Medicine by Alexandros G. Sfakianakis,Anapafseos 5 Agios Nikolaos 72100 Crete Greece,00302841026182,00306932607174,alsfakia@gmail.com,
Αρχειοθήκη ιστολογίου
-
►
2023
(272)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (141)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (131)
-
►
2022
(2066)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (80)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (170)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (190)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (203)
-
►
2021
(7399)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (186)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (472)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (851)
-
►
2020
(2517)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (792)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (21)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (28)
-
►
2019
(12076)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (19)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (54)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (4765)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (5155)
-
▼
2018
(3144)
-
▼
Δεκεμβρίου
(3144)
-
▼
Δεκ 18
(271)
- Australia cuts research funding for universities
- A Rare Case of Neutrophil-Rich, ALK-Negative Anapl...
- “Migratory” Pattern of Corticosteroid-Related Mult...
- FDG PET/CT Imaging of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Wit...
- Concordance Between Intracervical and Fundal Injec...
- Incidental Detection of Plasma Cell Neoplasm on 18...
- Diagnostic Accuracy of 18F-FDG PET/CT in Patients ...
- Comparisons Between PET With 11C-Methyl-L-Methioni...
- Fast-track Radioiodine Ablation Therapy After Thyr...
- Understanding the effect of indoor air pollution o...
- Imaging and Treatment of Post–90Y Radioembolizatio...
- Point Spread Function Reconstruction for Integrate...
- Focal Myositis of the Leg Presenting as Fever of U...
- Correction to: Photobiomodulation with single and ...
- Evaluation of lung transplant perfusion using iodi...
- Pulmonary atresia and ventricular septal defect,Co...
- An accurate tool to detect cardiac amyloidosis
- Gujarati hypertensives
- contrast media-induced nonrenal adverse drug react...
- Phosphodiesterase 7B1 as therapeutic target for tr...
- Temporal and climate characteristics of respirator...
- Occurrences and patterns of residual organochlorin...
- The dominant nutrient foramen at the clavicular mi...
- Re: “Drug Use and Misuse in the Mountains: A UIAA ...
- A Clinical Trial Using Methylation Age to Evaluate...
- Comparison of two different laser photobiomodulati...
- Multi-response optimization to obtain better perfo...
- miR-100 maintains phenotype of tumor-associated ma...
- Atypical GATA transcription factor TRPS1 represses...
- Relationships between the properties of Spitsberge...
- Streptomyces canus GLY-P2 degrades ferulic and p-h...
- Higher Serum Uric Acid is a Risk Factor of Vertebr...
- Depression and Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: Bir...
- An Update on Addison’s Disease
- Effects of Environmental Variables on Spatiotempor...
- Identification of Core Gene Biomarkers in Patients...
- ICOS/ICOSL upregulation mediates inflammatory resp...
- MicroRNA-29a enhances autophagy in podocytes as a ...
- Resilience-based intervention for UK military recr...
- miR-100 maintains phenotype of tumor-associated ma...
- Atypical GATA transcription factor TRPS1 represses...
- Influence of shrub roots on soil macropores using ...
- Bioremediation of soil contaminated by hydrocarbon...
- Amendment of Caulerpa sertularioides marine alga w...
- How autochthonous microorganisms influence physiol...
- The distribution and accumulation of mercury and m...
- Vitamin C Attenuates Sodium Fluoride-Induced Mitoc...
- Serum periostin levels in adults of Chinese descen...
- Review of cold-induced urticaria characteristics, ...
- Classical and quantum computers are vying for supe...
- Spain to establish parliamentary office of science
- 2018 in news: The science events that shaped the year
- Daily briefing: The scientists who mattered in 2018
- Why a palm-fringed Pacific island harbours pools ...
- From the archive
- A ‘Ginsu shark’ lost a tooth in its Cretaceous di...
- [ASAP] Anthracene as a Launchpad for a Phosphinide...
- Neuroimaging features of fatal high-altitude cereb...
- VACTERL association – Ultrasound findings and auto...
- Author's Reply
- Role of 3D SPACE sequence and susceptibility weigh...
- Percentile reference curves for normal pancreatic ...
- Olfactory fossa depth: CT analysis of 1200 patients
- Drug-induced changes in dentate nuclei of cerebellum
- Isolated spontaneous cerebrospinal fluid rhinorrho...
- Adiós Amigo - Passing the baton
- Ultrasound elastography findings in piriformis mus...
- Clinicoradiologicial aspects of secretory carcinom...
- Magnetic resonance imaging of ankle ligaments: A p...
- Campomelic dysplasia with 10 pairs of ribs in a pr...
- Myocardial nulling pattern in cardiac amyloidosis ...
- Normal adrenal gland thickness on computerized tom...
- Collateral or fistula? Coronary artery as the prim...
- Dealing with technical challenges in embolization ...
- An Estimation of the Possible Migration Path of th...
- Deoxyribose and deoxysugar derivatives from photop...
- MiR-152-3p promotes the development of chronic mye...
- MicroRNA-490-3p inhibits inflammation and apoptosi...
- GluR1 protects hypoxic ischemic brain damage via a...
- Soil properties and earthworm populations associat...
- Microalgal biomass production through phycoremedia...
- Combined influence of the local atmosphere conditi...
- Long non-coding RNA H19 promotes the osteogenic di...
- MiR-143-3p regulates early cartilage differentiati...
- A ‘Ginsu shark’ lost a tooth in its Cretaceous di...
- Degradative enzymes for type II arabinogalactan si...
- Metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicu...
- Hypoxia is involved in hypoxic pulmonary hypertens...
- IL-9 exacerbates the development of chronic obstru...
- The Foundation of the Future of MCH
- Spain to establish parliamentary office of science
- Deoxyribose and deoxysugar derivatives from photop...
- [ASAP] Self-Sorting of Amphiphilic Copolymers for ...
- [ASAP] Synergetic Organocatalysis for Eliminating ...
- [ASAP] Copper-Catalyzed Radical 1,4-Difunctionaliz...
- What a partial US-government shutdown would mean f...
- The short- and long-term effects of nitrite on den...
- Nature’s 10: Ten people who mattered in science in...
- Why a palm-fringed Pacific island harbours pools ...
- Narrowing the rural oral healthcare gap: the 2017 ...
-
▼
Δεκ 18
(271)
-
▼
Δεκεμβρίου
(3144)
Ετικέτες
Πληροφορίες
Τρίτη 18 Δεκεμβρίου 2018
Australia cuts research funding for universities
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2CllVw6
A Rare Case of Neutrophil-Rich, ALK-Negative Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma in the Lung Mimicking a Pulmonary Abscess on 18F-FDG PET/CT
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2BsyBja
“Migratory” Pattern of Corticosteroid-Related Multifocal Bone Infarction on Bone Scintigraphy
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2QE4uzy
FDG PET/CT Imaging of Hepatocellular Carcinoma With Bile Duct Tumor Thrombus
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2Bslyyb
Concordance Between Intracervical and Fundal Injections for Sentinel Node Mapping in Patients With Endometrial Cancer?: A Study Using Intracervical Radiotracer and Fundal Blue Dye Injections
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2QHaKqc
Incidental Detection of Plasma Cell Neoplasm on 18F-Choline PET/CT Imaging
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2BxgGYj
Diagnostic Accuracy of 18F-FDG PET/CT in Patients With Biochemical Evidence of Recurrent, Residual, or Metastatic Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2QE4b7S
Comparisons Between PET With 11C-Methyl-L-Methionine and Arterial Spin Labeling Perfusion Imaging in Recurrent Glioblastomas Treated With Bevacizumab
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2Bt0I1x
Fast-track Radioiodine Ablation Therapy After Thyroidectomy Reduces Sick Leave in Patients With Differentiated Thyroid Cancer (FASTHYNA Trial)
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2QHaHL2
Understanding the effect of indoor air pollution on pneumonia in children under 5 in low- and middle-income countries: a systematic review of evidence
Abstract
Exposure to indoor air pollution increases the risk of pneumonia in children, accounting for about a million deaths globally. This study investigates the individual effect of solid fuel, carbon monoxide (CO), black carbon (BC) and particulate matter (PM)2.5 on pneumonia in children under 5 in low- and middle-income countries. A systematic review was conducted to identify peer-reviewed and grey full-text documents without restrictions to study design, language or year of publication using nine databases (Embase, PubMed, EBSCO/CINAHL, Scopus, Web of Knowledge, WHO Library Database (WHOLIS), Integrated Regional Information Networks (IRIN), the World Meteorological Organization (WMO)-WHO and Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Exposure to solid fuel use showed a significant association to childhood pneumonia. Exposure to CO showed no association to childhood pneumonia. PM2.5 did not show any association when physically measured, whilst eight studies that used solid fuel as a proxy for PM2.5 all reported significant associations. This review highlights the need to standardise measurement of exposure and outcome variables when investigating the effect of air pollution on pneumonia in children under 5. Future studies should account for BC, PM1 and the interaction between indoor and outdoor pollution and its cumulative impact on childhood pneumonia.
from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2EthaSC
Imaging and Treatment of Post–90Y Radioembolization Radiation Dermatitis
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2QGwaUi
Point Spread Function Reconstruction for Integrated 18F-FET PET/MRI in Patients With Glioma: Does It Affect SUVs and Respective Tumor-to-Background Ratios?
