Journal of International Medical Research, Ahead of Print.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2EAFpOu
Medicine by Alexandros G. Sfakianakis,Anapafseos 5 Agios Nikolaos 72100 Crete Greece,00302841026182,00306932607174,alsfakia@gmail.com,
Αρχειοθήκη ιστολογίου
-
►
2023
(272)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (141)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (131)
-
►
2022
(2066)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (80)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (170)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (190)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (203)
-
►
2021
(7399)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (186)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (472)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (851)
-
►
2020
(2517)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (792)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (21)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (28)
-
▼
2019
(12076)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (19)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (54)
-
▼
Φεβρουαρίου
(4765)
-
▼
Φεβ 26
(201)
- Successful treatment of an adult with Kasabach-Mer...
- MicroRNA-590-5p antagonizes the inhibitory effect ...
- Radiofrequency catheter ablation for paroxysmal at...
- Association of ENAM, TUFT1, MMP13, IL1B, IL10 and ...
- Multiorgan involvement by amyloid light chain amyl...
- Nitrogen deposition effect on forest litter decomp...
- Self‐Assembled and Size‐Controllable Oligonucleoti...
- The Isolation and Characterization of Kronos, a No...
- The impact of fertilizers on the uptake of mangane...
- Dispatch: South Australia to Colorado
- Harnessing Intramolecular Rotation to Enhance Two‐...
- Complications of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopa...
- Endogenous arginase 2 as a potential biomarker for...
- Cell division cycle associated 5 promotes colorect...
- Glutamine synthetase is necessary for sarcoma adap...
- Dispatch: South Australia to Colorado
- A Longitudinal Analysis of Pressurized Wideband Ab...
- Benefit of Higher Maximum Force Output on Listenin...
- A Comparison of Electrical Stimulation Levels Acro...
- Different Associations between Auditory Function a...
- Compact, Consumer “Stemoscope” Recently Launched
- Artificial Intelligence Shows Promise For Identify...
- CTA, transcranial Doppler not accurate in screenin...
- Cardiac MRI-derived T2 mapping may help heart fail...
- Urgo Medical announces NICE recommendation of Urgo...
- An inexpensive monitoring approach to procedures u...
- BD receives FDA 510(k) clearance of WavelinQ 4F en...
- Three interconnected global pandemics threaten hum...
- High-profile subscription journals critique Plan S
- US adopts science-based guidance for chemical-atta...
- Vertical variation of bulk and metabolically activ...
- [ASAP] Titanium-Based Nanoscale Metal–Organic Fram...
- [ASAP] Spatially Selective and Density-Controlled ...
- [ASAP] Drastically Reduced Ion Mobility in a Nanop...
- [ASAP] Self-Assembling Micelles Based on an Intrin...
- [ASAP] Correction to “Intrinsic Reactivity of Diat...
- [ASAP] Solution NMR Analysis of Ligand Environment...
- [ASAP] Porosity Dependence of Compression and Latt...
- [ASAP] Pickering Emulsion-Derived Liquid–Solid Hyb...
- [ASAP] Regioselective Hydrogenation of a 60-Carbon...
- [ASAP] Substrate-Driven Transient Self-Assembly an...
- [ASAP] Correction to “Graphene Nanoribbons Derived...
- High-profile subscription journals critique Plan S
- US adopts science-based guidance for chemical-atta...
- Renal Epithelioid Angiomyolipoma Undergoing Aggres...
- The 10-Min Holistic Self-Care for Patients with Br...
- Relation of High Social Capital to Preferable Emot...
- Multimodality imaging of small bowel neoplasms
- Nutrient removal in an algal membrane photobioreac...
- Evaluation of underground hydraulic fracturing usi...
- Temporomandibular pain in adolescents with a histo...
- Acute Stress Facilitates LTD Induction at Glutamat...
- Glutamine synthetase is necessary for sarcoma adap...
- The Role of NMDA Receptors in Alzheimer's Disease.
- Improved Wavelet Threshold for Image De-noising.
- Novel Terpolymers from Borane Initiated Copolymeri...
- Biochemical profiles of two thermostable and organ...
