg as equivalent to 1/10 of lethal dose 50% (LD50) of GBH to group III, and 160 mg/kg of NAC and 375 mg/kg of GBH together once per day as oral gavage to group IV for 8 weeks. While GBH decreased the levels of GSH in blood, liver, kidney, and brain tissues, it considerably increased malondialdehyde levels. On the contrary, these parameters happened to improve in the group supplied with NAC. Besides, it was seen that NAC was observed to improve the histopathologic changes in rat tissues induced by GBH. It was concluded that NAC protects oxidative stress and tissue damage induced by GBH in blood and tissue and this prophylactic effect could be attributed to its antioxidant and free radical sweeper character.
from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2E8R7hB
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Arising in Mucinous Cystic Neoplasm of Pancreas: A Case Report.
| Related Articles |
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Arising in Mucinous Cystic Neoplasm of Pancreas: A Case Report.
Am J Case Rep. 2019 Feb 24;20:242-247
Authors: Sawai H, Kurimoto M, Koide S, Kiriyama Y, Haba S, Matsuo Y, Morimoto M, Koide H, Kamiya A, Yamao K
Abstract
BACKGROUND Mucinous cystic neoplasm (MCN) of the pancreas is a rare mucin-producing cystic neoplasm that has a characteristic histological feature referred to as ovarian-type stroma (OS) underlying the epithelium. Pancreatic ductal carcinoma arises from MCN as a precursor lesion, but data on progression pathways are limited. CASE REPORT A 40-year-old female was referred to our hospital for further investigation of a pancreatic cyst. Further examination showed a 7.0 cm multilocular cyst in the pancreatic tail and a solid mass in the thick septum of the cystic tumor. Distal pancreatectomy and splenectomy were performed. Histological examination revealed a moderately differentiated invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) with a diameter of 0.5 cm in the thick septum of the cystic lesion and a cyst wall composed of epithelium with low-grade to severe dysplasia. The epithelium covered an OS. Pathological diagnosis was IDC arising in MCN of the pancreas. Immunohistochemical examination showed that MUC1 expression was negative in MCN but positive in IDC. KRAS mutation was observed in both MCN and IDC regions. CONCLUSIONS We present a rare case of moderately differentiated pancreatic IDC arising in MCN. To elucidate the underlying progression pathway, we explored the correlation between KRAS mutation and MUC expression as a clinicopathological parameter.
PMID: 30798329 [PubMed - in process]
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2NqFUxa
Changes in Clostridium ( Clostridioides ) difficile PCR-Ribotype Distribution and Antimicrobial Resistance in a German Tertiary Care Hospital Over the Last 10 Years
Abstract
Clostridium (Clostridioides) difficile ribotype 027 (RT027) was detected in Germany for the first time in 2007 during an outbreak in the region of Trier, Rhineland-Palatinate and is today the most prevalent ribotype (RT) in Europe. We aimed to determine the changes in RT distribution and corresponding antimicrobial resistance in clinical C. difficile isolates between two time points (2007 and 2017) in one tertiary care hospital in Germany. C. difficile isolates recovered in 2007 and in 2017 (80 isolates per year, respectively) from patients at a Tertiary Care University Hospital in North-Rhine Westphalia were analyzed. Isolates were characterized by ribotyping and susceptibility testing using gradient tests (metronidazole, vancomycin) and the disk diffusion method (moxifloxacin). Between 2007 and 2017, a clear switch from RT001 [18.75% (n = 15) in 2007 versus 3.75% (n = 3) in 2017 P = 0.003] to RT027 [0% in 2007 versus 21.25% (n = 17) in 2017] was evident. While minimal inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of vancomycin were stable, a significant metronidazole MIC creep was determined (MIC50 = 0.047 in 2007 versus MIC50 = 0.094 in 2017, P < 0.0001 using the Man–Whitney test). We detected one metronidazole-resistant isolate (0.6%). Interestingly, in total we encountered more isolates resistant to moxifloxacin in 2007 (42 (52.25%) than in 2017 [(30 (37.5%), P = 0.06)]). We could demonstrate that RT027 replaced RT001 in the last 10 years in our hospital. Furthermore, our data show a metronidazole MIC creep in C. difficile isolates over the last 10 years and an unexpected decrease of isolates resistant to moxifloxacin.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2EwndW4
When Jump Height is not a Good Indicator of Lower Limb Maximal Power Output: Theoretical Demonstration, Experimental Evidence and Practical Solutions
Abstract
Lower limb external maximal power output capacity is a key physical component of performance in many sports. During squat jump and countermovement jump tests, athletes produce high amounts of mechanical work over a short duration to displace their body mass (i.e. the dimension of mechanical power). Thus, jump height has been frequently used by the sports science and medicine communities as an indicator of the power output produced during the jump and by extension, of maximal power output capacity. However, in this article, we contend that squat jump and countermovement jump height are not systematically good indicators of power output produced during the jump and maximal power output capacity. To support our opinion, we first detail why, theoretically, jump height and maximal power output capacity are not fully related. Specifically, we demonstrate that individual body mass, push-off distance, optimal loading and the force-velocity profile confound the jump height–power relationship. We also discuss the relationship between squat jump or countermovement jump height and maximal power output capacity measured with a force plate based on data reported in the literature, which added to our own experimental evidence. Finally, we discuss the limitations of existing practical solutions (regression-based estimation equations and allometric scaling), and advocate using a valid, reliable and simple field-based procedure to compute individual power output produced during the jump and maximal power output capacity directly from jump height, body mass and push-off distance. The latter may allow researchers and practitioners to reduce bias in their assessment of lower limb mechanical power output by using jump height as an input with a simple yet accurate computation method, and not as the first/only variable of interest.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2tDZnl0
Αναζήτηση αυτού του ιστολογίου
! # Ola via Alexandros G.Sfakianakis on Inoreader
-
Does CBD Oil Lower Blood Pressure? This article was originally published at SundayScaries." Madeline Taylor POSTED ON January 13, 20...
-
Abstract Purpose Clinicians must balance the risks from hypotension with the potential adverse effects of vasopressors. Experts have rec...