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2BvXyKv
Focal Myositis of the Leg Presenting as Fever of Unknown Origin Detected by FDG PET/CT
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2QE5gwh
Correction to: Photobiomodulation with single and combination laser wavelengths on bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells: proliferation and differentiation to bone or cartilage
In the originally published article, the name of the 3rd and 4th authors were labeled incorrectly. The correct names are Mohammadreza Baghaban Eslaminejad and Leila Taghiyar. Also, affiliation 4 has been corrected.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2Brs8ET
Evaluation of lung transplant perfusion using iodine maps from novel spectral detector computed tomography
Nils Große Hokamp, Amit Gupta
DOI:10.4103/ijri.IJRI_35_18
We report the case of a 51-year-old patient who underwent bilateral lung transplantation and presented with an unstable condition and sepsis 6 days after transplantation. The performed contrast enhanced spectral detector computed tomography (CT) using a dual-layer detector showed absence of perfusion in the left lung on iodine maps, although branches of the pulmonary artery were patent. This prompted retrospective evaluation of CT images and total venous occlusion of the left pulmonary veins was found. Here, iodine maps helped in raising conspicuity of loss of lung perfusion.
http://www.ijri.org/currentissue.asp?sabs=y
Pulmonary atresia and ventricular septal defect,Coronary artery as the primary source of pulmonary blood flow
Anurag Yadav, Salil Bhargava, T B S Buxi, Krishna Sirvi
DOI:10.4103/ijri.IJRI_489_17
In patients with pulmonary atresia and ventricular septal defect (PA/VSD), a coronary artery being the primary source of pulmonary blood flow is a rare entity. We describe two cases of PA/VSD with coronary-to-pulmonary artery fistula with emphasis on the role of Computed Tomographic Angiography (CTA) in depicting all the sources of pulmonary blood supply, to predict surgical management and need for unifocalization of Major Aortopulmonary Collateral Arteries (MAPCA's).
http://www.ijri.org/currentissue.asp?sabs=y
An accurate tool to detect cardiac amyloidosis
Harshavardhan Mahalingam, Binita Riya Chacko, Aparna Irodi, Elizabeth Joseph, Leena R Vimala, Viji Samuel Thomson
DOI:10.4103/ijri.IJRI_84_18
Context: The pattern of myocardial nulling in the inversion scout sequence [time of inversion scout (TIS)] of cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is an accurate tool to detect cardiac amyloidosis. The pattern of nulling of myocardium and blood at varying times post gadolinium injection and its relationship with left ventricular mass (LVM) in amyloidosis have not been described previously. Aims: The aim is to study the nulling pattern of myocardium and blood at varying times in TIS and assess its relationship with LVM and late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) in amyloidosis. Materials and Methods: This was a retrospective study of 109 patients with clinical suspicion of cardiac amyloidosis who underwent MRI. Of these, 30 had MRI features of amyloidosis. The nulling pattern was assessed at 5 (TIS5min) and 10 (TIS10min) minutes (min) post contrast injection. Nulling pattern was also assessed at 3min (TIS3min) in four patients and 7min (TIS7min) in five patients. Myocardial mass index was calculated. Mann-Whitney U test was done to assess statistical difference in the myocardial mass index between patients with and without reversed nulling pattern (RNP) at TIS5min. Results: RNP was observed in 58% at TIS5minand 89.6% at TIS10min. Myocardial mass index was significantly higher in patients with RNP at TIS5min[mean = 94.87 g/m2; standard deviation (SD) =17.63) when compared with patients with normal pattern (mean = 77.61 g/m2; SD = 17.21) (U = 18; P = 0.0351). Conclusion: In cardiac amyloidosis, TIS sequence shows temporal variability in nulling pattern. Earlier onset of reverse nulling pattern shows a trend toward more LVM and possibly more severe amyloid load.
http://www.ijri.org/currentissue.asp?sabs=y
Gujarati hypertensives
Jayesh Dalpatbhai Solanki, Hemant B Mehta, Sunil J Panjwani, Hirava B Munshi, Chinmay J Shah
DOI:10.4103/jpp.JPP_59_18
Objective: To study the effect of different classes and combinations of antihypertensive agents on arterial stiffness and central hemodynamic parameters. Materials and Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted in 446 treated apparently healthy hypertensives. Oscillometric PWA was performed by Mobil-o-Graph (IEM, Germany) to derive cardiovascular parameters that were further analyzed in groups stratified by antihypertensive used. Study parameters were brachial hemodynamics (blood pressure (BP), heart rate, and rate pressure product); arterial stiffness (augmentation pressure, augmentation index, pulse wave velocity, total arterial stiffness, and pulse pressure amplification); and central hemodynamics (central BP, cardiac output, and stroke work). Statistical significance was kept at P < 0.05. Results: All groups were selected by matching of age, gender, and body mass index. They were comparable with major confounding factors. There was no difference between study parameters in hypertensives taking exclusive angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (ACEI), calcium channel blocker (CCB), or angiotensin II receptor blocker. Multitherapy showed better hemodynamics and monotherapy showed better stiffness parameters. Addition of CCB to ACEI did not make a difference except with diastolic BP. For most comparisons, most of the results lacked statistical significance. Conclusion: Discrete PWA parameters showed no class difference in hypertensives, treated by conventional monotherapy or combination, ACEI appears to be the best drug. This also indicates that early diagnosis and blood pressure control are more important than antihypertensive used.
http://www.jpharmacol.com/currentissue.asp?sabs=y
contrast media-induced nonrenal adverse drug reactions
Maurizio Sessa, Claudia Rossi, Annamaria Mascolo, Antonella Scafuro, Rosanna Ruggiero, Gabriella di Mauro, Salvatore Cappabianca, Roberto Grassi, Liberata Sportiello, Concetta Rafaniello
DOI:10.4103/jpp.JPP_92_18
The aim of this study was to investigate the scientific contribution of Italian clinical research for contrast media-induced nonrenal adverse drug reactions over the last three decades. Ovid Embase, Ovid MEDLINE, Web of Science, and Cochrane Methodology Register were used as data sources to identify Italian descriptive studies, observational studies, meta-analyses, and clinical trials assessing contrast media-induced nonrenal adverse drug reactions as a safety outcome. The population of interest was men and women exposed to a contrast medium. Between 1990 and 2017, 24 original articles investigating contrast-induced nonrenal adverse drug reactions were identified. The cohort study was the most representative study design (10/24; 41.7%). The 24 studies were conducted mainly as monocenter studies (14/24; 58.3%) and without receiving funding (17/24; 70.8%). Seventeen out of 24 studies provided a level of evidence ranging from III-2 (11/24; 45.8%) to IV (6/24; 25.0%) on a Merlin scale. In total, 14 of 24 (58.3%) studies were published in a scientific journal ranked in the first quartile of their subject area. The 24 original articles mainly focused on adverse drug reactions already observed during clinical trials (i.e., idiosyncratic systemic reactions). In conclusion, during the last three decades and a burst was not observed in the Italian clinical research investigating contrast-induced nonrenal adverse drug reactions. High-quality clinical research is needed especially for procedures to prevent the onset of the aforementioned events, to identify risk factors, to minimize the risk of their occurrence, and to optimize their related prognosis.
http://www.jpharmacol.com/currentissue.asp?sabs=y
Phosphodiesterase 7B1 as therapeutic target for treatment of cognitive dysfunctions in multiple sclerosis
DOI:10.4103/jpp.JPP_77_18
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune, chronic degenerative neuroinflammatory disorder affecting younger age groups of the United States of America and Europe. MS prevalence studies in India have shown that India is no longer a low-risk zone. Many studies have shown the seriousness of cognitive impairments (CIs) and its types caused in MS. In this review, the pathological basis for CI in various stages of MS was reviewed and revealed to provide a basis for the treatment. Role of phosphodiesterase 7B1 (PDE7B1) inhibitors in treating CI related to MS were also stated in this review. The literature for this review was collected from PubMed and Embase.
http://www.jpharmacol.com/currentissue.asp?sabs=y
Temporal and climate characteristics of respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis in neonates and children in Sousse, Tunisia, during a 13-year surveillance
Abstract
This study established the correlation between respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) bronchiolitis and climate factors in the area of Sousse, Tunisia, during 13 years (2003–2015), from neonates and children <= 5 years old and hospitalized in Farhat Hached University-Hospital of Sousse. The meteorological data of Sousse including temperature, rainfall, and humidity were obtained. RSV detection was carried out with the direct immunofluorescence assay. The impact of climate factors on viral circulation was statistically analyzed. From 2003 to 2015, the total rate of RSV bronchiolitis accounted for 34.5% and peaked in 2007 and 2013. RSV infection was higher in male cases and pediatric environment (p<0.001) and was detected in 47.3% of hospitalizations in intensive care units. The epidemic of this pathogen started in October and peaked in January (41.6%). When the infectivity of RSV was at its maximum, the monthly average rainfall was high (31 mm) and the monthly average temperature and the monthly average humidity were at their minimum (11 °C and 66%, respectively). RSV activity was negatively correlated with temperature (r = − 0.78, p = 0.003) and humidity (r = − 0.62, p = 0.03). Regression analysis showed that the monthly average temperature fits into a linear model (R2 = 61%, p < 0.01). No correlation between RSV activity and rainfall was observed (p = 0.48). The meteorological predictions of RSV outbreaks with specific Tunisian climate parameters will help in determining the optimal timing of appropriate preventive strategies. In the area of Sousse, preventive measures should be enhanced since October especially, when the temperature is around 11 °C and humidity is above 60%.
from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2LrFwxt
Occurrences and patterns of residual organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in cultured Chinese mitten crab ( Eriocheir sinensis ) in China: concentrations, sources, and a human health risk assessment
Abstract
Seventy Chinese mitten crab samples, encompassing a total of 2100 individuals, were collected from the main production areas in China. The objective was to assess the occurrences and patterns of 23 selected organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in the edible tissues and assess the associated dietary risk. Concentrations of total residual OCPs in the mitten crabs ranged from 0.72 to 51.51 μg kg−1, which was comparable to other global aquatic species. Dichlorodiphenyl trichloroethanes (DDTs) and hexachlorocyclohexanes (HCHs) were the two main contributors of total OCPs, with the detected values ranging from 0.14 to 30.89 μg kg−1 and 0.23 to 4.04 μg kg−1, respectively. Source analysis indicated the coexistence of both residual and recent DDT inputs, while there was no indication of HCH usage in the main production area of mitten crab. In terms of dietary risk, at least eight individual mitten crabs per day are permissible for consumption by local residents, indicating low risk from consumption. The results presented herein should guide the production and consumption of mitten crab, as well as promote the sustainable development of aquaculture in China.
from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2rLP8tQ
The dominant nutrient foramen at the clavicular midshaft: an anatomical study
Abstract
Background
The aim of the present study was to describe the prevalence and topography of the dominant nutrient foramen at the clavicle.
