|
Medicine by Alexandros G. Sfakianakis,Anapafseos 5 Agios Nikolaos 72100 Crete Greece,00302841026182,00306932607174,alsfakia@gmail.com,
Αρχειοθήκη ιστολογίου
-
►
2023
(272)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (141)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (131)
-
►
2022
(2066)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (80)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (170)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (190)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (203)
-
►
2021
(7399)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (186)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (472)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (851)
-
▼
2020
(2517)
-
▼
Δεκεμβρίου
(792)
-
▼
Δεκ 10
(50)
- Cadherins, Selectins, and Integrins in CAM-DR in L...
- Beyond TNBC: Repositioning of Clofazimine Against ...
- Neutrophils as Orchestrators in Tumor Development ...
- Qualitative MR Imaging Features for the Differenti...
- A Nomogram Based on Serum Biomarkers and Clinical ...
- Macrophages in Osteosarcoma Immune Microenvironmen...
- Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Extracrani...
- Types of Mastectomies and Immediate Reconstruction...
- Cepharanthine induces the proliferation of human d...
- The Role of Hippocampal Neurogenesis in ANT-DBS fo...
- Efficacy of antimicrobial photodynamic therapy wit...
- Antimicrobial peptides for the prevention and trea...
- PET detectives: Molecular imaging for phaeochromoc...
- NR5A1 c.991‐1G > C splice‐site variant causes fami...
- Klotho gene G395A and C1818T polymorphisms in acro...
- The use of growth hormone therapy in adults with P...
- Oxytocin in young children with Prader‐Willi syndrome
- Association of urinary free cortisol with bone for...
- SRY‐negative 46,XX testicular/ovotesticular DSD: l...
- Classification and morphology of middle mesial can...
- Peroneal Flap – How to Harvest and Clinical Apprai...
- Inferior Alveolar Nerve Reconstruction in Extensiv...
- Technical Principles and Clinical Workflow of Tran...
- The human melanocyte and melanoblast populations p...
- Efficacy and Safety of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Clust...
- Efficacy and Safety of Pembrolizumab (MK-3475) Plu...
- Pilot Study of a 1-Millimeter Resolution Clinical ...
- Systemic Inflammation Response Index Is a Predicto...
- Retention and survival rate of etanercept in psori...
- The Goldman‐Fox Syndrome: Treating and Preventing ...
- Evaluation of lens clarity in children with atopic...
- Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy in the treatmen...
- Increased risk of depression and impairment in qua...
- Scrotal erythema and geographic tongue subsequent ...
- Dermoscopic characterization of guttate psoriasis,...
- Skin manifestations in SARS‐CoV‐2 infection
- Topical and Systemic Retinoids for the Treatment o...
- Evaluation of Oral Isotretinoin Effects on Hearing...
- Losartan for treatment of epidermolysis bullosa – ...
- investigation of thyroid blood tests and thyroid u...
- Rituximab in Practice: Clinical Evaluation of Pati...
- The Most Common Allergens
- The risk for severe COVID 19 in patients with auto...
- Hypertrichosis and hair repigmentation in patients...
- Adalimumab in the management of hidradenitis suppu...
- Unsuccessful palliative treatment of extraocular s...
- Ectropion surgery might not be a long‐term solutio...
- Can Rituximab Be Used In The Treatment Of Pemphigu...
- The additive efficacy of therapeutic low‐intensity...
- Safety and efficacy profile of oral cyclosporine v...