- Interplay of lncRNA H19/miR-675 and lncRNA NEAT1/m...
- Aptamer functionalized curcumin-loaded human serum...
- Management of HER2-Positive Early Breast Cancer.
- Comparison of 4 FDA-approved mechanical thrombecto...
- Radiation exposure and operation time in percutane...
- Future Oncology; +23 new citations
- Daily briefing: Clinical trial will target Alzheim...
- Cell division cycle associated 5 promotes colorect...
- Integrated phenotypic screening and activity-based...
- Accessory right V6 behind the bronchus intermedius...
- CDKL1 promotes the chemoresistance of human oral s...
- In vitro activity and mode of action of phenolic c...
- Male reprotoxicity associated with Sophora japonic...
- Astaxanthin Combine With Human Serum Albumin To Ab...
- Silencing the PIK3CA Gene Enhances the Sensitivity...
- Anticancer effect of pan-PI3K inhibitor on multipl...
- The new 6q27 tumor suppressor DACT2, frequently si...
- [Toxicity of immune checkpoints inhibitors].
- Noncoding RNA-nucleated heterochromatin spreading ...
- Clinical Practice Guideline: Tonsillectomy in Chil...
- Systemic Bevacizumab for Hereditary Hemorrhagic Te...
- Response to the Letter to the Editor: "Ciprofloxac...
- Response to "Systemic Bevacizumab for Hereditary H...
- Highlights from the Current Issue: January 2019.
- Ciprofloxacin Otic Suspension and Permanent Periph...
- Congratulations 2019.
- Characterizing organic carbon dynamics during bios...
- Treatment Strategies in Diffuse Midline Gliomas Wi...
- Clindamycin: An Unusual Cause of Acute Kidney Injury.
- Detection of Longitudinal Microstructural Changes ...
- The Coming of Age of Breast Tomosynthesis in Scree...
- MRI Screening for Cerebral Aneurysm in Adult Polyc...
- epilepsy treatment; +27 new citations
- Endogenous arginase 2 as a potential biomarker for...
- Daily briefing: Clinical trial will target Alzheim...
- Challenges and support for quality of life of yout...
- Interventions on children’s and adolescents’ physi...
- Environmental etiology of gastric cancer in Iran: ...
- Aluminium foil dampened the adverse effect of 2100...
- Methylene blue dye removal on silver nanoparticles...
- Treatment of intravitreal bevacizumab combined wit...
- Comparative study of photodynamic activity of meth...
- Correction to: Outpatient erbium:YAG (2940 nm) las...
-
▼
Φεβ 26
(201)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (5155)
-
►
2018
(3144)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (3144)
Ετικέτες
Πληροφορίες
Τρίτη 26 Φεβρουαρίου 2019
Successful treatment of an adult with Kasabach-Merritt syndrome using thalidomide, vincristine, and prednisone
MicroRNA-590-5p antagonizes the inhibitory effect of high glucose on osteoblast differentiation by suppressing Smad7 in MC3T3-E1 cells
Journal of International Medical Research, Ahead of Print.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2VmWwIR
Radiofrequency catheter ablation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: outcomes during a 3-year follow-up period
Journal of International Medical Research, Ahead of Print.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2EzBQYD
Association of ENAM, TUFT1, MMP13, IL1B, IL10 and IL1RN gene polymorphism and dental caries susceptibility in Chinese children
Journal of International Medical Research, Ahead of Print.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2Vowe9f
Multiorgan involvement by amyloid light chain amyloidosis
Journal of International Medical Research, Ahead of Print.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2EAayl1
Nitrogen deposition effect on forest litter decomposition is interactively regulated by endogenous litter quality and exogenous resource supply
Abstract
Background and aims
Atmospheric nitrogen (N) deposition affects litter decomposition. However, how endogenous litter quality and exogenous resource supply alter the N deposition effect on litter decomposition and deposited N immobilized by microbes remains unclear.
Methods
We conducted a laboratory experiment to examine how the N deposition effect on litter decomposition varies with endogenous litter quality (needle litter with higher C/nutrients, low quality litter versus leaf litter with low C/nutrients, high quality litter) and exogenous resource supply (five treatments: N addition alone; N plus non-N nutrient and/or carbon addition; control) using a 15N tracing method.