Methods
317 macerated human clavicles (167 right and 150 left) were available for the study. After detecting the dominant nutrient foramen, the total distance from the sternal surface to the examined nutrient foramen was measured. A foramen index (FI) was used for further data processing.
Results
We detected a dominant foramen in 300/317 (94.64%) clavicles, which was located in the middle third in 287/300 (95.7%) clavicles. The average clavicular length was measured at 14.9 cm ± 1.0 cm (range 11.6–17.5 cm) with an average foraminal distance from the sternoclavicular joint surface of 7.9 cm ± 1.3 cm (range 0.9–12.6 cm) in total. The mean FI was 53.2% ± SD 7.4% (range 5.5–79.3%).
Conclusion
The present study provides a topographic mapping of the foraminal area (46–60% of the total clavicular length). The findings help to assess clavicular fracture patterns, which pass through the foraminal area.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2R7gysC
Re: “Drug Use and Misuse in the Mountains: A UIAA MedCom Consensus Guide for Medical Professionals” by Donegani et al. (High Alt Med Biol 17:157–184)
High Altitude Medicine &Biology, Ahead of Print.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2Ls9YaA
A Clinical Trial Using Methylation Age to Evaluate Current Antiaging Practices
Rejuvenation Research, Ahead of Print.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2Sb97xB
Comparison of two different laser photobiomodulation protocols on the viability of random skin flap in rats
Abstract
To identify the best low level laser photobiomodulation application site at the same irradiation time to increase the viability of the skin flap in rats. Eighteen male rats (Rattus norvegicus: var. Albinus, Rodentia Mammalia) were randomly distributed into three groups (n = 6). Group I (GI) was submitted to simulated laser photobiomodulation; group II (GII) was submitted to laser photobiomodulation at three points in the flap cranial base, and group III (GIII) was submitted to laser photobiomodulation at 12 points distributed along the flap. All groups were irradiated with an Indium, Galium, Aluminum, and Phosphorus diode laser (InGaAlP), 660 nm, with 50 mW power, irradiated for a total time of 240 s in continuous emission mode. The treatment started immediately after performing the cranial base random skin flap (10 × 4 cm2 dimension) and reapplied every 24 h, with a total of five applications. The animals were euthanized after the evaluation of the percentage of necrosis area, and the material was collected for histological analysis on the seventh postoperative day. GII animals presented a statistically significant decrease for the necrosis area when compared to the other groups, and a statistically significant increase in the quantification of collagen when compared to the control. We did not observe a statistical difference between the TGFβ and FGF expression in the different groups evaluated. The application of laser photobiomodulation at three points of the flap cranial base was more effective than at 12 points regarding the reduction of necrosis area.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2BshX3a
Multi-response optimization to obtain better performance and emission level in a diesel engine fueled with water-biodiesel emulsion fuel and nanoadditive
Abstract
The present study aims to investigate the optimum condition of stationary diesel engine's operating parameters to obtain better performance and emission level, where the diesel engine is fueled with different concentrations of soybean biodiesel (SB), water, and alumina (Al) nanoadditive. Taguchi method coupled with gray relational analysis has been implemented in this study to obtain the optimum concentration of SB, water, and Al nanoparticle, and statistical analysis of variance (ANOVA) is applied to obtain the individual response of operating parameters on overall engine performance and emission level. Various concentration of SB (10%, 20%, and 30%), water (10%, 20%, and 30%), and Al nanoparticle (50 ppm, 100 ppm, and 150 ppm) are mixed with base diesel (BD) by mechanical agitation and followed by an ultra-sonication process. The fuel properties are measured based on EN590 standards, and the experiments are conducted in a single-cylinder, four-stroke, natural aspirated stationary diesel engine based on an L9 orthogonal array fuel combination. From the obtained gray relational co-efficient (GRC) and signal-to-noise (S/N) ratio, the optimum concentration of SB, water, and nanoadditive are identified as 20%, 10%, and 100 ppm, respectively, and a confirmation experiment has also been carried out to confirm the improvements at optimum condition. The ANOVA results imply that water concentration (WC) has the maximum influence on overall diesel engine's performance and emission level followed by nanoparticle and SB concentrations. Overall, it can be concluded that the engine exhibits better performance and greener emissions at optimal condition.
from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2A8puEh
miR-100 maintains phenotype of tumor-associated macrophages by targeting mTOR to promote tumor metastasis via Stat5a/IL-1ra pathway in mouse breast cancer
miR-100 maintains phenotype of tumor-associated macrophages by targeting mTOR to promote tumor metastasis via Stat5a/IL-1ra pathway in mouse breast cancer
miR-100 maintains phenotype of tumor-associated macrophages by targeting mTOR to promote tumor metastasis via Stat5a/IL-1ra pathway in mouse breast cancer, Published online: 19 December 2018; doi:10.1038/s41389-018-0106-y
miR-100 maintains phenotype of tumor-associated macrophages by targeting mTOR to promote tumor metastasis via Stat5a/IL-1ra pathway in mouse breast cancerfrom A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2SUVF11
Atypical GATA transcription factor TRPS1 represses gene expression by recruiting CHD4/NuRD(MTA2) and suppresses cell migration and invasion by repressing TP63 expression
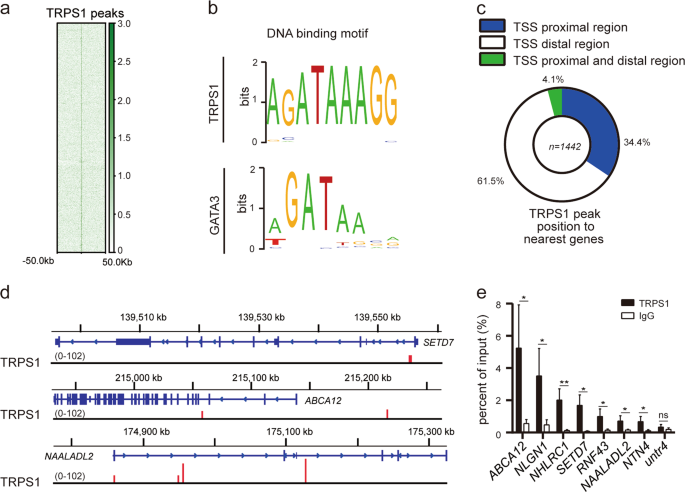
Atypical GATA transcription factor TRPS1 represses gene expression by recruiting CHD4/NuRD(MTA2) and suppresses cell migration and invasion by repressing TP63 expression
Atypical GATA transcription factor TRPS1 represses gene expression by recruiting CHD4/NuRD(MTA2) and suppresses cell migration and invasion by repressing <i>TP63</i> expression, Published online: 19 December 2018; doi:10.1038/s41389-018-0108-9
Atypical GATA transcription factor TRPS1 represses gene expression by recruiting CHD4/NuRD(MTA2) and suppresses cell migration and invasion by repressing TP63 expressionfrom A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2CkLQnp
Relationships between the properties of Spitsbergen soil, number and biodiversity of rhizosphere microorganisms, and heavy metal concentration in selected plant species
Abstract
Aims
The aim of this study was to cross correlate data on physico-chemical parameters of soil with rhizosphere microorganisms and plant species in order to gain more knowledge about formation of soil and development of plants in the face of the changing climate on Spitsbergen and relations between them.
Methods
We investigated physico-chemical parameters of soil samples and the number and biodiversity of microorganisms, bacteria (oligotrophic and copiotrophic), and fungi. Moreover, heavy metal concentrations in 6 species of vascular plants collected in different areas were analysed.
Results
The soil samples varied considerably in pH – from acid to alkaline, texture – from sand to loamy sand, and C:N ratio – from very low to high. In the soils, only partial Cd elevation expressed as the geoaccumulation index (Igeo) and the enrichment factor (EF) was detected. In the plants, the most significantly elevated concentrations of heavy metals expressed as Igeo and EF as well as the biological accumulation factor, bioconcentration factor, and translocation factor were detected in Salix polaris, Dryas octopetala, and Draba corymbosa. The high number of bacteria corresponded with an increase in the ecophysiological diversity index and the low colony development index, whereas a reverse relationship was found for fungi.
