Journal of International Medical Research, Ahead of Print.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2I0xMEv
Medicine by Alexandros G. Sfakianakis,Anapafseos 5 Agios Nikolaos 72100 Crete Greece,00302841026182,00306932607174,alsfakia@gmail.com,
Αρχειοθήκη ιστολογίου
-
►
2023
(272)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (141)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (131)
-
►
2022
(2066)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (80)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (170)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (190)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (203)
-
►
2021
(7399)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (186)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (472)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (851)
-
►
2020
(2517)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (792)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (21)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (28)
-
▼
2019
(12076)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (19)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (54)
-
▼
Φεβρουαρίου
(4765)
-
▼
Φεβ 07
(197)
- Correlation between diaphragmatic sagittal rotatio...
- Spherical silica nanoparticles promote malignant t...
- Curcumin regulates the miR-21/PTEN/Akt pathway and...
- Application of second-generation Shikani optical s...
- Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma in adolescents: imag...
- Toxicity and developmental effect of cucurbitacin ...
- Modelling aggregate exposure to pesticides from di...
- Laparoscopic Microwave Ablation of Hepatocellular ...
- Understanding how estuarine hydrology controls amm...
- Distribution of Mycelia of Morchella esculenta in ...
- Community-Level Physiological Profiling for Microb...
- Delineation of proapoptotic signaling of anthracen...
- LEF1-AS1 contributes to proliferation and invasion...
- Systematic review and meta-analysis on the associa...
- Punishment as Moral Fortification and Non-Consensu...
- Cadmium in Groundwater Consumed in the Rural Areas...
- Biocontrol of Brettanomyces/Dekkera bruxellensis i...
- Preparation of montmorillonite grafted polyacrylic...
- Root uptake of atenolol, sulfamethoxazole and carb...
- How a hiring quota failed
- Fusion of heart rate variability and salivary cort...
- Publisher Correction: Actively personalized vaccin...
- Quake-prone Myanmar leads the way in seismic monit...
- Daily briefing: Stunning ‘light pillars’ in the sk...
- ‘Diet drugs’ suppress mosquitoes’ thirst for blood
- Author Correction: GABAA receptor signalling mecha...
- Arctic hunters, see-through squid and star birth —...
- 3D printed implant treats spinal cord injury
- New Biosensor Accurately Measures Glucose in Saliva
- Cadmium level in brain correlates with memory impa...
- Combustion and emission characteristics for a mari...
- Enhanced performance of alkali-modified Bi 2 WO 6 ...
- Influence of the residence time of street trees an...
- Purification of water contaminated with Hg using h...
- Control of NO x emissions by air staging in small-...
- Study of MoO 3 -γAl 2 O 3 catalysts behavior in se...
- Enhanced activity and substrate tolerance of 7α-hy...
- [ASAP] Exploring the Cytotoxicity, Uptake, Cellula...
- [ASAP] Crucial Role of Surface Hydroxyls on the Ac...
- [ASAP] Amphiphilic Block Copolymer-Guided Fabrica...
- [ASAP] Asymmetric Total Synthesis of Cerorubenic A...
- [ASAP] Transferrin-Appended Nanocaplet for Transce...
- [ASAP] Three-dimensional Salphen-based Covalent–Or...
- Genomic Characterization of the Zinc Transcription...
- Understanding lipogenesis by dynamically profiling...
- Publisher Correction: Actively personalized vaccin...
- Structural basis for blue-green light harvesting a...
- The secret(ing) life of the tumor stroma
- New Products
- Transcending boundaries
- T cells traffic at fever pitch
- News at a glance
- ChAT-ty T cells fight viral infection
- Aerosol-driven droplet concentrations dominate cov...
- Dynamic gating of infrared radiation in a textile
- Airport construction threatens Incan heartland
- Gut bacteria linked to mental well-being and depre...
- Indonesian earthquake broke a geologic speed limit
- Eliminating nonradiative decay in Cu(I) emitters: ...
- Pills give patients a shot inside the stomach
- Schema cells in the macaque hippocampus
- Space magnet homes in on dark matter clue
- Comment on "Friction at the bed does not control f...
- Virtual copy of ransacked museum comes to Mosul
- Abstract concepts in the primate brain
- The new potato
- [ASAP] Fluorination Effects on Indacenodithienothi...
- Daily briefing: Stunning ‘light pillars’ in the sk...
- ‘Diet drugs’ suppress mosquitoes’ thirst for blood
- Author Correction: GABAA receptor signalling mecha...
- Magnesium
- Loneliness and social isolation causal association...
- Maintaining relevance in HIV systematic reviews: a...
- Prevalence and determinants of mental distress amo...
- Color clustering segmentation framework for image ...
- Evaluation of Metabolic Defects in Fatty Acid Oxid...
- Anomalous anastomosis between the external carotid...
- Endoscopic vitrectomy in endophthalmitis: initial ...
- Stable salts of the hexacarbonyl chromium(I) catio...
- Cryo-EM structure of the homohexameric T3SS ATPase...
- 24-nt reproductive phasiRNAs are broadly present i...
- Post-translational regulation of lipogenesis via A...
- Disorder in Mn+1AXn phases at the atomic scale
- Sensory neuron lineage mapping and manipulation in...
- Mosaic deletion patterns of the human antibody hea...
- Differential influences of environment and self-mo...
- Orthognathic Surgery for Patients with Cleft Lip a...
- What is the difference between irony and sarcasm? ...
- Early prediction of long-term tactile object recog...
- Everyday taxi drivers: Do better navigators have l...
- Visuomotor adaptation in the absence of input from...
- The evolution of the temporoparietal junction and ...
- Wearing Prisms to Hear Differently: After-Effects ...
- A commentary on Popescu et al.’s paper on the brai...
- Comparison of short-term heart rate variability in...
- Immune microenvironment of triple-negative breast ...
- Stereotactic radiosurgery with concurrent HER2-dir...
- Preclinical characterization of SHR6390, a novel C...
- Salt-Inducible Kinase 2: An Oncogenic Signal Trans...
- Tumor Tissue Explant Culture of Patient-Derived Xe...
-
▼
Φεβ 07
(197)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (5155)
-
►
2018
(3144)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (3144)
Ετικέτες
Πληροφορίες
Πέμπτη 7 Φεβρουαρίου 2019
Correlation between diaphragmatic sagittal rotation and pulmonary dysfunction in patients with ankylosing spondylitis accompanied by kyphosis
Spherical silica nanoparticles promote malignant transformation of BEAS-2B cells by stromal cell-derived factor-1α (SDF-1α)
Journal of International Medical Research, Ahead of Print.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2GhgIbD
Curcumin regulates the miR-21/PTEN/Akt pathway and acts in synergy with PD98059 to induce apoptosis of human gastric cancer MGC-803 cells
Journal of International Medical Research, Ahead of Print.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2HYDl6p
Application of second-generation Shikani optical stylet in critically ill patients undergoing cerebral aneurysm embolization
Journal of International Medical Research, Ahead of Print.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2GcYFDu
Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma in adolescents: imaging findings of a consecutive 7-year case series
Journal of International Medical Research, Ahead of Print.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2HYDjvj
Toxicity and developmental effect of cucurbitacin E from Citrullus colocynthis L. (Cucurbitales: Cucurbitaceae) against Spodoptera litura Fab. and a non-target earthworm Eisenia fetida Savigny
Abstract
Pest management with natural botanical insecticides is a significant implementation for the sustainability of agroecosystem by reducing the unnecessary risk from the inputs of synthetic insecticides. In this research, we isolated the bioactive compound cucurbitacin E from Citrullus colocynthis (L.) Schrad, and their toxicological effects were screened against different larval instars of Spodoptera litura. The bioactive compound cucurbitacin E was chemically characterized through TLC, FT-IR, and NMR analyses. The larval mortality bioassay revealed that the larvae exposed to cucurbitacin E at the discriminating dose of 50 ppm display higher mortality rate against second (93.8%), third (86.4%), and fourth (73.2%) instar respectively. The lethal concentrations (LC50 and LC90) was detected as 15.84 and 67.60 ppm for third instar respectively. The sub-lethal concentration of cucurbitacin E (2, 4, and 6 ppm) intentionally altered the percentage of survival, pupation, fecundity, and egg hatchability of S. litura. Moreover, antifeedant activity of cucurbitacin E was analyzed using choice-based test. In addition, we found the toxic effects of cucurbitacin E (50 and 100 ppm) and chemical pesticides (cypermethrin and monocrotophos) against terrestrial beneficial earthworm Eisenia fetida, and the result revealed that cucurbitacin E has no harmful effect on non-target organism. Hence, the present study reveals that cucurbitacin E might be a part of a new biorational product alternative to synthetic pesticides.
from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2Gy1zlx
Modelling aggregate exposure to pesticides from dietary and crop spray sources in UK residents
Abstract
Human exposure to pesticide mixtures can occur from the diet and other sources. Realistic exposure and risk assessments should include multiple sources and compounds and include the relative hazards of the different compounds. The EU-funded Euromix project is developing new web-based tools to facilitate these calculations. A case study is presented that exemplifies their use for a population of UK residents, including exposure from crop-spraying. A UK pesticide usage survey provided information on real pesticide combinations applied to crops of wheat, potatoes, sugar beet and dessert apples. This information was combined with outputs from two alternative simulation models of spray drift to estimate dermal, oral and inhalation exposures of residents. These non-dietary exposures were combined with dietary exposure estimates using the Monte Carlo Risk Assessment software to produce a distribution of aggregated and cumulative exposures. Compounds are weighted by relative potency to generate a measure of overall risk. Uncertainty quantification was also included in the distribution of exposures. These tools are flexible to allow diverse sources of exposure and can provide important information to decision-makers and help to prioritise testing of pesticide mixtures. Including non-dietary sources changed the prioritisation of pesticide mixtures, when compared to dietary exposure alone.
from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2E1DO3N
Laparoscopic Microwave Ablation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma at Liver Surface: Technique Effectiveness and Long-Term Outcomes
Technology in Cancer Research &Treatment, Volume 18, Issue , January 2019.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2GeGddH
Understanding how estuarine hydrology controls ammonium and other inorganic nitrogen concentrations and fluxes through the subtropical Jiulong River Estuary, S.E. China under baseflow and flood-affected conditions
Abstract
Higher nitrogen fluxes through estuaries increase the risk of harmful algal blooms, may expand eutrophication and can cause hypoxia within estuaries and the adjacent coastal areas. However, the key factors controlling dissolved inorganic nitrogen (DIN) concentrations and export from hydrologically dynamic and turbid estuarine systems are still poorly understood. A series of cruises with high spatial resolution under different hydrological conditions were conducted in 2015–2016 across the Jiulong River Estuary (JRE) continuum, including the estuarine turbidity maximum (ETM). During baseflow, ETMs were more intense during spring tides than neap tides due to stronger net sediment resuspension. The turbidity maxima were stronger and generally further downstream under flood-affected conditions. Based on the distribution of ammonium on the salinity gradient in the low salinity region of the estuary (< 2 PSU), we grouped all the cruises into "NH4 Addition Pattern (AP)" and "NH4 Removal Pattern (RP)". During baseflow, AP occurred during neap tides and RP during spring tides. An important source of ammonium to the water column was from resuspended sediments and their pore waters. Based on property-salinity plots, nitrification was likely one of the most important transformation processes in the turbid water column of the JRE, resulting in the net removal of ammonium and the net addition of nitrite. It was more intense during spring tides because there were more suspended particles carrying nitrifying bacteria. There was a major addition of DIN from estuarine processes in addition to the extra nitrogen flushed from the catchment during flood-affected flow, in particular during the first flood of the year, compared with a comparatively minor addition during baseflow. This additional DIN was likely from the breakdown products of particulate organic nitrogen accumulated in sediments which were then resuspended under flood-affected conditions.