Results
Nitrogen deposition increased the % mass and % N remaining across the decomposition process. Adding non-N nutrients increased the N deposition effect on % mass and % N remaining in the decomposing high quality litter but not in the low quality litter. Moreover, the % P remaining was increased in the low quality litter but was decreased in the high quality litter under N deposition. However, adding N and non-N nutrients together increased the % P remaining in both decomposing litters. The immobilized exogenous 15N abundance (IEN) was much higher in the decomposing low quality litter than high quality litter. For low quality litter, resource addition treatments affected IEN, but their effects depended on decomposition stages. For high quality litter, carbon addition alone generally increased IEN across the 720 days.
Conclusions
Nitrogen deposition effect on litter decomposition could be altered by exogenous resource supply, but the pattern ultimately depended on endogenous litter quality. Nitrogen deposition generally suppressed the litter decomposition and non-N nutrients addition enhanced the inhibition effects of N deposition on litter decomposition, especially of high quality litter, while lower quality litter tended to immobilize more exogenous deposited N. Thus, the magnitude of both non-N nutrient availability and litter quality needs to be taken into consideration when assessing the effects of N deposition on litter decomposition.
from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2GMXtHm
Self‐Assembled and Size‐Controllable Oligonucleotides Nanospheres for Effective Antisense Gene Delivery via Endocytosis‐Independent Pathway
The development of efficient gene delivery vectors has experienced two major challenges, endo/lysosomal escape and intracellular release. To address these problems, we developed an oligonucleotides (ONs) template‐assisted polymerization approach to create ONs nanospheres as gene vectors. In this approach, guanidinium‐containing strained disulfide monomers were organized on the ONs templates, greatly increasing their local effective concentrations. Consequently, ring‐opening disulfide‐exchange polymerization between monomers was accelerated, further facilitating the self‐assembly of ONs nanospheres. These nanospheres were size controllable by varying the length of ONs templates. Importantly, nanospheres could be directly delivered into cytosol via an endocytosis‐independent pathway and followed by intracellular depolymerisation in the reductive cytosolic environment to release the packaged ONs, resulting in efficient gene silence. By taking advantages of facile assembly, direct intracellular delivery and good biocompatibility, ONs nanospheres hold great promise as candidates for gene therapy.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2SZ8r2S
The Isolation and Characterization of Kronos, a Novel Caulobacter Rhizosphere Phage that is Similar to Lambdoid Phages
Abstract
Despite their ubiquity, relatively few bacteriophages have been characterized. Here, we set out to explore Caulobacter bacteriophages (caulophages) in the rhizosphere and characterized Kronos, the first caulophage isolated from the rhizosphere. Kronos is a member of the Siphoviridae family since it has a long flexible tail. In addition, an analysis of the Kronos genome indicated that many of the predicted proteins were distantly related to those of bacteriophages in the lambdoid family. Consistent with this observation, we were able to demonstrate the presence of cos sites that are similar to those found at the ends of lambdoid phage genomes. Moreover, Kronos displayed a relatively rare head and tail morphology compared to other caulophages but was similar to that of the lambdoid phages. Taken together, these data indicate that Kronos is distantly related to lambdoid phages and may represent a new Siphoviridae genus.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2BWVT1o
The impact of fertilizers on the uptake of manganese in Cherry Belle radish plants: implications for human health
Abstract
Miracle-Gro Singles, Miracle-Gro Shake and Feed, and Vigoro fertilizers are associated with net loss/enhancement of Mn, up to an order of magnitude when referenced to controls in soil, radish vegetables, and radish leaves; Mn enhancements are a factor of 4 to 65 below the daily required intake for humans (2–5.5 mg/day). Manganese levels were measured by atomic absorption spectrometry (AAS). Control soil, radish vegetables, and radish leaves contained 65 μg/g to 146 μg/g (median = 108), 65 μg/g to 357 μg/g (median = 281), and 185 μg/g to 401 μg/g (median = 323) of Mn, correspondingly. Manganese uptake was ten times greater in radish leaves compared to radish vegetables and enhanced by a factor of 3 in soils. Edible radish leaves/vegetables contain 65 times less than human Mn daily requirements. This equates eating 140 lb/day of radish vegetables/leaves. The fertilizers have a minor impact on Mn accumulation in radish leaves/vegetables. The USDA Nutrient Database for radish (0.69 μg/g of Mn) contradicts this notion as one would need to consume ~ 7 to 18 lb/day of radish to satisfy their daily intake. This study complements investigations showing that fertilizers induce minimal uptake of heavy metals in food; simultaneously, the net loss of Mn amounts observed in some samples of radish leaves and vegetables is analogous to the dilution effect of minerals/nutrients in edibles. Although a deficiency/excess of Mn in one's diet may lead to adverse health effects, background inhalation exposure in general public, occupational, and emergency response settings has a greater influence on one's propensity toward developing adverse health effects related to Mn inhalation exposure.