Conclusions
There was no significant impact of the geochemical properties on the total content of heavy metals in soil. The similar position of Cd and Pb in the order of heavy metal accumulation in the soil and plants was confirmed. TF showed that mainly these two metals were transported efficiently from roots to shoots. In the plants, the metals were distributed depending on the life form and their higher levels were detected in the woody perennials, e.g. S. polaris, D. octopetala, D. corymbosa, than in the herbaceous perennials. Very high numbers of culturable microorganisms were determined, regardless of the soil properties and plant species, which indicated that they were involved in the transformation of compounds containing C, N, and P and in the availability of heavy metals. The microorganisms and plants colonizing Spitsbergen soils showed great plasticity and adaptability to low temperatures and elevated Cd content.
from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2A5PMqB
Streptomyces canus GLY-P2 degrades ferulic and p-hydroxybenzoic acids in soil and affects cucumber antioxidant enzyme activity and rhizosphere bacterial community
Abstract
Aims
The present study was conducted to investigate the effectiveness of Streptomyces (GLY-P2) in degradation of ferulic acid (FA) and p-hydroxybenzonic acid (PHBA) in the rhizosphere of cucumbers by assaying the alteration of antioxidant enzymes activities and rhizospheric microbial community.
Methods
GLY-P2 was isolated, identified as Streptomyces canus, and applied to cucumber-planted soil containing FA and PHBA.
Results
Optimal conditions for FA and PHBA degradation by GLY-P2 were 40 °C, pH 7, and 0.2 g l−1 mixture of FA and PHBA. During the degradation, vanillin, vanillic acid, and protocatechoic acid were metabolites; and activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, ascorbate peroxidase (APX), and dehydroascorbate reductase in GLY-P2 were induced. When inoculated into cucumber-planted soil containing 220 μg g−1 mixture of FA and PHBA, GLY-P2 degraded FA and PHBA in soil, improved plant growth, and decreased malonaldehyde, superoxide radical, and hydrogen peroxide levels in leaves. GLY-P2 also enhanced activities of SOD, catalase, glutathione peroxidase, APX, monodehydroascorbate reductase, dehydroascorbate reductase, and glutathione reductase, increased contents of ascorbate and glutathione, and elevated transcript levels of copper/zinc SOD, manganese SOD, catalase, and APX in leaves. Moreover, GLY-P2 changed soil bacterial richness, diversity, and community composition, and increased phosphatase, catalase, urease, and sucrase activities in rhizospheric soil.
Conclusion
GLY-P2 mitigates FA and PHBA stress in cucumber by activating leaf antioxidant enzymes and affecting soil bacterial community.
from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2Sex33u
Higher Serum Uric Acid is a Risk Factor of Vertebral Fractures in Postmenopausal Women with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus

Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes
DOI: 10.1055/a-0815-4954
Purpose Serum uric acid (UA) level may affect bone metabolism because it has an anti-oxidative effect. However, whether serum UA level is associated with a fracture risk in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is unclear. We thus aimed to clarify the association between serum UA and bone parameters in T2DM. Methods We conducted a cross-sectional study to investigate the association of serum UA with bone mineral density (BMD) at lumbar spine (LS) and femoral neck (FN), bone turnover markers such as osteocalcin and urine type I collagen cross-linked N-telopeptide (uNTX), and the prevalence of vertebral fractures (VF) in 356 postmenopausal women and 512 men with T2DM. Results Multiple regression analyses adjusted for age, duration of diabetes, hemoglobin A1c, body mass index and log (serum creatinine) showed that serum UA level was significantly and negatively associated with uNTX in postmenopausal women with T2DM, whereas it was not associated with osteocalcin or BMD at each site. In men, serum UA was not associated with BMD or bone turnover markers. Because postmenopausal women with VF were significantly older and had longer duration of diabetes, higher serum creatinine level and lower BMD than those without it, logistic regression analyses adjusted for these confounding factors were performed. Higher serum UA level was significantly associated with the presence of VF. Conclusions The present study showed that higher serum UA is a risk factor for VF independently of BMD in postmenopausal women with T2DM.
[...]
© Georg Thieme Verlag KG Stuttgart · New York
Article in Thieme eJournals:
Table of contents | Abstract | Full text
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2LnvZrb
Depression and Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: Birds of a Feather, But When do They Flock Together?
Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes
DOI: 10.1055/a-0808-4269
The association between diabetes and depression is well recognised. Similarly, diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) is a frequent complication of diabetes. Given the high prevalence of these conditions individually, it is hardly surprising they frequently interact, conferring additional morbidity and a higher mortality risk. Despite this, the specific clinical characteristics that underpin co-morbid depression and DPN remain unclear. Additionally, there is insufficient insight into causal pathways and temporal trends. High-quality epidemiological data is limited, but they suggest that these conditions may share certain common risk factors, although there are also distinct differences such as gender. Improved insights into the risk factors for the co-existence of DPN and depression may help towards improved screening for and treatment of these conditions.
[...]
© Georg Thieme Verlag KG Stuttgart · New York
Article in Thieme eJournals:
Table of contents | Abstract | Full text
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2rFFZTM
An Update on Addison’s Disease
Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes
DOI: 10.1055/a-0804-2715
Addison's disease – the traditional term for primary adrenal insufficiency (PAI) – is defined as the clinical manifestation of chronic glucocorticoid- and/or mineralocorticoid deficiency due to failure of the adrenal cortex which may result in an adrenal crisis with potentially life-threatening consequences. Even though efficient and safe pharmaceutical preparations for the substitution of endogenous gluco- and mineralocorticoids are established in therapy, the mortality in patients with PAI is still increased and the health-related quality of life (HRQoL) is often reduced.PAI is a rare disease but recent data report an increasing prevalence. In addition to the common "classical" causes of PAI like autoimmune, infectious, neoplastic and genetic disorders, other iatrogenic conditions – mostly pharmacological side effects (e. g., adrenal haemorrhage associated with anticoagulants, drugs affecting glucocorticoid synthesis, action or metabolism and some of the novel anti-cancer checkpoint inhibitors) are contributing factors to this phenomenon.Due to the rarity of the disease and often non-specific symptoms at least in the early stages, PAI is frequently not considered resulting in a delayed diagnosis. Successful therapy is mainly based on adequate patient education as a cornerstone in the prevention and management of adrenal crisis. A focus of current research is in the development of pharmacokinetically optimized glucocorticoid preparations as well as regenerative therapies.
[...]
© Georg Thieme Verlag KG Stuttgart · New York
Article in Thieme eJournals:
Table of contents | Abstract | Full text
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2LnvRId
Effects of Environmental Variables on Spatiotemporal Variations of Nitrous Oxide Fluxes in the Pristine Riparian Marsh, Northeast China
Abstract
Nitrous oxide (N2O) is an important greenhouse gas, and the riparian marsh plays an important role in modulating atmospheric concentrations of N2O. To investigate the effects of environmental variables on spatiotemporal variations of N2O fluxes in the pristine riparian marsh, the static chamber-GC techniques were used to explore the spatiotemporal variations of N2O fluxes in Calamagrostis angustifolia swamp meadow marsh (CASMM), Ecotone wetland (EW) and Carex Schmidtii Meinsh. marsh (CSMM) along the pristine riparian in Sanjiang Plain during one year. During non-growing season (October, 2015 to April, 2016), the variability of N2O fluxes in the three marshes were not significantly different (P > 0.05). However, during growing season (May to October, 2016), both variability differences of N2O fluxes between CSMM and EW, and between CSMM and CASMM were significant (P < 0.01). Atmospheric temperature, soil NH4+-N content and soil volumetric moisture content were the driving factors during non-growing season. During growing season, soil NH4+-N and NO3−-N content were the driving factors among interactions of multiple environmental variables. CASMM and EW became the sinks of N2O during non-growing season but converted to the source of N2O during growing season. However, CSMM became all sink of N2O during every season.
from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2EyIdvA
Identification of Core Gene Biomarkers in Patients with Diabetic Cardiomyopathy
Diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a disorder of the myocardium in diabetic patients, which is one of the critical complications of diabetes giving rise to an increased mortality. However, the underlying mechanisms of DCM remain incompletely understood presently. This study was designed to screen the potential molecules and pathways implicated with DCM. GSE26887 involving 5 control individuals and 7 DCM patients was selected from the GEO database to identify the differentially expressed genes (DEGs). DAVID was applied to perform gene ontology (GO) and the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analyses. A protein-protein interaction (PPI) network was also constructed to visualize the interactions among these DEGs. To further validate significant genes and pathways, quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) and Western blot were performed. A total of 236 DEGs were captured, including 134 upregulated and 102 downregulated genes. GO, KEGG, and the PPI network disclosed that inflammation, immune disorders, metabolic disturbance, and mitochondrial dysfunction were significantly enriched in the development of DCM. Notably, IL6 was an upregulated hub gene with the highest connectivity degree, suggesting that it may interact with a great many molecules and pathways. Meanwhile, SOCS3 was also one of the top 15 hub genes in the PPI network. Herein, we detected the protein level of STAT3 and SOCS3 in a mouse model with DCM. Western blot results showed that the protein level of SOCS3 was significantly lower while phosphorylated-STAT3 (P-STAT3) was activated in mice with DCM. In vitro results also uncovered the similar alterations of SOCS3 and P-STAT3 in cardiomyocytes and cardiac fibroblasts induced by high glucose (HG). However, overexpression of SOCS3 could significantly reverse HG-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy and collagen synthesis of cardiac fibroblasts. Taken together, our analysis unveiled potential biomarkers and molecular mechanisms in DCM, which could be helpful to the diagnosis and treatment of DCM.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2R2jhUe
ICOS/ICOSL upregulation mediates inflammatory response and endothelial dysfunction in type 2 diabetes mellitus
OBJECTIVE: ICOS/ICOSL plays a crucial part in various disease-mediated immune responses. However, the exact role of ICOS/ICOSL in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) development remains unexplored. This study aims to investigate the role of ICOS/ICOSL in the pathogenesis of T2DM.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: Human peripheral blood T-lymphocytes (CD3) and umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were treated with high-glucose (HG) or advanced glycation end products (AGEs). A portion of CD3 cells was co-cultured with HUVECs and treated with different mediums or anti-ICOS mAbs. The ICOS/ICOSL and caspase-3 protein expression was measured by Western blotting. ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay), MTT (3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide), and NOx production assays were respectively used to detect cytokines level, cell viability and the production of NOx.