from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2Gy4Ilt
Distribution of Mycelia of Morchella esculenta in Wild Field
Abstract
It was well-known that Morchella esculenta has a life cycle including vegetative hyphae, sclerotia, primordia, and fruiting bodies, but there is no report yet about the influence of mycelial mass on fruiting process. Since 2014, we have developed an ELISA method to detect the content of Morchella esculenta. In this study, we utilized this method to measure the mycelia content, and find the correlation between mycelial content and fruiting in the wild. The study demonstrated the changes of mycelial concentration at different location around fruiting spot.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2RNpgIw
Community-Level Physiological Profiling for Microbial Community Function in Broiler Ceca
Abstract
Poultry production is a major agricultural output worldwide. It is known that the gut health of broilers is essential for their growth and for providing wholesome products for human consumption. Previously, the microbial diversity of broiler ceca was studied at the genetic level. However, the functional diversity and metabolic activity of broiler cecal bacterial communities are not fully investigated. Recently, the EcoPlates™ from Biolog, Inc. have been used for characterizing bacterial communities from various environments. In this study, we applied these plates to physiologically profile cecal bacterial communities in broilers. The ceca were aseptically excised from 6-week-old broilers, and their contents were suspended in phosphate buffered saline. The cultures in the EcoPlates™ were incubated at 42 °C for 5 days in an OmniLog® system. Responses of the bacterial communities to the various chemicals as carbon sources were measured on formazan production. The results show sigmoidal growth curves with three phases in all 12 cecal samples. Cecal bacterial communities could not use 11 carbon substrates for carbon sources; instead, they used pyruvic acid methyl ester, glycogen, glucose-1-phosphate and N-acetyl-d-glucosamine most frequently. Each bacterial community metabolized various numbers of the substrates at different rates among broilers. In the future, modification of the culture conditions to mimic the gut environment is needed. More investigations on the effects of nutrients, Salmonella or Campylobacter on physiological functions of cecal bacterial communities will provide insights into the improvement of animal well-being, saving production expenditures for producers and providing safer poultry products for human consumption.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2WMhyCh
Delineation of proapoptotic signaling of anthracene-shelled M 2 L 4 metallacapsules and their synergistic activity with curcumin in cisplatin-sensitive and resistant tumor cell lines
Summary
Since the introduction of cisplatin into clinical practice a few decades ago, the topic of metal-based drugs has expanded significantly. Recent examples emphasize on metallosupramolecules as an emerging class of compounds with diverse properties. They can trigger unique cellular events in malignant cells or serve as molecular hosts for various biologically active compounds, including anticancer agents. The anthracene-shelled M2L4 coordination nanocapsules under research have already proved very high anticancer potency with remarkable selectivity and lack of cross-resistance. In this study, we provide an oncopharmacological evaluation of the Pt(II)- and Pd(II)-clipped M2L4 nanocapsules; we report a thorough analysis of their synergistic effects in combined treatments with the pleiotropic anticancer agent curcumin. We examined changes in cellular expression of several apoptosis-related proteins in a panel of tumor cell lines with different chemosensitivity towards cisplatin, i.e. HT-29, HL-60 and its resistant strains HL-60/CDDP and HL-60/Dox, in order to assess the molecular mechanisms of their antitumor activity The results of the immunoassay concluded activation of the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway in all the screened tumor lines. A prevalent modulation of the extrinsic apoptotic signaling cascade was observed in the chemoresistant variants. Curcumin interactions of the tested compounds were estimated against the cisplatin-refractory cell line HT-29 via the Chou-Talalay method (CTM), whereby the palladium species yielded superior synergistic activity as compared to their platinum analogues.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2TC0sVR
LEF1-AS1 contributes to proliferation and invasion through regulating miR-544a/ FOXP1 axis in lung cancer
Summary
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are increasingly recognized as important regulators in tumor development. This study aims to investigate the potential role oflncRNALEF1-AS1, in the progression of lung cancer. Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) and western blot assays showed that LEF1-AS1 was upregulated while miR-544a was downregulated in lung cancer specimens and cells. Overexpression of LEF1-AS1 led to the enhancement of cell proliferation and invasion, revealed by CCK-8 assay and transwell assay. A negative correlation was found between LEF1-AS1 and miR-544a. BLAST analysis and dual-luciferase assay confirmed that FOXP1 is a downstream effector of miR-544a. Therefore, the LEF1-AS1/miR-544a/FOXP1 axis is an important contributor to lung cancer progression. Collectively, our novel data uncovers a new mechanism that governs tumor progression in lung cancer and provides new targets that may be used for disease monitoring and therapeutic intervention of lung cancer.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2Bp7tlY
Systematic review and meta-analysis on the association between phthalates exposure and insulin resistance
Abstract
This study aims to provide an overview of human studies on the association of exposure to phthalates and insulin resistance. We systematically searched human studies available until 15 January 2018.We conducted a literature search in Scopus, ISI Web of Science, PubMed, Google Scholar, and Cochrane Collaboration. We used the following keywords to identify relevant articles: "phthalate", "phthalate ester", "metabolic syndrome", "insulin resistance", "glucose intolerance", and "diabetes". For analyzing data, we conducted meta-analysis using the Stata software. We appraised each study to examine the sources of heterogeneity, including difference in clinical outcomes and exposure measurements. To determine the robustness and whether some of the factors have the highest impact on the results of the present meta-analysis, several sensitivity analyses were conducted. Sensitivity analysis showed that by removing studies with the highest weight and age groups, no change was observed in heterogeneity. Moreover, with excluding the study conducted in Europe, the results remained unchanged and constant. In addition, the funnel plot and Egger's tests were executed to access publication bias. Both the funnel plots and Egger's test did not show any evidence of publication bias (P = 0.31). In the random effects meta-analysis of all studies (n = 8), the pooled correlation coefficient between phthalate exposure and HOMA-IR was 0.10 (95% CI; 0.07–0.12, P < 0.001), with significant heterogeneity (P < 0.001, I2 = 85.5%). Our findings revealed positive association between exposure to phthalate metabolites and increased HOMA-IR; this association remained significant even after adjusting the analysis for multiple confounding variables.
from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2SffxA5
Punishment as Moral Fortification and Non-Consensual Neurointerventions
Abstract
The purpose of this paper is twofold. First, I defend and expand the Fortificationist Theory of Punishment (FTP). Second, I argue that this theory implies that non-consensual neurointerventions – interventions that act directly on one's brain – are permissible. According to the FTP, punishment is justified as a way of ensuring that citizens who infringe their duty to demonstrate the reliability of their moral powers will thereafter be able to comply with it. I claim that the FTP ought to be expanded to include citizens' interest in developing their moral powers. Thus, states must ensure that their citizens develop their moral reliability, not only because they must enforce their citizens' compliance with certain duties, but also because states have the duty to maintain the conditions for stability and satisfy their citizens' interest in developing their moral powers. According to this account of the FTP, if neurointerventions are the only or best way of ensuring that offenders can discharge their fortificational duties, states have strong reasons to provide these interventions.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2DZKlMk
Cadmium in Groundwater Consumed in the Rural Areas of Gonabad and Bajestan, Iran: Occurrence and Health Risk Assessment
Abstract
Evidences show that high levels of cadmium intake may be contributing to a wide range of deleterious health effects. This study was performed to estimate the concentration of cadmium and the health risk to human by cadmium through the ingestion of groundwater in 39 rural areas of Gonabad and Bajestan, eastern Iran. The mean cadmium concentrations in groundwater in the studied rural areas of Gonabad and Bajestan ranged from 0.087 to 14.32 μg/L and from 0.417 to 18.36 μg/L, respectively. Health risk quotient for cadmium contamination for 16 and 38% of children and infants in rural areas of Gonabad and Bajestan, respectively, was more than 1 which causes non-carcinogenic risk to the local population. The carcinogenic risk of cadmium in drinking water for adults, children, and infants in 16, 33, and 33% of studied rural areas of Gonabad and Bajestan, respectively, was higher than the safe limit of 1.0 × 10−4. For rural areas of Bajestan, the cancer risk in 42, 52, and 52% of adults, children, and infants was above the safe limit. It was strongly suggested that the accessible procedures of treatment should be taken for a portion of contaminated rural areas before the distribution of the groundwater for the local population.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2ULVJkD
Biocontrol of Brettanomyces/Dekkera bruxellensis in alcoholic fermentations using saccharomycin-overproducing Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains
Abstract
Microbial contamination of alcoholic fermentation processes (e.g. winemaking and fuel-ethanol production) is a serious problem for the industry since it may render the product unacceptable and/or reduce its productivity, leading to large economic losses. Brettanomyces/Dekkera bruxellensis is one of the most dangerous microbial contaminant of ethanol industrial fermentations. In the case of wine, this yeast species can produce phenolic compounds that confer off-flavours to the final product. In fuel-ethanol fermentations, D. bruxellensis is a persistent contaminant that affects ethanol yields and productivities. We recently found that Saccharomyces cerevisiae secretes a biocide, which we named saccharomycin, composed of antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) derived from the glycolytic enzyme glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH). Saccharomycin is active against several wine-related yeast species, namely D. bruxellensis. However, the levels of saccharomycin naturally secreted by S. cerevisiae during alcoholic fermentation are not sufficient to ensure the complete death of D. bruxellensis. Therefore, the aim of the present work was to construct genetically modified S. cerevisiae strains to overproduce these GAPDH-derived AMPs. The expression levels of the nucleotides sequences encoding the AMPs were evaluated in the modified S. cerevisiae strains by RT-qPCR, confirming the success of the recombinant approach. Furthermore, we confirmed by immunological tests that the modified S. cerevisiae strains secreted higher amounts of the AMPs by comparison with the non-modified strain, inducing total death of D. bruxellensis during alcoholic fermentations.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2ShjSmg
Preparation of montmorillonite grafted polyacrylic acid composite and study on its adsorption properties of lanthanum ions from aqueous solution
Abstract
Montmorillonite grafted polyacrylic acid composite (GNM) was prepared by using ultraviolet radiation grafting method in this work. The synthesized materials were characterized by XRF, SEM, FTIR, XRD, TG, and XPS. The experimental equilibrium data indicates that the adsorbent is suitable for the Langmuir model and belongs to the pseudo-second-order kinetic model. The entire adsorption process is spontaneous, endothermic, and chaotically enhanced by thermodynamic analysis. The maximum adsorption capacity of La(III) by GNM was 280.54 mg/g at 313.15 K. In addition, the regeneration experiment shows that the adsorbent has good reusability and stable desorption efficiency. This study demonstrates that GNM has high adsorption performance and La(III) adsorption and regeneration capabilities to solve the water pollution caused by rare earth ions and regeneration capabilities for La(III).