from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2XzWa3M
Dispatch: South Australia to Colorado
Dispatch: South Australia to Colorado
Dispatch: South Australia to Colorado, Published online: 27 February 2019; doi:10.1038/d41586-019-00715-8
Postdocs considering an international move should plan early and allow plenty of time to adjust, says Atma Ivancevic.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2BOPd5B
Harnessing Intramolecular Rotation to Enhance Two‐photon Imaging of Aβ Plaques Through Minimizing Background Fluorescence
The aggregation of Aβ‐proteins in senile plaques is a critical event during the development of Alzheimer's disease, and the postmortem detection of Aβ‐rich proteinaceous deposits via fluorescent staining remains one of the most robust diagnostic tools. In animal models, fluorescence imaging can be employed to follow the progression of the disease and among imaging methods two‐photon microscopy (TPM) has emerged as one of the most powerful. To date, several near‐infrared‐emissive two‐photon dyes with a high affinity for Aβ‐fibrils have been developed, but there has often been a tradeoff between excellent two‐photon cross sections and large fluorescence signal to background ratios. In the current work, we introduced a TICT‐based de‐excitation pathway, resulting in a remarkable fluorescence increase of ~167‐fold in the presence of Aβ‐fibrils, while maintaining an excellent two‐photon cross section, allowing high contrast ex vivo and in vivo TPM imaging. Overall, the results suggest that adopting TICT de‐excitation in two‐photon fluorophores may represent a general method to overcome the probe brightness vs. probe signal to background tradeoff.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2GNEgp2
Complications of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography: an imaging review
Abstract
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) has currently become an inseparable tool in the gastroenterologist's armamentarium for treatment of pancreaticobiliary disorders. Given the increase in number of therapeutic ERCP procedures today, the need for prompt and correct diagnosis of its complications is pivotal. This review discusses the mechanisms, risk factors, imaging findings and general management aspects of common and rare complications of ERCP. Furthermore, the review elaborates on imaging indications, recommended protocol and normal imaging findings post ERCP.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2NvLOx7
Endogenous arginase 2 as a potential biomarker for PEGylated arginase 1 treatment in xenograft models of squamous cell lung carcinoma
Endogenous arginase 2 as a potential biomarker for PEGylated arginase 1 treatment in xenograft models of squamous cell lung carcinoma
Endogenous arginase 2 as a potential biomarker for PEGylated arginase 1 treatment in xenograft models of squamous cell lung carcinoma, Published online: 26 February 2019; doi:10.1038/s41389-019-0128-0
Endogenous arginase 2 as a potential biomarker for PEGylated arginase 1 treatment in xenograft models of squamous cell lung carcinomafrom A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2IGrwlG
Cell division cycle associated 5 promotes colorectal cancer progression by activating the ERK signaling pathway
Cell division cycle associated 5 promotes colorectal cancer progression by activating the ERK signaling pathway
Cell division cycle associated 5 promotes colorectal cancer progression by activating the ERK signaling pathway, Published online: 26 February 2019; doi:10.1038/s41389-019-0123-5
Cell division cycle associated 5 promotes colorectal cancer progression by activating the ERK signaling pathwayfrom A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2TiQewE