RESULTS: HG and AGEs significantly upregulated ICOS/ICOSL expressions in T cells and HUVECs. T cell contact with HUVECs secreted more IFN-γ, IL-4, and IL-10 compared to non-contact cells, while cytokines from IL-6-, IL-1β-, and CM- (the conditioned medium) treated cells did not differ from the control. A significant increase of IL-8 and IL-6 was found in HUVECs under both contact and non-contact conditions vs. control cells. Similar results were also observed in the comparison between CM1- (T cell condition medium) or CM2- (co-culture condition medium) treated cells and control cells. However, CM1 and CM2 treatment significantly inhibited cell viability and increased caspase-3 and NOx production; blocking ICOS/ICOSL remarkably decreased cytokines secretion, enhanced cell viability and reduced caspase-3 and NOx production.
CONCLUSIONS: HG and AGEs cause T cell inflammatory response and vascular endothelial dysfunction by upregulating ICOS/ICOSL, which may be one of the possible mechanisms of cardiovascular complications development in T2DM patients.
L'articolo ICOS/ICOSL upregulation mediates inflammatory response and endothelial dysfunction in type 2 diabetes mellitus sembra essere il primo su European Review.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2Cl8Kvd
MicroRNA-29a enhances autophagy in podocytes as a protective mechanism against high glucose-induced apoptosis by targeting heme oxygenase-1
OBJECTIVE: To evaluate the effects of miR-29a on the high glucose (HG)-induced apoptosis and the correlation between miR-29a and heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) and the underlying molecular mechanism.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: The cell apoptosis was analyzed by the flow cytometry, and the cells autophagy was evaluated using the transmission electron microscopy. Luciferase reporter assay was carried out to detect the correlation between miR-29a and HO-1. Besides, reverse transcription-PCR and Western blot were applied to detect the mRNA and protein levels.
RESULTS: The expression of miR-29a was significantly decreased in the HG-treated podocytes. Besides, miR-29a overexpression could promote cellular autophagy and significantly reduce HG-induced podocytes apoptosis. Moreover, HO-1 was a direct target of miR-29a and the pre-autophagy and the anti-apoptotic effects of miR-29a on HG-treated podocytes could be significantly reversed by the HO-1 siRNA administration.
CONCLUSIONS: MiR-29a functionally promoted podocytes autophagy and inhibited apoptosis through the HO-1dependent pathway in the HG condition.
L'articolo MicroRNA-29a enhances autophagy in podocytes as a protective mechanism against high glucose-induced apoptosis by targeting heme oxygenase-1 sembra essere il primo su European Review.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2T0zRBf
Resilience-based intervention for UK military recruits: a randomised controlled trial
Objectives
We evaluated a military resilience intervention which aimed to help UK military recruits to manage their personal health and well-being more effectively.
MethodsTrainers within six pre-existing training teams were randomly allocated by team to deliver a resilience-based intervention (SPEAR) or usual training (control) during recruit training. 23 trainers delivered SPEAR; 18 delivered the control training. 707 recruits participated (n=358 SPEAR and n=349 controls). Outcome measures were obtained before and after recruit training and 3 months later. Measures of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), common mental disorder (CMD) symptoms, alcohol use, homesickness and mental health stigmatisation were obtained at baseline. Repeat baseline scales plus measures of help-seeking, cohesion, leadership and training impact were obtained at the two follow-up points.
ResultsResponse rates were 91.7% (baseline), 98.1% (post) and 73.6% (follow-up). Following adjustment for potential confounders, levels of PTSD, CMD symptoms, alcohol misuse, help-seeking and homesickness were not significantly different between groups at any measurement point. Stigmatisation was significantly lower among SPEAR recipients at baseline but was not significantly different at the two follow-up points. Following adjustment for mental health confounders, there were no significant between-group differences in perceptions of leadership and cohesion and in ratings of six training outcomes at the two follow-up points.
ConclusionsWe found no evidence that resilience-based training had any specific benefit to the health and well-being of UK military recruits.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2Cl93Gn
miR-100 maintains phenotype of tumor-associated macrophages by targeting mTOR to promote tumor metastasis via Stat5a/IL-1ra pathway in mouse breast cancer
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2PLvV5d
Atypical GATA transcription factor TRPS1 represses gene expression by recruiting CHD4/NuRD(MTA2) and suppresses cell migration and invasion by repressing TP63 expression

from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2UTqKE6
Influence of shrub roots on soil macropores using X-ray computed tomography in a shrub-encroached grassland in Northern China
Abstract
Purpose
The relationship between soil macropore and plant roots warrants special attention because it influences the behavior of water in soil. However, the influence of shrub roots on soil macropores in shrub-encroached grasslands is poorly understood. The objectives of this study were to quantify soil macropores and root architecture in a shrub-encroached grassland in northern China, and to reveal the relationship between shrub roots and soil macropore.
Materials and methods
In this study, treatments were performed that corresponded to three successional states of the shrub C. microphylla L. with three different shrub densities. At each site, three undisturbed soil cores were excavated under the shrub canopies, and a Philips medical scanner was used to simultaneously visualize and quantify the soil and root architectures.
Results and discussion
Strong positive correlations between root volume, length, and surface area and the solid surface/solid volume ratio were found, and greater root growth was noted in more porous soil. The results highlighted that the soil macropore characteristics corresponded well with the root characteristics of the soils for the three treatments. Soil macroporosity and macropore volume increased with increasing shrub root network density. In addition, the influence of plant roots on soil macropores increased with increasing shrub encroachment. The study confirmed that the large number of macropores found in the soils under shrubs was attributed to the great degree of root development there.
Conclusions
The greater degree of macroporosity under shrubs was attributed to the larger root network density, which might cause greater amounts of water to be concentrated in the deep soil layer by macropore flow under shrub patches. The influence of plant roots on soil macropores increased with increasing shrub encroachment.
from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2rHRoSZ
Bioremediation of soil contaminated by hydrocarbons with the combination of three technologies: bioaugmentation, phytoremediation, and vermiremediation
Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to evaluate the removal of total petroleum hydrocarbons (TPH), alkanes and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH).
Materials and methods
Using phytoremediation (Panicum maximum) (G), vermiremediation (Pontoscolex corethrurus) (E), and bioaugmentation (encapsulated bacterial consortium) (B), individually and in combination, in contaminated soil by oil (PS) with sterilized (St) and non-sterilized treatments. Grass and earthworm biomass and the number of cocoons were determined after 112 days.
Results and discussion
The biomass of the P. maximum increased significantly from 1.7 to 2.6-folds overtime when it was cultivated in contaminated soil, either alone, in combination with earthworms, or with the bacterial consortium. After 112 days, the earthworm biomass significantly increased 2.0–2.6-folds with the highest increase in combination with the bacterial (PS+E+B), and its population increased from 4.9 to 8.5 times. P. corethrurus was not affected by the contamination so that deposition and hatch of cocoons (12–20) were observed. In sterilized treatments, no earthworms were detected after 112 days, which indicated that soil microorganisms are necessary for the earthworm's survival and colonization. Most alkane and PAH removal occurred within 28 days; at 112 days, the alkane was 78.5–94.5% and the PAH 54.5–77.2% in non-sterilized soil. Panicum maximum treatment (SP+G) removed 74–99% of alkanes from C10 to C38 and also removed PAHs in 43–50% (2–3 rings), 46–90% (4 rings), 73% (5 rings), and 59% (6 rings) after 112 days. The combination of the grass with P. corethrurus and the bacterial increased the PAHs removal of 2 and 3 rings (54–62%), 4 rings (56–92%), 5 rings (80%), and 6 rings (70%) after 112 days. In non-sterilized treatments, the highest TPH removal was with earthworms plus bacterial (E+B) (86.4%), followed by E+G+B (82.7%) and B (82.6%).