from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2DhLNIz
Root uptake of atenolol, sulfamethoxazole and carbamazepine, and their transformation in three soils and four plants
Abstract
Soils can be contaminated by pharmaceuticals. The aim of this study was to evaluate the impact of soil conditions (influencing sorption and persistence of pharmaceuticals in soils) and plant type on the root uptake of selected pharmaceuticals and their transformation in plant-soil systems. Four plants (lamb's lettuce, spinach, arugula, radish) planted in 3 soils were irrigated for 20 days (26) with water contaminated by one of 3 pharmaceuticals (carbamazepine, atenolol, sulfamethoxazole) or their mixture. The concentrations of pharmaceuticals and their metabolites in soils and plant tissues were evaluated after the harvest. Sulfamethoxazole and atenolol dissipated rapidly from soils. The larger concentrations of both compounds and an atenolol metabolite were found in roots than in leaves. Sulfamethoxazole metabolites were below the limits of quantifications. Carbamazepine was stable in soils, easily uptaken, accumulated, and metabolized in plant leaves. The efficiency of radish and arugula (both family Brassicaceae) in metabolizing was very low contrary to the high and moderate efficiencies of lamb's lettuce and spinach, respectively. Compounds' transformations mostly masked the soil impact on their accumulation in plant tissues. The negative relationships were found between the carbamazepine sorption coefficients and its concentrations in roots of radish, lamb's lettuce, and spinach.
from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2Sk0CEO
How a hiring quota failed
How a hiring quota failed
How a hiring quota failed, Published online: 07 February 2019; doi:10.1038/d41586-019-00504-3
Imposing a quota to boost the numbers of female academic researchers might have backfired.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2t8JLpc
Fusion of heart rate variability and salivary cortisol for stress response identification based on adverse childhood experience
Abstract
Adverse childhood experiences have been suggested to cause changes in physiological processes and can determine the magnitude of the stress response which might have a significant impact on health later in life. To detect the stress response, biomarkers that represent both the Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal (HPA) axis are proposed. Among the available biomarkers, Heart Rate Variability (HRV) has been proven as a powerful biomarker that represents ANS. Meanwhile, salivary cortisol has been suggested as a biomarker that reflects the HPA axis. Even though many studies used multiple biomarkers to measure the stress response, the results for each biomarker were analyzed separately. Therefore, the objective of this study is to propose a fusion of ANS and HPA axis biomarkers in order to classify the stress response based on adverse childhood experience. Electrocardiograph, blood pressure (BP), pulse rate (PR), and salivary cortisol (SCort) measures were collected from 23 healthy participants; 11 participants had adverse childhood experience while the remaining 12 acted as the no adversity control group. HRV was then computed from the ECG and the HRV features were extracted. Next, the selected HRV features were combined with the other biomarkers using Euclidean distance (ed) and serial fusion, and the performance of the fused features was compared using Support Vector Machine. From the result, HRV-SCort using Euclidean distance achieved the most satisfactory performance with 80.0% accuracy, 83.3% sensitivity, and 78.3% specificity. Furthermore, the performance of the stress response classification of the fused biomarker, HRV-SCort, outperformed that of the single biomarkers: HRV (61% Accuracy), Cort (59.4% Accuracy), BP (78.3% accuracy), and PR (53.3% accuracy). From this study, it was proven that the fused biomarkers that represent both ANS and HPA (HRV-SCort) able to demonstrate a better classification performance in discriminating the stress response. Furthermore, a new approach for classification of stress response using Euclidean distance and SVM named as ed-SVM was proven to be an effective method for the HRV-SCort in classifying the stress response from PASAT. The robustness of this method is crucial in contributing to the effectiveness of the stress response measures and could further be used as an indicator for future health.
Graphical abstract

from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2MYGan6
Publisher Correction: Actively personalized vaccination trial for newly diagnosed glioblastoma
Publisher Correction: Actively personalized vaccination trial for newly diagnosed glioblastoma
Publisher Correction: Actively personalized vaccination trial for newly diagnosed glioblastoma, Published online: 07 February 2019; doi:10.1038/s41586-019-0959-z
Publisher Correction: Actively personalized vaccination trial for newly diagnosed glioblastomafrom A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2RJn6tC
Quake-prone Myanmar leads the way in seismic monitoring
Quake-prone Myanmar leads the way in seismic monitoring
Quake-prone Myanmar leads the way in seismic monitoring, Published online: 07 February 2019; doi:10.1038/d41586-019-00501-6
The fledgling democracy is opening up to the world – leading to a transformation in how it monitors earthquakes.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2Dfk7Eb
Daily briefing: Stunning ‘light pillars’ in the skies of subarctic Sweden
Daily briefing: Stunning 'light pillars' in the skies of subarctic Sweden
Daily briefing: Stunning 'light pillars' in the skies of subarctic Sweden, Published online: 07 February 2019; doi:10.1038/d41586-019-00528-9
The month's most spectacular science images, why science shies away from confronting organized research fraud and how the editors of Nature Methods evaluate papers.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2SyjNd5
‘Diet drugs’ suppress mosquitoes’ thirst for blood
'Diet drugs' suppress mosquitoes' thirst for blood
'Diet drugs' suppress mosquitoes' thirst for blood , Published online: 07 February 2019; doi:10.1038/d41586-019-00511-4
Method shows promise for disease control, but practical hurdles remain.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2HZQPit
Author Correction: GABAA receptor signalling mechanisms revealed by structural pharmacology
Author Correction: GABAA receptor signalling mechanisms revealed by structural pharmacology
Author Correction: GABA<sub>A</sub> receptor signalling mechanisms revealed by structural pharmacology, Published online: 07 February 2019; doi:10.1038/s41586-019-0929-5
Author Correction: GABAA receptor signalling mechanisms revealed by structural pharmacologyfrom A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2GvncTB
Arctic hunters, see-through squid and star birth — January’s best science images
Arctic hunters, see-through squid and star birth — January's best science images
Arctic hunters, see-through squid and star birth — January's best science images, Published online: 07 February 2019; doi:10.1038/d41586-019-00503-4
The month's sharpest science shots — selected by Nature's photo team.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2RNQOxP
3D printed implant treats spinal cord injury
Researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine and Institute of Engineering in Medicine have used rapid 3D printing technologies to create a spinal cord, then successfully implanted that scaffolding, loaded with neural stem cells, into sites of severe spinal cord injury in rats. The implants are intended to promote nerve growth across spinal cord injuries, restoring connections and lost function. In rat models, the scaffolds supported tissue regrowth, stem cell surviv...
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2TAgmzW
New Biosensor Accurately Measures Glucose in Saliva
The technology, originally acquired from the University of Newcastle in Australia, uses modified organic thin film transistors, which work in combination with glucose oxidase, to measure the concentration of glucose in a sample. The complete system consists of a Glucose Biosensor Unit, which does the measurements, and an accompanying smartphone app that talks to the biosensor and displays the readings once they're taken. Glucose in saliva is present in lower quantities than in blood,...
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2BoyzJV
Cadmium level in brain correlates with memory impairment in F1 and F2 generation mice: improvement with quercetin
Abstract
The increased exposure to cadmium (Cd) through environmental pollutants, food and cigarette smoke is a concern worldwide. The association of Cd with impaired learning disabilities led us to hypothesise that cadmium levels in brain tissue could be dose-dependently related to the extent of memory impairment and oxidative stress. In this study, we proposed to study whether cadmium exposure to dams could alter the brain Cd levels, memory parameters, antioxidant enzymes in brain and their gene expression in the F1-F2 generation mice and whether quercetin could modulate this effect. Animals were administered Cd alone and in combination with quercetin for 7 days during their gestation period. Their newborn pups (F1 and F2 mice) were reared until adulthood and were tested for memory using Morris water maze and step-down latency test. The brain tissue of F1 mice was collected. Cd levels were estimated using the atomic absorption spectrophotometer. G-S-transferase (GST) and catalase (CAT) activity were measured and fold increase in their respective gene expression was observed using the RT-PCR method. Cd levels were significantly increased in the brain tissue of animals exposed to Cd but cotreatment with quercetin showed decreased levels in both generations. Memory impairment was observed in animals of F1 generation exposed to Cd and cotreatment with quercetin (100 mg/kg) reversed this effect. Cd exposure significantly enhanced both activity and expression of GST and CAT in the brain tissue of F1 generation mice and quercetin attenuated this effect. In F2 generation, results were variable. GST activity and expression increased with Cd and decreased with quercetin cotreatment. However, CAT activity showed no significant change despite a decrease in gene expression. Quercetin cotreatment enhanced activity as well gene expression in F2 generation. Our study insinuates that Cd levels could act as a predictor of memory impairment and altered enzyme activity and gene expression in brain tissue. Quercetin helped to reduce Cd levels in brain tissue of F1 and F2 generation and modulated the antioxidant system of the cell by affecting expression of antioxidant enzymes at the transcription level.
from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2MYzUf6
Combustion and emission characteristics for a marine low-speed diesel engine with high-pressure SCR system
Abstract
In order to avoid the production of sulfates and nitrates in marine diesel engines that burn sulfur-containing fuels, the operating temperature of their high-pressure selective catalytic reduction (HP-SCR) systems should be higher than 320 °C. For marine low-speed diesel engines, only the pre-turbine exhaust gas temperature can meet this requirement under specific conditions, with the main engine modulation method helping to increase the exhaust gas temperature. However, the main engine modulation method brings down the power output and fuel economy of the main engine and causes the matching problem of the turbine and the other devices with the main engine. The original engine model of the marine low-speed diesel engine and the high-pressure SCR system configuration model have been constructed using one-dimensional simulation software. In addition, the performance of the high-pressure SCR system under the conditions of low-sulfur and high-sulfur exhaust gas was thoroughly analyzed. Moreover, the two main engine modulation schemes of the scavenging bypass and the turbine exhaust bypass of the original engine matching with the high-pressure SCR system were studied. The study found that the weighted average value of the NOx under the condition of low-sulfur exhaust gas met with the requirement of the IMO Tier III regulations when the low-speed diesel engine was matched with the high-pressure SCR system. However, the weighted average value of the NOx under the condition of high-sulfur exhaust gas was slightly higher than that required by the IMO Tier III regulation. In addition, the optimal main engine modulation scheme for this low-speed diesel engine was clarified by comparing the effects of the scavenging bypass and the turbine exhaust bypass modulation on the exhaust performance, and the working performance of the original engine. With an opening of 0.4 of the CBV valve under 25% engine load, the weighted average NOx of the original exhaust gas was 3.38 g/(kW·h), the power had decreased by 0.7%, and the fuel consumption had increased by 1.0%. Furthermore, when the EGB valve opening was 0.3, the weighted average value of NOx was 3.31 g/(kW·h), the power had reduced by 2.4% and the fuel consumption had increased by 2.5%. Both modulation scheme methods made the exhaust performance of the original engine meet the requirements of the IMO Tier III emission regulations, but the scavenging bypass modulation scheme had less impact on the original engine's performance.
from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2TE4UmP
Enhanced performance of alkali-modified Bi 2 WO 6 /Bi 0.15 Ti 0.85 O 2 toward photocatalytic oxidation of HCHO under visible light
Abstract
Photocatalytic oxidation of formaldehyde (HCHO) is considered as one of the promising ways to resolve indoor air HCHO pollution. TiO2 has been well known as the most extended application in photocatalysis due to its strong oxidizing ability and stability. Owing to high activity under visible light irradiation, TiO2 and Bi2O3 doping mixed with Bi2WO6 was analyzed in this study. The formation of two kinds of heterojunction caused efficient charge separation, leading to the effective reduction in the recombination of photo-generated electron and hole. The special structure and enhanced performance of these catalysts were analyzed. For the first time, the loading of alkali salts was researched for photocatalytic oxidation. In order to understand the reaction mechanism of alkali salts enhanced effects, the catalysts were investigated by using BET, XRD, UV–Vis, FT-IR, SEM, and XPS. The results found more than 2 wt% of Na2SO4 loading and the mixed methods with different solutions were key factors affecting the performance of catalysts. Nearly 92% HCHO conversion could be completed over Bi2WO6/Bi0.15Ti0.85O2 (Na2SO4), and the concentration of HCHO was only 0.07 mg/m3 for 24 h, which was below the limit of specification in China. The results also indicated that the solution mixing method was more favorable to increase the HCHO conversion due to decrease the size of Bi0.15Ti0.85O2 particles. The catalysts with Na2SO4 loading provided more surface-adsorbed oxygen that facilitated the desorption of CO2 and markedly increased the photocatalytic oxidation of HCHO.