Glutamine synthetase is necessary for sarcoma adaptation to glutamine deprivation and tumor growth
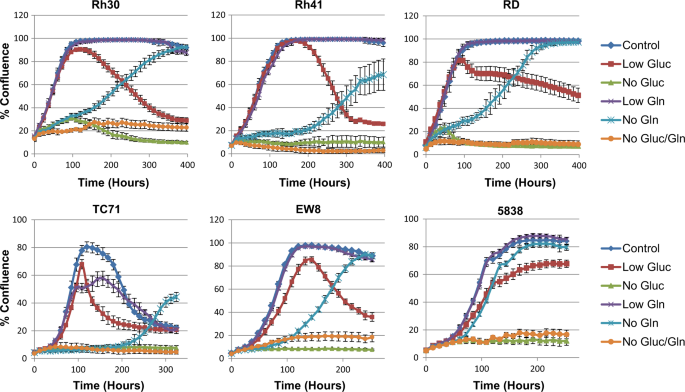
Glutamine synthetase is necessary for sarcoma adaptation to glutamine deprivation and tumor growth
Glutamine synthetase is necessary for sarcoma adaptation to glutamine deprivation and tumor growth, Published online: 26 February 2019; doi:10.1038/s41389-019-0129-z
Glutamine synthetase is necessary for sarcoma adaptation to glutamine deprivation and tumor growthfrom A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2ID6WCT
A Longitudinal Analysis of Pressurized Wideband Absorbance Measures in Healthy Young Infants
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2ICMz8F
Benefit of Higher Maximum Force Output on Listening Effort in Bone-Anchored Hearing System Users: A Pupillometry Study
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2Te1mej
A Comparison of Electrical Stimulation Levels Across Ears for Children With Sequential Bilateral Cochlear Implants
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2IEbDwi
Different Associations between Auditory Function and Cognition Depending on Type of Auditory Function and Type of Cognition
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2Tm8YeA
Compact, Consumer “Stemoscope” Recently Launched
This device is appropriately named the "Stemoscope," as it is designed for science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) education. However, the company has shown the device being used for other purposes, such as listening to a pet's heart beats or even to the sounds of a tree. From a relative standpoint, we compared the Stemoscope to the Littmann Classic III and Littmann Master Cardiology stethoscopes that are widely used in healthcare. In regular patient care, the head of the ...
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2XqCkry
Artificial Intelligence Shows Promise For Identifying Undiagnosed NASH
The algorithm employs the principles of "deep learning" to recognize clinical characteristics common to patients with NASH. The initial results are encouraging, but the software is expected to become increasingly smart, improving both specificity and sensitivity, as it incorporates mo re data, said Kathryn Starzyk, MSc, the senior director of real-world evidence at OM1 Inc., the Boston-based firm that is developing the system. The gold standard for a diagnosis of NASH is a liver biopsy, bu...
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2Sp5PX2
CTA, transcranial Doppler not accurate in screening for delayed ischemia following brain hemorrhage
DCI is a "dreaded" secondary complication that arises after aneurysmal SAH, wrote J. Joep van der Harst, MD, of the University of Groningen, The Netherlands, and colleagues. CTA and TCD are both commonly used screening tools in these patients, but the optimal screening modality is still a matter of debate. In the study, van der Harst et al. included 59 patients with aneurysmal SAH who were treated at the University of Groningen's neurocritical and neurosurgical units between 2013 and 2016....
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2XqXHZG
Cardiac MRI-derived T2 mapping may help heart failure patients
In the study, Carlos Galan-Arriola, DVM, with the National Center for Cardiovascular Research in Madrid, and colleagues sought to identify early serial cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) markers of anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity. Anthracycline is a popular class of chemotherapy drug and contributes to heart failure in up to 25 percent of patients. Galan-Arriola studied 15 pigs which were administered either three or five biweekly intracoronary doxorubicin doses and followed with CMR ex...