Conclusions
The use of endogeic earthworms and plants species from the same contaminated field can be an efficient alternative for increasing hydrocarbon removal.
from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2LqVfg6
Amendment of Caulerpa sertularioides marine alga with sulfur-containing materials to accelerate Cu removal from aqueous media
Abstract
This study reports a new approach of alga amendment in a live mode. The Caulerpa sertularioides alga was modified with sulfur-containing materials of methionine (C5H11NO2S) and sodium sulfate (Na2SO4) to more concentrate the sulfur content of the yielded biomass (adsorbent). The simple and amended C. sertularioides alga was fully characterized with FTIR, SEM, EDX, BET, BJH, and pHzpc techniques. The copper adsorption from aqueous media was done by three adsorbents of C. sertularioides-simple (CSS), C. sertularioides-Na2SO4 (CSN), and C. sertularioides-C5H11NO2S (CSC). The parameters of pH (2–6), adsorbent dosage (2–10 g/L), and contact time (3–80 min) were optimized at 5, 5 g/L, and 60 min, respectively. According to Langmuir isotherm (the best-fitted model), the maximum adsorption capacity of CSN (98.04 mg/g) was obtained 2.4 times higher than CSC (40.73 mg/g) and 9.5 times higher than CSS (10.29 mg/g). The Cu adsorption process by the adsorbents was best-fitted pseudo-second-order kinetic model. The CSN, CSC, and CSS biomasses were successfully reused 5, 4, and 4 times, respectively. The thermodynamic study revealed that the copper adsorption process by CSN is exothermic and non-spontaneous. Finally, the suitability of adsorbents prepared from algae was tested by cleaning a simulated wastewater.
from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2EEuNiT
How autochthonous microorganisms influence physiological status of Zea mays L. cultivated on heavy metal contaminated soils?
Abstract
The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of autochthonous microorganisms present in soil collected from heavy metal (HM) uncontaminated (Pb ≈ 59 mg kg−1, Cd ≈ 0.4 mg kg−1, Zn ≈ 191 mg kg−1), moderately (Pb ≈ 343 mg kg−1, Cd ≈ 12 mg kg−1, Zn ≈ 1876 mg kg−1), and highly (Pb ≈ 1586 mg kg−1, Cd ≈ 57 mg kg−1, Zn ≈ 3280 mg kg−1) contaminated sites on Zea mays elemental composition, physiological status, and growth parameters. For this purpose, half of the collected soil was sterilized and soil characterization was performed. After 45 days of cultivation, the presence of HM in the soil negatively affected photosynthesis and transpiration rates, relative chlorophyll content, anthocyanins index, chlorophyll fluorescence parameters, and content of oxidative stress products (H2O2 and Malondialdehyde) of Zea mays, while soil sterilization had a positive effect on those parameters. Average percentage of colonization of root segments by arbuscular mycorrhiza fungi decreased with an increase of HM contamination in the soil. The increase in shoot concentration of HMs, particularly Cd and Zn, was a result of contaminated soils sterilization. Aboveground biomass of maize cultivated on sterilized soil was 3-fold, 1.5-fold, and 1.5-fold higher for uncontaminated, moderately contaminated and highly contaminated soils respectively when compared to nonsterilized soils. Contrary to our expectation, autochthonous microflora did not improve plant growth and photosynthetic performance; in fact, they had a negative effect on those processes although they did reduce concentration of HMs in the shoots grown on contaminated soils.
from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2EvXGNi
The distribution and accumulation of mercury and methylmercury in surface sediments beneath the East China Sea
Abstract
China is a massive mercury emitter, responsible for a quarter of the world's mercury emissions, which transit the atmosphere and accumulate throughout its watercourses. The Changjiang (Yangtze) River is the third largest river in the world, integrating mercury emissions over its 1.8 × 106 km2 catchment and channelling them to the East China Sea where they can be buried. Despite its potential global significance, the importance of the East China Sea as a terminal mercury sink remains poorly known. To address this knowledge gap, total mercury and methylmercury concentrations were determined from 51 surface sediment samples revealing their spatial distribution, whilst demonstrating the overall pollution status of the East China Sea. Sedimentary mercury distributions beneath the East China Sea are spatially heterogeneous, with high mercury concentrations (> 25 ng g−1) corresponding to areas of fine-grained sediment accumulation. In contrast, some sites of fine-grained sediment deposition have significantly lower values of methylmercury (< 15 ng g−1), such as the Changjiang estuary and some isolated offshore areas. Fine-grained particles and organic matter availability appear to exert the dominant control over sedimentary mercury distribution in the East China Sea, whereas in situ methylation serves as an additional control governing methylmercury accumulation. Estimated annual sedimentary fluxes of mercury in the East China Sea are 51 × 106 g, which accounts for 9% of China's annual mercury emissions.
from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2EDRymW
Vitamin C Attenuates Sodium Fluoride-Induced Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis via Sirt1-SOD2 Pathway in F9 Cells
Abstract
Increasing evidence has suggested an important role played by reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the pathogenesis of fluorosis. Accumulating evidence demonstrates that vitamin C administration ameliorate sodium fluoride (NaF)-induced oxidative stress. However, the potentially beneficial effects of vitamin C against NaF-induced cytotoxicity and the underlying molecular mechanisms of this protection are not fully understood. Here, we found that NaF stimulated cytotoxicity, increased mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (mROS) production, and induced apoptosis in F9 embryonic carcinoma cells. Consistent with this finding, NaF exposure was associated with decreased Sirtuin 1 (Sirt1) protein expression, thus promoted the acetylation of manganese superoxide dismutase (SOD2), a key enzyme involved in regulating mROS production. However, all NaF-induced mitochondrial oxidative injuries were efficiently ameliorated by overexpression of Sirt1 or incubation with Mito-TEMPO (a SOD2 mimetic). Moreover, pretreatment with vitamin C enhanced the expression of Sirt1 and decreased NaF-induced mitochondrial oxidative stress and apoptosis. Knockdown of Sirt1 blocked the vitamin C-mediated reduction in mROS and apoptosis via inhibiting Sirt1-SOD2 signaling. Importantly, sodium-dependent vitamin C transporter 2 (SVCT-2) siRNA was found to partially block the ability of vitamin C to promote Sirt1/SOD2 signaling. In summary, our data indicate that Sirt1 plays a pivotal role in the ability of vitamin C to stimulate SOD2 activity and attenuate mitochondrial oxidative stress, which partially through vitamin C receptor in NaF-induced F9 cells injury.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2rM09eA
Serum periostin levels in adults of Chinese descent: an observational study
Periostin has been shown to be a marker of Type 2 airway inflammation, associated with airway eosinophilia. It has a potential role in identifying asthmatics who may be responsive to treatment with monoclonal ...
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2Lp2nK7
Review of cold-induced urticaria characteristics, diagnosis and management in a Western Canadian allergy practice
Cold-induced urticaria is a significant condition, especially among young females. Despite the morbidity of this disease, studies that fully characterize the disease are limited.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2rLnvkC
Classical and quantum computers are vying for superiority
Classical and quantum computers are vying for superiority
Classical and quantum computers are vying for superiority, Published online: 18 December 2018; doi:10.1038/d41586-018-07801-3
There are two research routes to the supercomputers of the future. Which side are you on?from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2rJBKqe
Spain to establish parliamentary office of science
Spain to establish parliamentary office of science
Spain to establish parliamentary office of science , Published online: 18 December 2018; doi:10.1038/d41586-018-07823-x
Nation's parliament has budgeted for a new office next year, following push from a grassroots scientists' movement.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2S9uY8C
2018 in news: The science events that shaped the year
2018 in news: The science events that shaped the year
2018 in news: The science events that shaped the year, Published online: 18 December 2018; doi:10.1038/d41586-018-07685-3
Wildfires, cosmic rays and ancient-human hybrids are some of this year's top stories.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2SSMDl9
Daily briefing: The scientists who mattered in 2018
Daily briefing: The scientists who mattered in 2018
Daily briefing: The scientists who mattered in 2018, Published online: 18 December 2018; doi:10.1038/d41586-018-07835-7
The ten people who made an impact in science, for good or bad. Plus, 'social punishments' for scientific misconduct, and a glimmer of hope for the Paris climate accord.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2ECrfxf
Why a palm-fringed Pacific island harbours pools of ice
Why a palm-fringed Pacific island harbours pools of ice
Why a palm-fringed Pacific island harbours pools of ice , Published online: 18 December 2018; doi:10.1038/d41586-018-07822-y
Hawaiian peaks host icy pockets year-round, but the cold spots are at risk from climate change.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2GpdQul
From the archive
From the archive
From the archive, Published online: 18 December 2018; doi:10.1038/d41586-018-07806-y
How Nature reported a strange apparition in 1918, and the latest Christmas toys in 1968.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2PIHBpm
A ‘Ginsu shark’ lost a tooth in its Cretaceous dinner
A 'Ginsu shark' lost a tooth in its Cretaceous dinner
A 'Ginsu shark' lost a tooth in its Cretaceous dinner , Published online: 18 December 2018; doi:10.1038/d41586-018-07832-w
Some 85 million years ago, an apex predator chomped on a flying reptile.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2rIGVXh
[ASAP] Anthracene as a Launchpad for a Phosphinidene Sulfide and for Generation of a Phosphorus–Sulfur Material Having the Composition P2S, a Vulcanized Red Phosphorus That Is Yellow

from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2Cl9Y9r
Neuroimaging features of fatal high-altitude cerebral edema
Indian Journal of Radiology and Imaging 2018 28(4):401-405