Graphical abstract

from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2BpZtky
Influence of the residence time of street trees and their soils on trace element contamination in Paris (France)
Abstract
With the actual increasing interest for urban soils, the evaluation of soil contamination by trace elements and the dynamics of this contamination appear mandatory to preserve plant and thereby human health. Street trees and the associated soil placed in pits located nearby roads could represent convenient indicators of urban and vehicle traffic influences on soils and plants. However, data on these soils remain scarce, many studies investigating park soils rather than street tree soils. Furthermore, trace elements could be one of the main factors causing the observed urban tree decline, while practitioners more and more question the possible reuse of these soils after the death of trees as well as tree litter collected in the streets. We evaluated the contamination in anthropogenic trace elements (TE), namely Zn, Pb, and Cd, of street trees (Tilia tomentosa) and their soils distributed all over Paris (France). Street tree soils are imported from rural areas at the plantation of each new tree so that tree age corresponds to the time of residence of the soil within an urban environment allowing the evaluation of temporal trends on TE concentration in soils and trees. The TE concentration revealed an important soil pollution, especially for the older soils (mean age of 80 years old). The consideration of the residence time of trees and soils in an urban environment evidenced an accumulation of Zn and Pb (ca. 4.5 mg kg−1 year−1 and 4 mg kg−1 year−1 for Zn and Pb, respectively). However, leaf concentrations in TE were low and indicate that soil-root transfer was not significant compared to the contamination by atmospheric deposition. These results underlined the necessity to deepen the evaluation of the recycling of urban soils or plants submitted to urban contamination.
from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2TDxJQi
Purification of water contaminated with Hg using horizontal subsurface constructed wetlands
Abstract
As a global pollutant, Hg (Hg) since the turn of the last century has received increased attention. Decreasing the emission of Hg into the food chain and the atmosphere is an effective way to reduce the Hg damage. The current study provided information about pilot-scale horizontal subsurface flow (HSSF) constructed wetlands (CWs) to remove different Hg species in polluted water. Synthetic wastewater was fed to two HSSF CWs, one was planted with Acorus calamus L and the other was unplanted as a control. The total Hg (THg), dissolved Hg (DHg), and particulate Hg (PHg) from five sites along the HSSF CWs were analyzed to describe the process of Hg removal. Results show that the CWs have high removal efficiency of Hg which is more than 90%. The removal efficiencies of THg and DHg from the unplanted CW were 92.1 ± 3.6% and 72.4 ± 13.1%, respectively. While, the removal efficiencies of THg and DHg in planted CW were 95.9 ± 7.5% and 94.9 ± 4.9%, which were higher than that in blank CW. The PHg was mainly removed in the first quarter of the CWs, which was also revealed by the partition coefficient Kd. To a certain extent, the effect of plants depends on the hydraulic retention time (HRT). The results in the current study show the potential of the HSSF-CWs for restoration from Hg-contaminated water.
from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2BA6vDx
Control of NO x emissions by air staging in small- and medium-scale biomass pellet boilers
Abstract
The effect of air staging strategies on NOx control was investigated on a 210-kW small-scale biomass boiler (SBB) and a 1.4-MW medium-scale biomass boiler (MBB). Considering the de-NOx effect, as well as the convenience and economy for future wide use, the structures of the secondary air duct and the fuel feed tube were innovatively designed to solve the problems of the traditional prototype. The preliminary experiment showed that the lowest NOx emission was achieved when the air excess (ε) was equal to 2.04. Then, additional operating modes were conducted on the MBB to further optimize the air staging strategies. The optimal air staging strategy of the MBB (the secondary to primary air flow ratio (λ) and the ε were equal to 0.13 and 0.76, respectively) could decrease the NOx emission from 338.12 to 148.14 mg/m3. Furthermore, the SO2 emissions and the lowest NOx emission of the SBB and the MBB could meet most emission standards of China and some developed countries. The thermogravimetric analysis (TG) and combustion characteristics of the wood fuel showed that the air staging was a suitable de-NOx technology for wood combustion, and the slagging was less likely to occur under the selected condition. Hence, the air staging technology was an effective and low-cost method for the emission reduction of biomass boilers. This study provided a practical basis for future research on the gas emission control of biomass boilers.
from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2TCuPLZ
Study of MoO 3 -γAl 2 O 3 catalysts behavior in selective catalytic reduction of SO 2 toxic gas to sulfur with CH 4
Abstract
In the present study, a detailed investigation was carried out on MoO3 alumina-supported catalysts behavior in selective catalytic reduction of SO2 to sulfur with CH4. At first, four different molybdenum catalysts with weight rates of 0, 5, 10, and 15 were impregnated on γ-alumina to be characterized using XRD, SEM, BET, BJH, and N2 adsorption. Then, to find the most active catalyst, temperature dependency test was performed on all of the prepared catalysts and the result representing Al2O3-Mo10 as the best catalyst. In next step, the effects of feed gas composition, space velocity, and long-term activity, as an important industrial factor, were tested on Al2O3-Mo10. It was revealed instantaneously from the beginning, MoO3 specie started to convert mainly into MoS2 and MoO2, and a minor part into Mo2C, which is terminated after 750 min achieving a stable condition. Thereafter, SO2 conversion and sulfur selectivity increased from 85.8 to 89.4% and 99.4 to 99.7%, respectively. XRD graph of the used catalyst and TPO thermogravimetric/mass-spectra proved possible happening of the proposed mechanism in long-term activity. At the end, mean activation energy was determined based on Arrhenius model in temperature range of 550 to 800 °C, with a value of 0.33 eV for Al2O3-Mo10.
from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2BoH1sG
Enhanced activity and substrate tolerance of 7α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase by directed evolution for 7-ketolithocholic acid production
Abstract
7-Ketolithocholic acid (7-KLCA) is an important intermediate for the synthesis of ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA). UDCA is the main effective component of bear bile powder that is used in traditional Chinese medicine for the treatment of human cholesterol gallstones. 7α-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (7α-HSDH) is the key enzyme used in the industrial production of 7-KLCA. Unfortunately, the natural 7α-HSDHs reported have difficulty meeting the requirements of industrial application, due to their poor activities and strong substrate inhibition. In this study, a directed evolution strategy combined with high-throughput screening was applied to improve the catalytic efficiency and tolerance of high substrate concentrations of NADP+-dependent 7α-HSDH from Clostridium absonum. Compared with the wild type, the best mutant (7α-3) showed 5.5-fold higher specific activity and exhibited 10-fold higher and 14-fold higher catalytic efficiency toward chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) and NADP+, respectively. Moreover, 7α-3 also displayed significantly enhanced tolerance in the presence of high concentrations of substrate compared to the wild type. Owing to its improved catalytic efficiency and enhanced substrate tolerance, 7α-3 could efficiently biosynthesize 7-KLCA with a substrate loading of 100 mM, resulting in 99% yield of 7-KLCA at 2 h, in contrast to only 85% yield of 7-KLCA achieved for the wild type at 16 h.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2tbuDHZ
[ASAP] Exploring the Cytotoxicity, Uptake, Cellular Response, and Proteomics of Mono- and Dinuclear DNA Light-Switch Complexes

from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2USXL2z
[ASAP] Crucial Role of Surface Hydroxyls on the Activity and Stability in Electrochemical CO2 Reduction

from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2UL4lb2
[ASAP] Amphiphilic Block Copolymer-Guided Fabrication of Stable and Highly Controlled Luminescent Copper Nanoassemblies

from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2t8nxUs
[ASAP] Asymmetric Total Synthesis of Cerorubenic Acid-III

from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2taQTSb
[ASAP] Transferrin-Appended Nanocaplet for Transcellular siRNA Delivery into Deep Tissues

from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2UJWjPH
[ASAP] Three-dimensional Salphen-based Covalent–Organic Frameworks as Catalytic Antioxidants

from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2t9aDWp
Genomic Characterization of the Zinc Transcriptional Regulatory Element Reveals Potential Functional Roles of ZNF658
Abstract
The zinc transcriptional regulatory element (ZTRE) is a newly reported binding motif for human zinc finger protein ZNF658, which alters gene expression in response to cellular zinc. The ZTRE has two nucleotide components—the palindromic flanking pairs and the bridging "N" bases between these flanks that range in number from 0 to 100. There are 12 pairs of ZTRE flanks (designated A-L). Three thousand five hundred twenty-five genes contain one or more ZTREs − 1000 to + 200 bp from their transcriptional start site (TSS). ZTRE-E is observed at a greater frequency, and ZTRE containing 25 bridging bases are less frequent, within − 200 bp from the TSS. The genes with ZTREs in this range are enriched in processes that may compensate zinc deficiency, while other genes with ZTREs outside this range are enriched in transcriptional activation processes. The division of ZTREs into two groups may imply a dual role of ZNF658, similar to the homologous yeast protein Zap1, via binding to low or high affinity sequences dependent upon cellular zinc. The KLF/Sp1-family binding motif is prevalent within the ZTRE "N" bridging bases, suggesting ZNF658 may compete with Sp1-like transactivators to suppress transcription.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2WXg3l0
Understanding lipogenesis by dynamically profiling transcriptional activity of lipogenic promoters in Yarrowia lipolytica
Abstract
Lipogenesis is a complicated process involving global transcriptional reprogramming of lipogenic pathways. It is commonly believed that nitrogen starvation triggers a metabolic shift that reroutes carbon flux from Krebs cycles to lipogenesis. In this study, we systematically surveyed and dynamically profiled the transcriptional activity of 22 lipogenic promoters aiming to delineate a picture how nitrogen starvation regulates lipogenesis in Y. lipolytica. These lipogenic promoters drive the expression of critical pathways that are responsible for the generation of reducing equivalents (NADPH), carbon backbones (acetyl-CoA, malonyl-CoA, DHAP, etc.), synthesis and degradation of fatty acids. Specifically, our investigated promoters span across an array of metabolic pathways, including glycolysis, Krebs cycle, pentose phosphate pathway, mannitol cycle, glutamine–GABA cycle, fatty acid and lipid synthesis, glyoxylate, β-oxidation, and POM (pyruvate–oxaloacetate–malate) cycle. Our work provides evidences that mannitol cycle, glutamine–GABA cycle and amino acid degradation, pyruvate oxidation, and acetate assimilation pathways are lipogenesis-related steps involved in generating cytosolic NADPH and acetyl-CoA precursors. This systematic investigation and dynamic profiling of lipogenic promoters may help us better understand lipogenesis, facilitate the formulation of structure-based kinetic models, as well as develop efficient cell factories for fuels and chemical production in oleaginous species.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2HY9J9l