-
▼
Δεκ 10
(50)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (21)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (28)
-
▼
Δεκεμβρίου
(792)
-
►
2019
(12076)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (19)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (54)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (4765)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (5155)
-
►
2018
(3144)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (3144)
Ετικέτες
Πληροφορίες
Πέμπτη 10 Δεκεμβρίου 2020
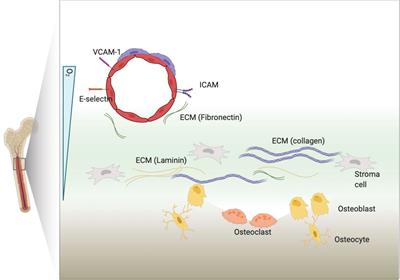
Cadherins, Selectins, and Integrins in CAM-DR in Leukemia
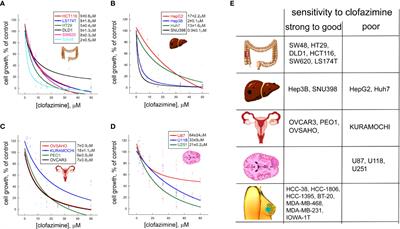
Beyond TNBC: Repositioning of Clofazimine Against a Broad Range of Wnt-Dependent Cancers
|
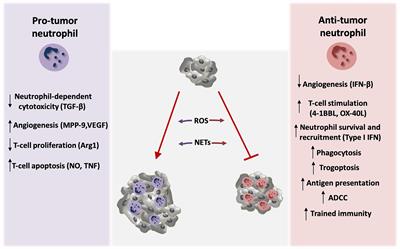
Neutrophils as Orchestrators in Tumor Development and Metastasis Formation
|
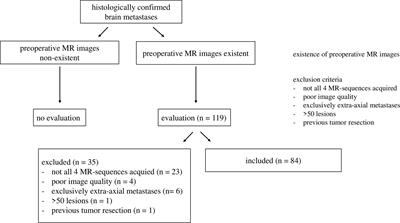
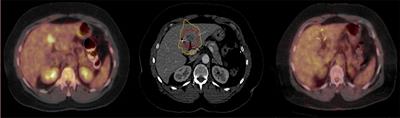
Qualitative MR Imaging Features for the Differentiation of Glioblastoma and Brain Metastases
|
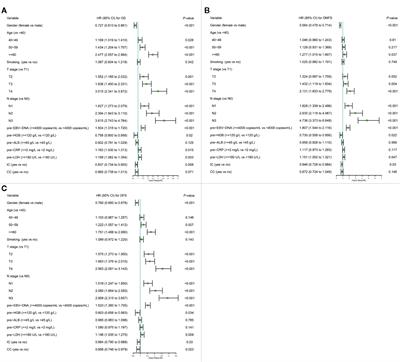
A Nomogram Based on Serum Biomarkers and Clinical Characteristics to Predict Survival in Patients With Non-Metastatic Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
|
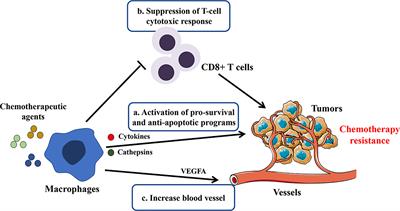
Macrophages in Osteosarcoma Immune Microenvironment: Implications for Immunotherapy
|
Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Extracranial Metastases From Primary Ovarian and Uterine Cancer
|
Types of Mastectomies and Immediate Reconstructions for Ipsilateral Breast Local Recurrences
|
Cepharanthine induces the proliferation of human dermal papilla cells and stimulates VEGF expression through increased intracellular calcium mobilization and HIF activation
|
The Role of Hippocampal Neurogenesis in ANT-DBS for LiCl-Pilocarpine-Induced Epileptic Rats
|
Efficacy of antimicrobial photodynamic therapy with Rose Bengal and blue light against cariogenic bacteria
|
Antimicrobial peptides for the prevention and treatment of dental caries
|
Αναζήτηση αυτού του ιστολογίου
! # Ola via Alexandros G.Sfakianakis on Inoreader
-
Does CBD Oil Lower Blood Pressure? This article was originally published at SundayScaries." Madeline Taylor POSTED ON January 13, 20...
-
Abstract Purpose Clinicians must balance the risks from hypotension with the potential adverse effects of vasopressors. Experts have rec...