Acute high-altitude cerebral edema can occur in an unacclimatised individual on exposure to high altitudes and sometimes it can be fatal. Here we have described the neuroimaging features of a patient who suffered from fatal high altitude cerebral edema. Available literature is reviewed. Probable pathogenesis is discussed. The risk of acute mountain sickness is reported up to 25% in individuals who ascend to an altitude of 3500 meter and in more than 50% subjects at an altitude of 6000 meter. The lack of availability of advanced imaging facilities at such a higher altitude makes imaging of such condition a less described entity.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2Ck7AzN
VACTERL association – Ultrasound findings and autopsy correlation
Indian Journal of Radiology and Imaging 2018 28(4):452-455
VACTERL (vertebral, anal, cardiac, tracheoesophagus, renal, and limbs) is an abbreviation for the congenital group of abnormalities, including vertebral or vascular anomalies, anal atresia, cardiac defects, tracheoesophageal – fistula/esophageal atresia, renal defects, and limbs defects. It is a rare association and not accidental event where several organs are affected by developmental defects during blastogenesis. The exact cause is unknown; however, several environmental and genetic factors are included in literature. Three components out of seven are used to label as VACTERL. The combination is necessary, but the patient may have other congenital malformations as well. We present here an antenatal scan with autopsy correlation of one of the forms of VACTERL association spectrum.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2Cloyy0
Author's Reply
Indian Journal of Radiology and Imaging 2018 28(4):482-482
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2SVODsN
Role of 3D SPACE sequence and susceptibility weighted imaging in the evaluation of hydrocephalus and treatment-oriented refined classification of hydrocephalus
Indian Journal of Radiology and Imaging 2018 28(4):385-394
Objective: The aim of our study was to evaluate the diagnostic utility of three-dimensional sampling perfection with application optimized contrast using different flip angle evolution (3D SPACE) sequence and Susceptibility Weighted Imaging (SWI) in hydrocephalus and to propose a refined definition and classification of hydrocephalus with relevance to the selection of treatment option. Materials and Methods: A prospective study of 109 patients with hydrocephalus was performed with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) brain using standardized institutional sequences along with additional sequences 3D SPACE and SWI. The images were independently read by two senior neuroradiologists and the etiopathogenesis of hydrocephalus was arrived by consensus. Results: With conventional sequences, 46 out of 109 patients of hydrocephalus were diagnosed as obstructive of which 21 patients showed direct signs of obstruction and 25 showed indirect signs. In the remaining 63 patients of communicating hydrocephalus, cause could not be found out in 41 patients. Whereas with 3D SPACE sequence, 88 patients were diagnosed as obstructive hydrocephalus in which all of them showed direct signs of obstruction and 21 patients were diagnosed as communicating hydrocephalus. By including SWI, we found out hemorrhage causing intraventricular obstruction in three patients and hemorrhage at various sites in 24 other patients. With these findings, we have classified the hydrocephalus into communicating and noncommunicating, with latter divided into intraventricular and extraventricular obstruction, which is very well pertaining to the selection of surgical option. Conclusion: We strongly suggest to include 3D SPACE and SWI sequences in the set of routine MRI sequences, as they are powerful diagnostic tools and offer complementary information regarding the precise evaluation of the etiopathogenesis of hydrocephalus and have an effective impact in selecting the mode of management.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2ClomyM
Percentile reference curves for normal pancreatic dimensions in Indian children
Indian Journal of Radiology and Imaging 2018 28(4):442-447
Objectives: This study aims at determining the normal pancreatic dimensions in pediatric age groups considering demographic parameters and thus developing percentile reference curves for normal pancreatic dimensions in Indian children. Setting and Design: It is a cross-sectional study. Materials and Methods: A hospital-based cross-sectional study was planned at a children hospital during July 2016–December 2017, in which the pancreatic dimensions of 1078 normal children in the age range of 1 month to 19 years were obtained through abdominal ultrasonography (USG). The demographic details like age and gender were obtained for each child. Statistical Analysis Used: Percentile reference curves were obtained with reference to age for each gender type independently. Generalized additive models for location, scale, and shape were used to obtain percentile plots for each pancreatic part. Results: The mean age of children was 6.65 ± 4.43 years and the male-to-female ratio was 1.63:1. The head, body, and tail dimensions increased with the age. For head, up to 25th percentile, the curves were similar for both genders, while subsequent curves were higher in males as compared to females. Similar was the observation for body of pancreas. For tail, up to 75th percentile, the curves were similar for both genders. Conclusion: The normal ranges can be supportive in diagnosis of illness related to pancreas. The dimensions within 5–95th percentile along with iso-echogenicity can be regarded as normal, while the dimensions beyond these limits along with change of echogenicity can be suspected for pancreatic disorders.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2SQRXFq
Olfactory fossa depth: CT analysis of 1200 patients
Indian Journal of Radiology and Imaging 2018 28(4):395-400
Background: Olfactory fossa (OF) is a depression in anterior cranial cavity whose floor is formed by cribriform plate of ethmoid. Lateral lamella, which forms its lateral boundary, is a thin plate of bone and is at risk of injury during functional endoscopic sinus surgery, especially when fossa is deep/asymmetric. Aims: To measure the variations in the depth of OF and categorize Kerala population as per Keros classification using computed tomography (CT). Settings and Design: This study was conducted in our institution from January 2016 to August 2017. Patients >16 years of age undergoing CT scan of paranasal sinuses (PNS) were included. Materials and Methods: Coronal PNS CT scan studies of 1200 patients were reviewed. The depth of OF was measured from vertical height of lateral lamella. Statistical Methods: Results were analyzed according to gender and laterality using independent sample t-test and Chi-square test. Results: The mean depth of OF was 5.26 ± 1.69 mm. Statistically significant difference was seen in the mean depth of OF between males and females but not between right and left sides. Keros type I was found on 420 sides (17.5%), type II in 1790 (74.6%), and type III on 190 sides (7.9%). Type III Keros was more on the right (9%) than left (6.8%) side, more in males (9.5%) than females (5.9%), and more among males on the right side (11.4%). Asymmetry in OF depth between two sides was seen in 75% of subjects. Conclusion: Prevalence of the dangerous type III OF, even though low, is significant especially among males and on the right side. Therefore, preoperative assessment of OF depth must be done to reduce iatrogenic complications.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2Cl1Fe1
Drug-induced changes in dentate nuclei of cerebellum
Indian Journal of Radiology and Imaging 2018 28(4):480-480
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2SR7wwW
Isolated spontaneous cerebrospinal fluid rhinorrhoea as a rare presentation of idiopathic intracranial hypertension: Case reports with comprehensive review of literature
Indian Journal of Radiology and Imaging 2018 28(4):406-411
Isolated cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) rhinorrhoea as a sole presenting symptom of idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH) is extremely rare. IIH typically presents with headache, pulsatile tinnitus, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and visual disturbance. We report two cases which presented with acute onset spontaneous CSF rhinorrhoea without any other symptom. In addition, we discuss in detail imaging features of IIH with review of its literature.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2ClOMjR
Adiós Amigo - Passing the baton
Indian Journal of Radiology and Imaging 2018 28(4):379-379
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2SR7qp4
Ultrasound elastography findings in piriformis muscle syndrome
Indian Journal of Radiology and Imaging 2018 28(4):412-418
Background: Piriformis muscle syndrome (PMS) is relatively less known and underestimated because it is confused with other clinical pathological conditions. Delays in its diagnosis may lead to chronic somatic dysfunction and muscle weakness. Objective: Here, we aimed to evaluate the diagnostic performance of the ultrasound elastography (UE) as an easy, less-invasive, and cost-effective method for early diagnosis of PMS. Materials and Methods: Twenty-eight cases clinically diagnosed as PMS at the outpatient clinic were evaluated by UE. The elastographic strain ratio was calculated by dividing the strain value of the subcutaneous fat tissue by the mean stress value of the muscle beneath. The diagnostic performances of the strain rate measures were compared using the receiver operating characteristic curve analysis. Results: Twenty-one (N = 21) cases were female, and seven (N = 7) of the cases were male. The mean age was 45 years (ranged 24–62 years). The strain rates of piriformis muscle (PM) and gluteus maximus (GM) muscles were significantly higher on the PMS-diagnosed side (P < 0.001). The cutoff value of UE strain ratio for the PM and GM were 0.878 [95% confidence interval (CI) 0.774–0.981] and 0.768 (95% CI 0.622–0.913), respectively, and the sensitivity and specificity values were, respectively, 80.95% and 85.71% for the PM, and they were, respectively, 85.71% and 66.67% for the GM. Conclusion: We showed that the muscle elasticity and tissue hardening increased on the problematic side both on PM and GM. UE may provide early diagnosis of PMS, thereby increasing the possibility of treatment with less invasive methods.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2CmNQf3
Clinicoradiologicial aspects of secretory carcinoma breast: A rare pediatric breast malignancy
Indian Journal of Radiology and Imaging 2018 28(4):448-451
Secretory carcinoma (juvenile carcinoma) is one of the very rare breast malignancy reported to be prevalent in pediatric age group. We report imaging and clinicopathological features of secretory carcinoma breast with distant and axillary metastasis, in an 11-year-old girl, who presented with a painful lump in right breast. Ultrasound revealed a well-defined, partially microlobulated hypoechoic mass with skin and pectoralis muscle involvement and a suspicious morphology right axillary lymph node. Color Doppler revealed increased vascularity in both the breast mass and suspicious axillary node. Magnetic resonance imaging helped in better evaluation of pectoralis muscle involvement. Computed tomography (CT) neck, chest, and abdomen revealed multiple fibronodular opacities in bilateral lung fields. 18 Flouro-Deoxy-Glucose Positron Emission Tomography (FDG PET-CT) showed a hypermetabolic retroareolar breast mass with multiple hypermetabolic bilateral lung nodules suggesting lung metastasis. The histopathology confirmed the diagnosis of secretory carcinoma. The patient was offered chemotherapy for 2 years and put on follow-up since then.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2SR7kOe