Publisher Correction: Actively personalized vaccination trial for newly diagnosed glioblastoma
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2I0gI1o
Structural basis for blue-green light harvesting and energy dissipation in diatoms
Diatoms are abundant photosynthetic organisms in aquatic environments and contribute 40% of its primary productivity. An important factor that contributes to the success of diatoms is their fucoxanthin chlorophyll a/c-binding proteins (FCPs), which have exceptional light-harvesting and photoprotection capabilities. Here, we report the crystal structure of an FCP from the marine diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum, which reveals the binding of seven chlorophylls (Chls) a, two Chls c, seven fucoxanthins (Fxs), and probably one diadinoxanthin within the protein scaffold. Efficient energy transfer pathways can be found between Chl a and c, and each Fx is surrounded by Chls, enabling the energy transfer and quenching via Fx highly efficient. The structure provides a basis for elucidating the mechanisms of blue-green light harvesting, energy transfer, and dissipation in diatoms.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2Slhj2v
Aerosol-driven droplet concentrations dominate coverage and water of oceanic low-level clouds
A lack of reliable estimates of cloud condensation nuclei (CCN) aerosols over oceans has severely limited our ability to quantify their effects on cloud properties and extent of cooling by reflecting solar radiation—a key uncertainty in anthropogenic climate forcing. We introduce a methodology for ascribing cloud properties to CCN and isolating the aerosol effects from meteorological effects. Its application showed that for a given meteorology, CCN explains three-fourths of the variability in the radiative cooling effect of clouds, mainly through affecting shallow cloud cover and water path. This reveals a much greater sensitivity of cloud radiative forcing to CCN than previously reported, which means too much cooling if incorporated into present climate models. This suggests the existence of compensating aerosol warming effects yet to be discovered, possibly through deep clouds.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2DkVo1d
Dynamic gating of infrared radiation in a textile
The human body absorbs and loses heat largely through infrared radiation centering around a wavelength of 10 micrometers. However, neither our skin nor the textiles that make up clothing are capable of dynamically controlling this optical channel for thermal management. By coating triacetate-cellulose bimorph fibers with a thin layer of carbon nanotubes, we effectively modulated the infrared radiation by more than 35% as the relative humidity of the underlying skin changed. Both experiments and modeling suggest that this dynamic infrared gating effect mainly arises from distance-dependent electromagnetic coupling between neighboring coated fibers in the textile yarns. This effect opens a pathway for developing wearable localized thermal management systems that are autonomous and self-powered, as well as expanding our ability to adapt to demanding environments.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2UIKGZm
Airport construction threatens Incan heartland
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2ULvuuA
Gut bacteria linked to mental well-being and depression
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2Sefqol
Indonesian earthquake broke a geologic speed limit
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2Dk8gEy
Eliminating nonradiative decay in Cu(I) emitters: >99% quantum efficiency and microsecond lifetime
Luminescent complexes of heavy metals such as iridium, platinum, and ruthenium play an important role in photocatalysis and energy conversion applications as well as organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs). Achieving comparable performance from more–earth-abundant copper requires overcoming the weak spin-orbit coupling of the light metal as well as limiting the high reorganization energies typical in copper(I) [Cu(I)] complexes. Here we report that two-coordinate Cu(I) complexes with redox active ligands in coplanar conformation manifest suppressed nonradiative decay, reduced structural reorganization, and sufficient orbital overlap for efficient charge transfer. We achieve photoluminescence efficiencies >99% and microsecond lifetimes, which lead to an efficient blue-emitting OLED. Photophysical analysis and simulations reveal a temperature-dependent interplay between emissive singlet and triplet charge-transfer states and amide-localized triplet states.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2RMS5oO
Pills give patients a shot inside the stomach
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2Sf5rPE
Schema cells in the macaque hippocampus
Concept cells in the human hippocampus encode the meaning conveyed by stimuli over their perceptual aspects. Here we investigate whether analogous cells in the macaque can form conceptual schemas of spatial environments. Each day, monkeys were presented with a familiar and a novel virtual maze, sharing a common schema but differing by surface features (landmarks). In both environments, animals searched for a hidden reward goal only defined in relation to landmarks. With learning, many neurons developed a firing map integrating goal-centered and task-related information of the novel maze that matched that for the familiar maze. Thus, these hippocampal cells abstract the spatial concepts from the superficial details of the environment and encode space into a schema-like representation.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2WOz3lq
Comment on "Friction at the bed does not control fast glacier flow"
Stearns and van der Veen (Reports, 20 July 2018, p. 273) conclude that fast glacier sliding is independent of basal drag (friction), even where drag balances most of the driving stress. This conclusion raises fundamental physical issues, the most striking of which is that sliding velocity would be independent of stresses imparted through the ice column, including gravitational driving stress.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2RMwnkz
Virtual copy of ransacked museum comes to Mosul
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2SeX6LG
[ASAP] Fluorination Effects on Indacenodithienothiophene Acceptor Packing and Electronic Structure, End-Group Redistribution, and Solar Cell Photovoltaic Response

from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2WWWMQG
Daily briefing: Stunning ‘light pillars’ in the skies of subarctic Sweden
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2HUWQg3
‘Diet drugs’ suppress mosquitoes’ thirst for blood
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2Bo3Yw3
Author Correction: GABAA receptor signalling mechanisms revealed by structural pharmacology
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2Gf8aSG
Loneliness and social isolation causal association with health-related lifestyle risk in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis protocol
The health impacts of loneliness and social isolation among older adults are widely acknowledged. Despite this, there is no consensus on the possible causal nature of this relationship, which could undermine e...
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2Dm0zOy
Maintaining relevance in HIV systematic reviews: an evaluation of Cochrane reviews
Research turnover in the HIV field is rapid, and as a result, maintaining high-quality, up-to-date, and relevant systematic reviews is a challenge. One approach is to frequently update published reviews.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2SeMufU
Prevalence and determinants of mental distress among university students in Ethiopia: a systematic review protocol
Mental distress is an important public health problem and becoming a common health problem among university students. This systematic review and meta-analysis will provide the pooled prevalence of mental distr...
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2DfQ3s3
Color clustering segmentation framework for image analysis of malignant lymphoid cells in peripheral blood
Abstract
Current computerized image systems are able to recognize normal blood cells in peripheral blood, but fail with abnormal cells like the classes of lymphocytes associated to lymphomas. The main challenge lies in the subtle differences in morphologic characteristics among these classes, which requires a refined segmentation. A new efficient segmentation framework has been developed, which uses the image color information through fuzzy clustering of different color components and the application of the watershed transformation with markers. The final result is the separation of three regions of interest: nucleus, entire cell, and peripheral zone around the cell. Segmentation of this zone is crucial to extract a new feature to identify cells with hair-like projections. The segmentation is validated, using a database of 4758 cell images with normal, reactive lymphocytes and five types of malignant lymphoid cells from blood smears of 105 patients, in two ways: (1) the efficiency in the accurate separation of the regions of interest, which is 92.24%, and (2) the accuracy of a classification system implemented over the segmented cells, which is 91.54%. In conclusion, the proposed segmentation framework is suitable to distinguish among abnormal blood cells with subtile color and spatial similarities.
Graphical Abstract

from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2GjGNXV
Evaluation of Metabolic Defects in Fatty Acid Oxidation Using Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells Loaded with Deuterium-Labeled Fatty Acids
Because tandem mass spectrometry- (MS/MS-) based newborn screening identifies many suspicious cases of fatty acid oxidation and carnitine cycle disorders, a simple, noninvasive test is required to confirm the diagnosis. We have developed a novel method to evaluate the metabolic defects in peripheral blood mononuclear cells loaded with deuterium-labeled fatty acids directly using the ratios of acylcarnitines determined by flow injection MS/MS. We have identified diagnostic indices for the disorders as follows: decreased ratios of d27-C14-acylcarnitine/d31-C16-acylcarnitine and d23-C12-acylcarnitine/d31-C16-acylcarnitine for carnitine palmitoyltransferase-II (CPT-II) deficiency, decreased ratios of d23-C12-acylcarnitine/d27-C14-acylcarnitine for very long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (VLCAD) deficiency, and increased ratios of d29-C16-OH-acylcarnitine/d31-C16-acylcarnitine for trifunctional protein (TFP) deficiency, together with increased ratios of d7-C4-acylcarnitine/d31-C16-acylcarnitine for carnitine palmitoyltransferase-I deficiency. The decreased ratios of d1-acetylcarnitine/d31-C16-acylcarnitine could be indicative of β-oxidation ability in patients with CPT-II, VLCAD, and TFP deficiencies. Overall, our data showed that the present method was valuable for establishing a rapid diagnosis of fatty acid oxidation disorders and carnitine cycle disorders and for complementing gene analysis because our diagnostic indices may overcome the weaknesses of conventional enzyme activity measurements using fibroblasts or mononuclear cells with assumedly uncertain viability.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2DhGetD
Anomalous anastomosis between the external carotid artery and vertebrobasilar artery via the hypoglossal canal: a case report and review of literature
Abstract
We report a case of an anomalous anastomosis formed between the external carotid artery (ECA) and the vertebrobasilar artery (VBA) and passing through the hypoglossal canal. A carotid–vertebrobasilar anastomosis of this kind is typically considered a variant of persistent primitive hypoglossal artery which usually originates from the internal carotid artery. However, the anastomotic vessel in this case had a common trunk with the occipital artery (OA), a remnant of the primitive proatlantal artery. The proximal and distal parts of the anastomotic vessel seemed to have been derived from the primitive proatlantal artery and the primitive hypoglossal artery, respectively. Thus, we propose that this ECA–VBA anastomosis, which passed through the hypoglossal canal and had a common trunk with the OA, be referred to as a dilated primitive hypoglossal–proatlantal anastomosis; that is, a dilated ascending pharyngeal artery rather than a variant of persistent primitive hypoglossal artery.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2Sy0YXx
Endoscopic vitrectomy in endophthalmitis: initial experience of 33 cases at a tertiary eye care center

from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2HWjaWT
Stable salts of the hexacarbonyl chromium(I) cation and its pentacarbonyl-nitrosyl chromium(I) analogue
Stable salts of the hexacarbonyl chromium(I) cation and its pentacarbonyl-nitrosyl chromium(I) analogue
Stable salts of the hexacarbonyl chromium(I) cation and its pentacarbonyl-nitrosyl chromium(I) analogue, Published online: 07 February 2019; doi:10.1038/s41467-019-08517-2
Carbonyl complexes have been studied extensively thanks to their rich substitution and redox chemistry, but most homoleptic transition metal carbonyl complexes isolated in the condensed phase are neutral or anionic. Here, the authors isolate two homoleptic carbonyl radical cations in the condensed phase; both 17-electron [Cr(CO)6]•+ salts.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2HUDlEB
Cryo-EM structure of the homohexameric T3SS ATPase-central stalk complex reveals rotary ATPase-like asymmetry
Cryo-EM structure of the homohexameric T3SS ATPase-central stalk complex reveals rotary ATPase-like asymmetry
Cryo-EM structure of the homohexameric T3SS ATPase-central stalk complex reveals rotary ATPase-like asymmetry, Published online: 07 February 2019; doi:10.1038/s41467-019-08477-7
Many Gram-negative bacteria rely on a type III secretion system (T3SS) for their pathogenicity. Here authors present the cryo-EM structure of the E.coli T3SS ATPase-central stalk complex, which forms a homohexameric, asymmetric pore with different functional states.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2IaDDHJ
24-nt reproductive phasiRNAs are broadly present in angiosperms
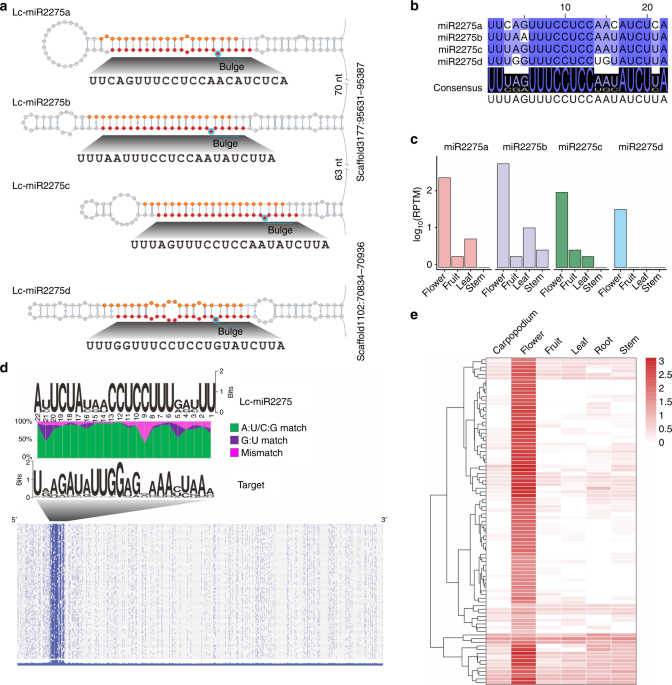
24-nt reproductive phasiRNAs are broadly present in angiosperms
24-nt reproductive phasiRNAs are broadly present in angiosperms, Published online: 07 February 2019; doi:10.1038/s41467-019-08543-0
24-nt phased siRNA (phasiRNA) regulate reproduction in grasses, yet are absent from Arabidopsis, and were thought to be monocot-specific. Here, Xia et al. show that 24-nt phasiRNAs are in fact broadly distributed among eudicots and are consistently enriched during meiosis, despite possibly arising from distinct biogenesis pathways.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2MS09DB
Post-translational regulation of lipogenesis via AMPK-dependent phosphorylation of insulin-induced gene
Post-translational regulation of lipogenesis via AMPK-dependent phosphorylation of insulin-induced gene
Post-translational regulation of lipogenesis via AMPK-dependent phosphorylation of insulin-induced gene, Published online: 07 February 2019; doi:10.1038/s41467-019-08585-4
Insulin-related gene (Insig) negatively regulates hepatic fatty acid synthesis, a process involved in development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Here, the authors show that AMPK activation by metformin promotes Insig phosphorylation, stabilizing it and inhibiting lipogenic gene expression. This is protective against steatosis in diabetic mice.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2GfLNwB
Disorder in Mn+1AXn phases at the atomic scale
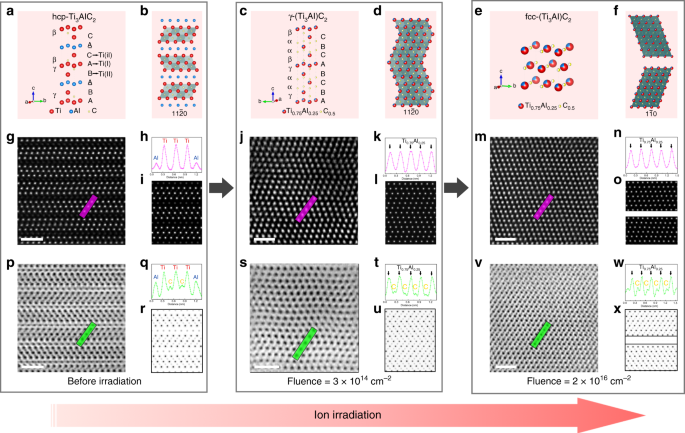
Disorder in Mn+1AXn phases at the atomic scale
Disorder in M<sub>n+1</sub>AX<sub>n</sub> phases at the atomic scale, Published online: 07 February 2019; doi:10.1038/s41467-019-08588-1
Highly ordered and compositionally complex ceramics are prone to disordering under irradiation, but exactly how is unclear. Here, the authors use high resolution microscopy to directly image the order-to-disorder phase transformations in Ti3AlC2 into otherwise unattainable solid solutions.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2GfihXx
Sensory neuron lineage mapping and manipulation in the Drosophila olfactory system
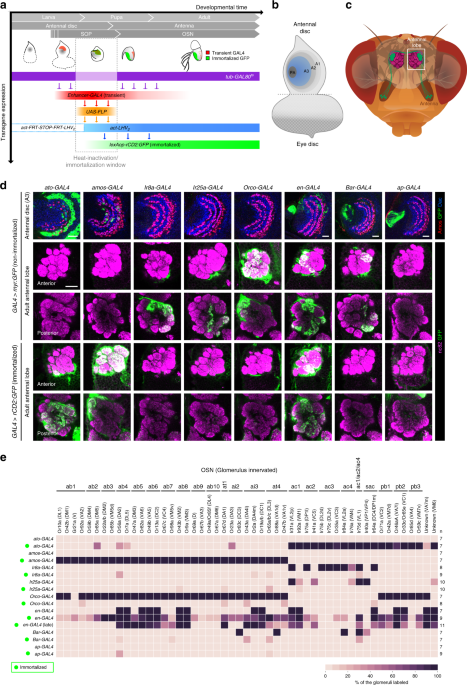
Sensory neuron lineage mapping and manipulation in the Drosophila olfactory system
Sensory neuron lineage mapping and manipulation in the <i>Drosophila</i> olfactory system, Published online: 07 February 2019; doi:10.1038/s41467-019-08345-4
Few tools exist to study molecular diversity during neurodevelopment. Here the authors apply a genetic immortalization method in Drosophila to generate a fate map of olfactory sensory lineages, examine the relationships of this map and the neuroanatomical, molecular and evolutionary properties of the mature circuits, and identify a novel factor controlling lineage development.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2SyiHhA
Mosaic deletion patterns of the human antibody heavy chain gene locus shown by Bayesian haplotyping
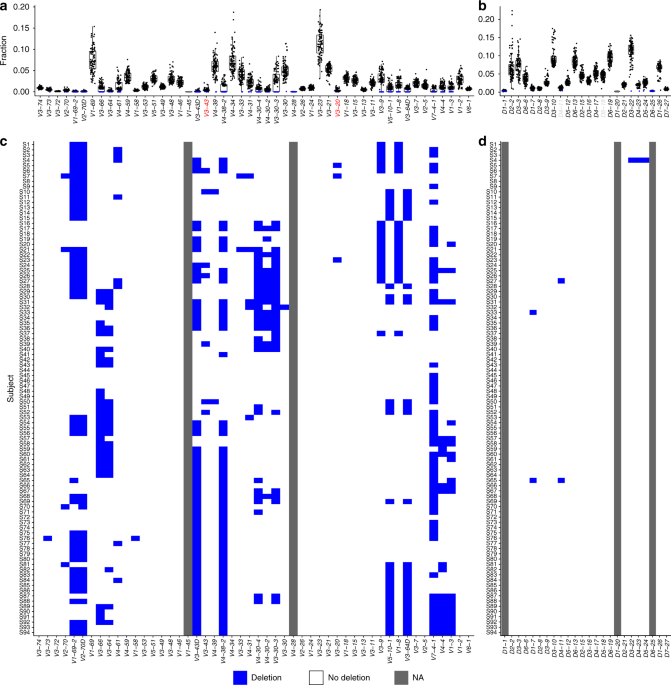
Mosaic deletion patterns of the human antibody heavy chain gene locus shown by Bayesian haplotyping
Mosaic deletion patterns of the human antibody heavy chain gene locus shown by Bayesian haplotyping, Published online: 07 February 2019; doi:10.1038/s41467-019-08489-3
High-throughput sequencing and analyzes of antibody repertoire provide important information on immune responses, but current methodologies are limited in sequence assembly precision and haplotype inference validity. Here the authors propose a new Bayesian haplotyping method, and attest its broad application with a large, multi-individual dataset.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2SDQ3LU
Differential influences of environment and self-motion on place and grid cell firing
Differential influences of environment and self-motion on place and grid cell firing
Differential influences of environment and self-motion on place and grid cell firing, Published online: 07 February 2019; doi:10.1038/s41467-019-08550-1
Place cells and grid cells are known to encode spatial information about an animal's location relative to the surrounding environment. Here, the authors show that place cells predominantly encode environmental sensory inputs, while grid cell activity reflects a greater influence of physical motion.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2StW129
Orthognathic Surgery for Patients with Cleft Lip and Palate
Publication date: Available online 6 February 2019
Source: Clinics in Plastic Surgery
Author(s): Andree-Anne Roy, Michael Alexander Rtshiladze, Kyle Stevens, John Phillips
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2BnmPHo
What is the difference between irony and sarcasm? An fMRI study
Publication date: Available online 7 February 2019
Source: Cortex
Author(s): Ruth Filik, Alexandra Țurcan, Christina Ralph-Nearman, Alain Pitiot
Abstract
Verbal irony is a figure of speech that communicates the opposite of what is said, while sarcasm is a form of irony that is directed at a person, with the intent to criticise. The current study used functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) with the aim of mapping the neural networks involved in the processing of sarcastic and non-sarcastic irony. Participants read short texts describing an interaction between two characters, which ended in either a literal, sarcastic, or non-sarcastic ironic comment. Results showed that the mentalising network (mPFC) and semantic network (IFG) were more activated for non-sarcastic irony than for literal controls. This would suggest that interpreting this kind of language involves understanding that the speaker does not mean what they literally say, as well as processes involved in conflict detection and resolution. Sarcastic irony recruited more of the semantic network, as well as areas associated with humour appreciation and subcortical structures, indicating that more complex neural mechanisms underlie the comprehension of sarcastic versus non-sarcastic irony.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2TAx3eI
Early prediction of long-term tactile object recognition performance after sensorimotor stroke
Publication date: Available online 7 February 2019
Source: Cortex
Author(s): Eugenio Abela, John H. Missimer, Manuela Pastore-Wapp, Werner Krammer, Roland Wiest, Bruno J. Weder
Abstract
Until now tactile agnosia has been reported only in small, but detailed cross-sectional case studies. Here we show that multi-voxel pattern analysis (MVPA) of early diffusion-weighted lesion maps can be used to accurately predict long-term recovery of tactile object recognition (TOR) in 35 subjects with varying hand skill impairment and associated specific daily activity limitation after cortical sensori-motor stroke. Multiple regression analysis revealed the essentially dysfunctional subprocesses for object recognition in the specifically impaired subjects, i.e. grasping as determined by a subtest of Jebsen Taylor hand function test, and perception of macrogeometrical object properties. The Gaussian process regression of MVPA represents a function that relates a selection of lesioned voxels as input variables to TOR performance scores as target variables. On the behavioural level, patients fell into three recovery subgroups, depending on TOR performance over the observation period. Only baseline motor hand skill and shape discrimination were significantly correlated with the TOR trajectories. To define functionally meaningful voxels, we combined information from MVPA of lesion maps and a priori knowledge of regions of interest derived from a data bank for shape recognition. A high significance for the predicted TOR performances over nine months could be verified by permutation tests, leading us to expect that the model generalises to larger patient cohorts with first cortical ischemic stroke. The lesion sites of the persistently impaired subjects exhibited an overlap with critical areas related to the MVPA prediction map in the cytoarchitectonic areas PFt of inferior parietal lobule and OP1 of parietal operculum which are associated with higher order sensory processing. This ultimate check corroborated the significance of the MVPA map for the prediction of tactile object recognition. The clinical implication of our study is that neuroimaging data acquired immediately after first stroke could facilitate individual forecasting of post-stroke recovery.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2BotuRD
Everyday taxi drivers: Do better navigators have larger hippocampi?