Magnetic resonance imaging of ankle ligaments: A pictorial essay
Indian Journal of Radiology and Imaging 2018 28(4):419-426
Ankle trauma is commonly encountered and is most often a sprain injury affecting the ligaments. Accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment rest on knowledge of complex ligamentous anatomy of ankle and the entire spectrum of pathologies. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the imaging modality of choice for diagnosing ligament pathologies because of its multiplanar capability and high soft tissue contrast. With MRI, it is possible to triage and attribute the cause of post traumatic ankle pain to bone, ligament, or tendon pathologies, which otherwise overlap clinically. In this pictorial essay, emphasis is given to the intricate and unique anatomy and orientation of ankle ligaments. Pathologies of ankle ligaments have been elaborated.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2CmVdDd
Campomelic dysplasia with 10 pairs of ribs in a preterm neonate: A case report
Indian Journal of Radiology and Imaging 2018 28(4):456-459
Campomelic dysplasia (CD) is a rare form of skeletal dysplasia (incidence 1:200,000 births) which is associated with characteristic phenotypes including bowing of the limbs, a narrow thoracic cage, 11 pairs of ribs, hypoplastic scapulae, macrocephaly, flattened supraorbital ridges and nasal bridge, cleft palate, and micrognathia. In addition to the skeletal abnormalities, hydrocephalus, hydronephrosis, and congenital heart disease have been reported. We describe a preterm neonate who presented with respiratory failure and clinical features of CD. Our case had only 10 pairs of ribs, and to the best of our knowledge this is the first case report of CD with 10 pairs of ribs.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2SW7ROO
Myocardial nulling pattern in cardiac amyloidosis on time of inversion scout magnetic resonance imaging sequence – A new observation of temporal variability
Indian Journal of Radiology and Imaging 2018 28(4):427-432
Context: The pattern of myocardial nulling in the inversion scout sequence [time of inversion scout (TIS)] of cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is an accurate tool to detect cardiac amyloidosis. The pattern of nulling of myocardium and blood at varying times post gadolinium injection and its relationship with left ventricular mass (LVM) in amyloidosis have not been described previously. Aims: The aim is to study the nulling pattern of myocardium and blood at varying times in TIS and assess its relationship with LVM and late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) in amyloidosis. Materials and Methods: This was a retrospective study of 109 patients with clinical suspicion of cardiac amyloidosis who underwent MRI. Of these, 30 had MRI features of amyloidosis. The nulling pattern was assessed at 5 (TIS5min) and 10 (TIS10min) minutes (min) post contrast injection. Nulling pattern was also assessed at 3min (TIS3min) in four patients and 7min (TIS7min) in five patients. Myocardial mass index was calculated. Mann-Whitney U test was done to assess statistical difference in the myocardial mass index between patients with and without reversed nulling pattern (RNP) at TIS5min. Results: RNP was observed in 58% at TIS5minand 89.6% at TIS10min. Myocardial mass index was significantly higher in patients with RNP at TIS5min[mean = 94.87 g/m2; standard deviation (SD) =17.63) when compared with patients with normal pattern (mean = 77.61 g/m2; SD = 17.21) (U = 18; P = 0.0351). Conclusion: In cardiac amyloidosis, TIS sequence shows temporal variability in nulling pattern. Earlier onset of reverse nulling pattern shows a trend toward more LVM and possibly more severe amyloid load.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2CmV02T
Normal adrenal gland thickness on computerized tomography in an Asian Indian adult population
Indian Journal of Radiology and Imaging 2018 28(4):465-469
Context: The size and morphology of the adrenal glands are affected by several physiological and pathological conditions. Radiologists need to be aware of the normal thickness of adrenal gland to accurately assess patients with suspected adrenal pathology. However, there is limited data on the normal size of the adrenal glands. Moreover, this has not been studied in our population. Aims: To study the normal thickness of adrenal gland on computerized tomography (CT) in Indian adult population. Settings and Design: Retrospective study in a tertiary care hospital in Southern India. Subjects and Methods: Our study included 586 adults who underwent a CT abdominal angiogram over 15 months, and excluding patients with clinical or imaging evidence of adrenal disease. The measurements made included: the maximum thickness of the body, medial and lateral limbs, measured perpendicular to the long axis. Results: The median age was 51 (range: 18–85) years. The mean maximum thickness of the adrenal body, medial, and lateral limbs were 7.2 ± 1.8, 4.1 ± 1.1, and 4.3 ± 1.1 mm on the right side and 8.8 ± 1.9, 4.7 ± 1.1, and 4.9 ± 1.3 mm on the left. The cumulative thickness of the body and the limbs were 15.6 ± 3.7 mm and 18.4 ± 3.8 mm on the right and left sides, respectively. There was a statistically significant difference in all the measurements between the right and left adrenal glands (all P values = 0.000) and between men and women, being larger in men (P value <0.05). Among our patients 27% had at least one adrenal gland body measuring ≥10 mm in thickness. Conclusions: Our study has defined the normal range of adrenal gland thickness in an Asian Indian adult population, which may be used as a baseline reference for future research and as a reference for radiological reporting.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2SUxXln
Collateral or fistula? Coronary artery as the primary source of pulmonary blood flow in a patient with pulmonary atresia and ventricular septal defect
Indian Journal of Radiology and Imaging 2018 28(4):433-435
In patients with pulmonary atresia and ventricular septal defect (PA/VSD), a coronary artery being the primary source of pulmonary blood flow is a rare entity. We describe two cases of PA/VSD with coronary-to-pulmonary artery fistula with emphasis on the role of Computed Tomographic Angiography (CTA) in depicting all the sources of pulmonary blood supply, to predict surgical management and need for unifocalization of Major Aortopulmonary Collateral Arteries (MAPCA's).
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2CmRENv
Dealing with technical challenges in embolization of a rare aberrant left inferior bronchial artery arising from the left gastric artery in a patient with massive hemoptysis
Indian Journal of Radiology and Imaging 2018 28(4):476-479
Bronchial artery embolization is an established intervention for management of recurrent massive hemoptysis in a majority of patients. The source of bleeding in a majority of cases is systemic arteries – orthotopic bronchial arteries, anomalous bronchial arteries, or nonbronchial systemic collaterals. We report a case of an aberrant left inferior bronchial artery arising from the left gastric artery (LGA) in a patient with massive hemoptysis. Such origin from infradiaphragmatic vessels and specially left gastric arteries is very rare and needs to be considered by interventional radiologists and pulmonologists in case with hemoptysis disproportionate to supply by orthotopic arteries. Technical challenges were present in the present case in the form of an aneurysm in the aberrant artery and nontarget hepatic and gastric branches arising from LGA. Appropriate selection of hardware and embolic agents was done to deal with the clinical situation.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2SZOlBj
An Estimation of the Possible Migration Path of the Pacific Oyster ( Crassostrea gigas ) Along the Northern Coast of Patagonia
Abstract
In 1981, the Pacific oyster Crassostrea (Magallana) gigas was illegally introduced for aquaculture purposes in San Blas Bay located on the southern coast of Buenos Aires Province, Argentina. The presence and colonization of oysters north of Río Negro Province, 100 km to the southwest of San Blas Bay, was reported in 2005. There remains a controversy about whether or not the oyster was capable of migrating southwest to Río Negro Province from San Blas Bay, which motivates the present investigation. While one part of the local community supports that the Pacific oyster migrated naturally southwestwards reaching the northern coast of Río Negro in 2005, another faction denies this hypothesis. The aim of this work is to determine whether or not the planktonic larvae of this invasive species could have reached the mouth of Río Negro. We assume that the oyster can produce larvae after 2 years of being set on the bottom and the larvae can drift as zooplankton during 1 month. Longshore mean current was considered as the single forcing in natural transporting of oyster larvae along the coast. Shallow water wave parameters were computed from deep water wave parameters obtained from the Simulated WAves Nearshore (SWAN) model driven by NCEP/NCAR I global reanalysis. The migration path was computed from longshore current intensities, which were estimated using the modified experimental expression given by Longuet-Higgins. Results obtained in this paper support the possibility that the Pacific oyster larvae could have arrived at Río Negro Province, between 2002 and 2005.
from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2Rbc9Fb
Deoxyribose and deoxysugar derivatives from photoprocessed astrophysical ice analogues and comparison to meteorites
Deoxyribose and deoxysugar derivatives from photoprocessed astrophysical ice analogues and comparison to meteorites
Deoxyribose and deoxysugar derivatives from photoprocessed astrophysical ice analogues and comparison to meteorites, Published online: 18 December 2018; doi:10.1038/s41467-018-07693-x
Sugars are known to form from the UV photoprocessing of ices under astrophysical conditions. Here, the authors report the detection of deoxyribose, the sugar of DNA, and other deoxysugars from the UV photoprocessing of H2O:CH3OH ice mixtures, which are compared with materials from carbonaceous meteorites.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2EuotJC
Αναζήτηση αυτού του ιστολογίου
! # Ola via Alexandros G.Sfakianakis on Inoreader
-
Does CBD Oil Lower Blood Pressure? This article was originally published at SundayScaries." Madeline Taylor POSTED ON January 13, 20...
-
Abstract Purpose Clinicians must balance the risks from hypotension with the potential adverse effects of vasopressors. Experts have rec...