Publication date: Available online 7 February 2019
Source: Cortex
Author(s): Steven M. Weisberg, Nora S. Newcombe, Anjan Chatterjee
Abstract
Work with non-human animals and human navigation experts (London taxi drivers) suggests that the size of the hippocampus, particularly the right posterior hippocampus in humans, relates to navigation expertise. Similar observations, sometimes implicating other sections of the hippocampus, have been made for aging populations and for people with neurodegenerative diseases that affect the hippocampus. These data support the hypothesis that hippocampal volume relates to navigation ability. However, the support for this hypothesis is mixed in healthy, young adults, who range widely in their navigation ability. Here, we administered a naturalistic navigation task that measures cognitive map accuracy to a sample of 90 healthy, young adults who also had MRI scans. Using a sequential analysis design with a registered analysis plan, we did not find that navigation ability related to hippocampal volume (total, right only, right posterior only). We conclude that navigation ability in a typical population does not correlate with variations in hippocampal size, and consider possible explanations for this null result.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2TBt3e3
Visuomotor adaptation in the absence of input from early visual cortex
Publication date: Available online 7 February 2019
Source: Cortex
Author(s): Christopher L. Striemer, James T. Enns, Robert L. Whitwell
Abstract
Prism adaptation is a time-honored tool for studying how the motor system adapts to sensory perturbations. Past research on the neural substrates of prism adaptation has implicated the posterior parietal cortex (PPC) and the cerebellum, under the assumption that these structures gain their visual input from the dominant retinogeniculate pathway to V1. Here we question whether this pathway is even required for visuomotor adaptation to occur. To investigate this, we examined prism adaptation in 'MC,' someone who is blind to static stimuli following bilateral lesions that encompass much of her occipital cortex and the caudal-most areas of ventrotemporal cortex. Remarkably, MC shows evidence of prism adaptation that is similar to healthy control participants. First, when pointing with either the left or the right hand, MC shows spatial realignment; the classical after-effect exhibited by most people when adapting to displacing prisms. Second, MC demonstrates strategic recalibration – a reduction in her pointing error over time – that is similar in magnitude to healthy controls. These findings suggest that the geniculostriate pathway is not necessary for visuomotor adaptation to take place. Alternatively, we suggest that an extrageniculostriate pathway which provides visual inputs to the cerebellum from area MT and the PPC via the dorsolateral pons plays a significant and appreciable role in the guidance of unconscious, automatic visuomotor adaptation.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2BotrFr
The evolution of the temporoparietal junction and posterior superior temporal sulcus
Publication date: Available online 7 February 2019
Source: Cortex
Author(s): Gaurav H. Patel, Carlo Sestieri, Maurizio Corbetta
Abstract
The scale at which humans can handle complex social situations is massively increased compared to other animals. However, the neural substrates of this scaling remain poorly understood. In this review, we discuss how the expansion and rearrangement of the temporoparietal junction and posterior superior temporal sulcus (TPJ-pSTS) may have played a key role in the growth of human social abilities. Comparing the function and anatomy of the TPJ-pSTS in humans and macaques, which are thought to be separated by 25 million years of evolution, we find that the expansion of this region in humans has shifted the architecture of the dorsal and ventral processing streams. The TPJ-pSTS contains areas related to face-emotion processing, attention, theory of mind operations, and memory; its expansion has allowed for the elaboration and rearrangement of the cortical areas contained within, and potentially the introduction of new cortical areas. Based on the arrangement and the function of these areas in the human, we propose that the TPJ-pSTS is the basis of a third frontoparietal processing stream that underlies the increased social abilities in humans. We then describe a model of how the TPJ-pSTS areas interact as a hub that coordinates the activities of multiple brain networks in the exploration of the complex dynamic social scenes typical of the human social experience.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2TBnEDL
Wearing Prisms to Hear Differently: After-Effects of Prism Adaptation on Auditory Perception
Publication date: Available online 7 February 2019
Source: Cortex
Author(s): Carine Michel, Clémence Bonnet, Baptiste Podor, Patrick Bard, Bénédicte Poulin-Charronnat
Abstract
Numerous studies showed that, after adaptation to a leftward optical deviation, pseudoneglect behavior (overrepresentation of the left part compared to the right part of the space) becomes neglect-like behavior (overrepresentation of the right part compared to the left part of the space). Cognitive after-effects have also been shown in cognitive processes that are not intrinsically spatial in nature, but show spatial association as numbers or letters. The space-auditory frequency association (with low frequencies on the left and high frequencies on the right) raises the question of whether prism adaptation can produce after-effects on auditory perception. We used a new experimental protocol, named the 'auditory interval bisection judgment', where participants had to estimate what limit of an auditory interval (low or high) a target frequency was closer to. We calculated the subjective auditory interval center. In pretest, there was a spontaneous bias of the subjective center of the auditory interval toward the lower limit. That was the first demonstration of pseudoneglect behavior in auditory frequency representation. ANOVA realized on all participants did not show significant results of prism adaptation, but a posteriori analyses on musicians showed that, after adaptation to a leftward optical deviation, there were more target frequencies perceived as closer to the lower limit of the auditory interval. This result corroborates the shift of the subjective center of the auditory interval toward high frequency limit. These innovative results are discussed in terms of putative neural substrates underpinning the transfer of visuomotor plasticity to auditory frequency perception.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2BpgwD4
A commentary on Popescu et al.’s paper on the brain-structural correlates of mathematical expertise
Publication date: Available online 6 February 2019
Source: Cortex
Author(s): Delazer Margarete, Zamarian Laura
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2TBnEnf
Comparison of short-term heart rate variability indexes evaluated through electrocardiographic and continuous blood pressure monitoring
Abstract
Heart rate variability (HRV) analysis represents an important tool for the characterization of complex cardiovascular control. HRV indexes are usually calculated from electrocardiographic (ECG) recordings after measuring the time duration between consecutive R peaks, and this is considered the gold standard. An alternative method consists of assessing the pulse rate variability (PRV) from signals acquired through photoplethysmography, a technique also employed for the continuous noninvasive monitoring of blood pressure. In this work, we carry out a thorough analysis and comparison of short-term variability indexes computed from HRV time series obtained from the ECG and from PRV time series obtained from continuous blood pressure (CBP) signals, in order to evaluate the reliability of using CBP-based recordings in place of standard ECG tracks. The analysis has been carried out on short time series (300 beats) of HRV and PRV in 76 subjects studied in different conditions: resting in the supine position, postural stress during 45° head-up tilt, and mental stress during computation of arithmetic test. Nine different indexes have been taken into account, computed in the time domain (mean, variance, root mean square of the successive differences), frequency domain (low-to-high frequency power ratio LF/HF, HF spectral power, and central frequency), and information domain (entropy, conditional entropy, self entropy). Thorough validation has been performed using comparison of the HRV and PRV distributions, robust linear regression, and Bland–Altman plots. Results demonstrate the feasibility of extracting HRV indexes from CBP-based data, showing an overall relatively good agreement of time-, frequency-, and information-domain measures. The agreement decreased during postural and mental arithmetic stress, especially with regard to band-power ratio, conditional, and self-entropy. This finding suggests to use caution in adopting PRV as a surrogate of HRV during stress conditions.
Graphical abstract

from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2DWQuJ8
Immune microenvironment of triple-negative breast cancer in African-American and Caucasian women.
| Related Articles |
Immune microenvironment of triple-negative breast cancer in African-American and Caucasian women.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2019 Feb 06;:
Authors: O'Meara T, Safonov A, Casadevall D, Qing T, Silber A, Killelea B, Hatzis C, Pusztai L
Abstract
PURPOSE: African-American (AA) patients with triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) are less likely to achieve pathologic complete response from neoadjuvant chemotherapy and have poorer prognosis than Caucasian patients with TNBC, suggesting potential biological differences by race. Immune infiltration is the most consistent predictive marker for chemotherapy response and improved prognosis in TNBC. In this study, we test the hypothesis that the immune microenvironment differs between AA and Caucasian patients.
METHODS: RNA-seq expression data were obtained from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database for 162 AA and 697 Caucasian breast cancers. Estrogen receptor (ER)-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (HER2)-positive, and TNBC subtypes were included in the analyses. Tumor infiltrating lymphocyte (TIL) counts, immunomodulatory scores, and molecular subtypes were obtained from prior publications for a subset of the TNBC cases. Differences in immune cell distributions and immune functions, measured through gene expression and TIL counts, as well as neoantigen, somatic mutation, amplification, and deletion loads, were compared by race and tumor subtype.
RESULTS: Immune metagene analysis demonstrated marginal immune attenuation in AA TNBC relative to Caucasian TNBC that did not reach statistical significance. The distributions of immune cell populations, lymphocyte infiltration, molecular subtypes, and genomic aberrations between AA and Caucasian subtypes were also not significantly different. The MHC1 metagene demonstrated increased expression in AA ER-positive cancers relative to Caucasian ER-positive cancers.
CONCLUSIONS: This study suggests that the immunological differences between AA and Caucasian breast cancers represented by TCGA data are subtle, if they exist at all. We observed no consistent racial differences in immune gene expression or TIL counts in TNBC by race. However, this study cannot rule out small differences in immune cell subtype distribution and activity status that may not be apparent in bulk RNA analysis.
PMID: 30725384 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher]
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2GuM7GW
Stereotactic radiosurgery with concurrent HER2-directed therapy is associated with improved objective response for breast cancer brain metastasis.
| Related Articles |
Stereotactic radiosurgery with concurrent HER2-directed therapy is associated with improved objective response for breast cancer brain metastasis.
Neuro Oncol. 2019 Feb 06;:
Authors: Kim JM, Miller JA, Kotecha R, Chao ST, Ahluwalia MS, Peereboom DM, Mohammadi AM, Barnett GH, Murphy ES, Vogelbaum MA, Angelov L, Abraham J, Moore H, Budd GT, Suh JH
Abstract
Background: Patients with breast cancer positive for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) remain at high risk of intracranial relapse following treatment and experience increased rates of intracranial failure after stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS). We hypothesized that the addition of concurrent lapatinib to SRS would improve intracranial complete response rates.
Methods: Patients with newly diagnosed HER2-amplified breast cancer brain metastases from 2005-2014 who underwent SRS were included and divided into 2 cohorts based on timing of treatment with lapatinib. Outcome variables included the proportion of patients who achieved an intracranial complete response or progressive disease according to the RECIST 1.1 criteria, as well as individual lesion response rates, distant intracranial failure, and radiation necrosis.
Results: Eighty-four patients with 487 brain metastases met inclusion criteria during the study period. Over 138 treatment sessions, 132 lesions (27%) were treated with SRS and concurrent lapatinib, while 355 (73%) were treated with SRS without lapatinib. Compared with patients treated with SRS alone, patients treated with concurrent lapatinib had higher rates of complete response (35% vs 11%, P = 0.008). On a per-lesion basis, best objective response was superior in the concurrent lapatinib group (median 100% vs 70% reduction, P < 0.001). Concurrent lapatinib was not associated with an increased risk of grade 2+ radiation necrosis (1.0% with concurrent lapatinib vs 3.5% without, P = 0.27). Lapatinib had no protective effect on distant intracranial failure rates (48% vs 49%, P = 0.91).
Conclusion: The addition of concurrent lapatinib to SRS was associated with improved complete response rates among patients with HER2-positive brain metastases.
Key Points: 1.Complete response rates were higher with concurrent SRS and lapatinib compared with SRS alone. 2.Best objective response and complete response increased as lapatinib was administered closer to SRS. 3.There was no difference in the rate of radiation necrosis between the 2 cohorts.
PMID: 30726965 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher]
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2UISI4p
Preclinical characterization of SHR6390, a novel CDK 4/6 inhibitor, in vitro and in human tumor xenograft models.
| Related Articles |
Preclinical characterization of SHR6390, a novel CDK 4/6 inhibitor, in vitro and in human tumor xenograft models.
Cancer Sci. 2019 Feb 06;:
Authors: Long F, He Y, Fu H, Li Y, Bao X, Wang Q, Wang Y, Xie C, Lou L
Abstract
Inhibition of the cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 4/6-retinoblastoma (RB) pathway is an effective therapeutic strategy against cancer. Here, we performed a preclinical investigation of the antitumor activity of SHR6390, a novel CDK4/6 inhibitor. SHR6390 exhibited potent antiproliferative activity against a wide range of human RB-positive tumor cells in vitro, and exclusively induced G1 arrest as well as cellular senescence, with a concomitant reduction in the levels of Ser780-phosphorylated RB protein. Compared with the well-known CDK4/6 inhibitor, palbociclib, orally administered SHR6390 led to equivalent or improved tumor efficacy against a panel of carcinoma xenografts, and produced marked tumor regression in some models, in association with sustained target inhibition in tumor tissues. Furthermore, SHR6390 overcame resistance to endocrine therapy and HER2-targeting antibody in ER-positive and HER2-positive breast cancer, respectively. Moreover, SHR6390 combined with endocrine therapy exerted remarkable synergistic antitumor activity in ER-positive breast cancer. Taken together, our findings indicate that SHR6390 is a novel CDK4/6 inhibitor with favorable pharmaceutical properties for use as an anticancer agent. This article is protected by copyright. All rights reserved.
PMID: 30724426 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher]
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2DWeXyb
Salt-Inducible Kinase 2: An Oncogenic Signal Transmitter and Potential Target for Cancer Therapy.
| Related Articles |
Salt-Inducible Kinase 2: An Oncogenic Signal Transmitter and Potential Target for Cancer Therapy.
Front Oncol. 2019;9:18
Authors: Chen F, Chen L, Qin Q, Sun X
Abstract
Salt-inducible kinase (SIK), which belongs to the sucrose non-fermenting 1/AMP-activated protein kinase family, was first discovered in the adrenal cortex of a rat on a high-salt diet. As an isoform of the SIK family, SIK2 modulates various biological functions and acts as a signal transmitter in various pathways. Compared with that in adjacent normal tissues, the expression of SIK2 is significantly higher in multiple types of tumors, which indicates its pivotal effect in oncogenesis. Studies on SIK2 have recently underlined its role in several signaling pathways, including the PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway, the Hippo-YAP pathway, the LKB1-HDAC axis, and the cAMP-PKA axis. Moreover, a few small-molecule SIK2 inhibitors have been found to be able to rescue the oncogenicity of SIK2 during tumor development and reverse its abnormal activation of downstream pathways. In this mini-review, we discuss the results of in vivo and in vitro studies regarding the SIK2 mechanism in different signaling pathways, particularly their regulation of cancer cells. This work may provide new ideas for targeting SIK2 as a novel therapeutic strategy in tumor therapy.
PMID: 30723708 [PubMed]
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2Gu8MDq
Tumor Tissue Explant Culture of Patient-Derived Xenograft as Potential Prioritization Tool for Targeted Therapy.
| Related Articles |
Tumor Tissue Explant Culture of Patient-Derived Xenograft as Potential Prioritization Tool for Targeted Therapy.
Front Oncol. 2019;9:17
Authors: Ghosh S, Prasad M, Kundu K, Cohen L, Yegodayev KM, Zorea J, Joshua BZ, Lasry B, Dimitstein O, Bahat-Dinur A, Mizrachi A, Lazar V, Elkabets M, Porgador A
Abstract
Despite of remarkable progress made in the head and neck cancer (HNC) therapy, the survival rate of this metastatic disease remain low. Tailoring the appropriate therapy to patients is a major challenge and highlights the unmet need to have a good preclinical model that will predict clinical response. Hence, we developed an accurate and time efficient drug screening method of tumor ex vivo analysis (TEVA) system, which can predict patient-specific drug responses. In this study, we generated six patient derived xenografts (PDXs) which were utilized for TEVA. Briefly, PDXs were cut into 2 × 2 × 2 mm3 explants and treated with clinically relevant drugs for 24 h. Tumor cell proliferation and death were evaluated by immunohistochemistry and TEVA score was calculated. Ex vivo and in vivo drug efficacy studies were performed on four PDXs and three drugs side-by-side to explore correlation between TEVA and PDX treatment in vivo. Efficacy of drug combinations was also ventured. Optimization of the culture timings dictated 24 h to be the time frame to detect drug responses and drug penetrates 2 × 2 × 2 mm3 explants as signaling pathways were significantly altered. Tumor responses to drugs in TEVA, significantly corresponds with the drug efficacy in mice. Overall, this low cost, robust, relatively simple and efficient 3D tissue-based method, employing material from one PDX, can bypass the necessity of drug validation in immune-incompetent PDX-bearing mice. Our data provides a potential rationale for utilizing TEVA to predict tumor response to targeted and chemo therapies when multiple targets are proposed.
PMID: 30723707 [PubMed]
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2DW3D5a
The Expression Patterns of FAM83H and PANX2 Are Associated With Shorter Survival of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Patients.
| Related Articles |
The Expression Patterns of FAM83H and PANX2 Are Associated With Shorter Survival of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Patients.
Front Oncol. 2019;9:14
Authors: Kim KM, Hussein UK, Bae JS, Park SH, Kwon KS, Ha SH, Park HS, Lee H, Chung MJ, Moon WS, Kang MJ, Jang KY
Abstract
FAM83H is primarily known for its role in amelogenesis; however, recent reports suggest FAM83H might be involved in tumorigenesis. Although the studies of FAM83H in kidney cancer are limited, a search of the public database shows a significant association between FAM83H and pannexin-2 (PANX2) in clear cell renal cell carcinomas (CCRCCs). Therefore, we evaluated the clinicopathological significance of the immunohistochemical expression of FAM83H and PANX2 in 199 CCRCC patients. The expression of FAM83H and PANX2 were significantly associated with each other. In univariate analysis, individual, and co-expression pattern of FAM83H and PANX2 was significantly associated with shorter overall survival (OS) and relapse-free survival (RFS) of CCRCC patients: nuclear expression of FAM83H (OS; P < 0.001, RFS; P < 0.001), cytoplasmic expression of FAM83H (OS; P < 0.001, RFS; P < 0.001), nuclear expression of PANX2 (OS; P < 0.001, RFS; P < 0.001), cytoplasmic expression of PANX2 (OS; P < 0.001, RFS; P < 0.001), co-expression pattern of nuclear FAM83H and nuclear PANX2 (OS; P < 0.001, RFS; P < 0.001). In multivariate analysis, nuclear expression of FAM83H (OS; P < 0.001, RFS; P = 0.003) and the co-expression pattern of nuclear FAM83H and PANX2 (OS; P < 0.001, RFS; P < 0.001) were independent indicators of shorter survival of CCRCC patients. Cytoplasmic expression of FAM83H was associated with shorter RFS (P = 0.030) in multivariate analysis. In Caki-1 and Caki-2 CCRCC cells, knock-down of FAM83H decreased PANX2 expression and cell proliferation, and overexpression of FAM83H increased PANX2 expression and cell proliferation. These results suggest that FAM83H and PANX2 might be involved in the progression of CCRCC in a co-operative manner, and their expression might be used as novel prognostic indicators for CCRCC patients.
PMID: 30723706 [PubMed]
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2GuM266
Sources of Frustration Among Patients Diagnosed With Renal Cell Carcinoma.
| Related Articles |
Sources of Frustration Among Patients Diagnosed With Renal Cell Carcinoma.
Front Oncol. 2019;9:11
Authors: Bergerot CD, Battle D, Bergerot PG, Dizman N, Jonasch E, Hammers HJ, George DJ, Bex A, Ljungberg B, Pal SK, Staehler MD
Abstract
Despite numerous therapeutic advances in renal cell carcinoma (RCC), little is known about patients' perspectives on cancer care. An international survey was conducted to identify points of frustration associated with cancer care reported by patients with RCC. Data were obtained from an online survey, conducted from April 1 to June 15, 2017, through social media and patient networking platforms. This survey obtained baseline demographic, clinicopathologic, and treatment-related information. Open-ended questions accessed sources of frustration in cancer-related care and patients' suggestions for amelioration. Responses were categorized and reviewed by independent reviewers. A qualitative analysis was performed and the Kruskal-Wallis test was used to define associations between baseline characteristics and sources of frustration. Among 450 patients surveyed, 71.5% reported sources of frustration, classified as either emotional (48.4%) or practical (23.1%). The most common were fear of recurrence/progression (15.8%), distrust of their cancer care system (12.9%), and lack of appropriate information (9.8%). Female gender and non-clear cell histology were associated with both types of frustration, and older age was linked to practical sources of frustration. Patients suggested solutions included greater compassion among health care practitioners (20.7%), better access to information (15.1%) and research to improve their chances of being cured (14.7%). Sources of frustration related to emotional and practical causes were identified amongst patients with RCC. Certain demographic and clinical characteristics were associated with more sources of frustration. This study provides the first characterization of specific ways to improve the patient experience by addressing common frustrations.
PMID: 30723705 [PubMed]
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2DZCAWV
Αναζήτηση αυτού του ιστολογίου
! # Ola via Alexandros G.Sfakianakis on Inoreader
-
Abstract Purpose Clinicians must balance the risks from hypotension with the potential adverse effects of vasopressors. Experts have rec...
-
Does CBD Oil Lower Blood Pressure? This article was originally published at SundayScaries." Madeline Taylor POSTED ON January 13, 20...