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2SpOgWM
Urgo Medical announces NICE recommendation of UrgoStart for diabetic and venous ulcers
The conclusion of the NICE medical technology guidance is that UrgoStart is associated with increased wound healing compared with non-interactive dressings and could result in fewer ulcer-related amputations. The committee recognised that the treatment is also associated with significant cost savings for the UK National Health Service (NHS) and improved quality of life for patients. Graham Bowen, clinical lead for Podiatry, Solent NHS Trust, and chair of Foot in Diabetes UK said "This is t...
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2XsoKUn
An inexpensive monitoring approach to procedures under local anaesthesia
"In our hospital, we really prefer the regional anaesthesia", Storck said at Controversies & Updates in Vascular Surgery (CACVS; 7–9 February, Paris, France), "and if you do carotid surgery under general anaesthesia there is some monitoring necessary." Storck highlighted the need for neuromonitoring to detect stroke or clamping ischaemia in patients undergoing carotid surgery—vascular or endovascular—under general anaesthetic, and then pointed to a different monitoring approach when working u...
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2SvNIia
BD receives FDA 510(k) clearance of WavelinQ 4F endoAVF system
In the USA alone, there are more than 440,000 patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) who are surviving on haemodialysis. EndoAVF systems provide clinicians with a minimally invasive arteriovenous fistula (AVF) creation alternative to open surgery. The WavelinQ 4F, with a slim profile, increases the anatomical AVF location options and enables additional venous wrist access points (ulnar vein or radial vein), providing increased procedural flexibility for physicians while reducing risk of...
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2XnMQQg
Three interconnected global pandemics threaten humanity
Researchers have called it a "global-syndemic". The three biggest threats that humanity is confronted with in today's world: obesity, undernourishment and climate change, initially appear to be separate issues. However, according to a report published in The Lancet, these three pandemics are one massive danger and are intrinsically connected. Researchers hold "Big Food" industries responsible for this threat to humanity. "Over the last 20 years, obesity, undernutrition and climate chang...
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2StAXVs
High-profile subscription journals critique Plan S
High-profile subscription journals critique Plan S
High-profile subscription journals critique Plan S, Published online: 26 February 2019; doi:10.1038/d41586-019-00596-x
Publishers say that the bold open-access initiative rules out proven ways of opening up the literature.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2H4L7ti
US adopts science-based guidance for chemical-attack response
US adopts science-based guidance for chemical-attack response
US adopts science-based guidance for chemical-attack response, Published online: 26 February 2019; doi:10.1038/d41586-019-00646-4
Comprehensive guidelines recommend wiping down with dry, absorbent materials.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2Tj3hOH
Vertical variation of bulk and metabolically active prokaryotic community in sediment of a hypereutrophic freshwater lake
Abstract
This study was conducted to acquire novel insight into differences between bulk (16S rDNA) and metabolically active (16S rRNA) prokaryotic communities in the sediment of a hypereutrophic lake (Japan). In the bulk communities, the class Deltaproteobacteria and the order Methanomicrobiales were dominant among bacteria and methanogens. In the metabolically active communities, the class Alphaproteobacteria and the order Methanomicrobiales and the family Methanosaetaceae were frequently found among bacteria and methanogens. Unlike the bulk communities of prokaryotes, the composition of the metabolically active communities varied remarkably vertically, and their diversities greatly decreased in the lower 20 cm of sediment. The metabolically active prokaryotic community in the sediment core was divided into three sections based on their similarity: 0–6 cm (section 1), 9–18 cm (section 2), and 21–42 cm (section 3). This sectional distribution was consistent with the vertical pattern of the sedimentary stable carbon and nitrogen isotope ratios and oxidation–reduction potential in the porewater. These results suggest that vertical disturbance of the sediment may influence the communities and functions of metabolically active prokaryotes in freshwater lake sediments. Overall, our results indicate that rRNA analysis may be more effective than rDNA analysis for evaluation of relationships between actual microbial processes and material cycling in lake sediments.
from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2tIQHJX
[ASAP] Titanium-Based Nanoscale Metal–Organic Framework for Type I Photodynamic Therapy

from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2BUf6AN
[ASAP] Spatially Selective and Density-Controlled Activation of Interfacial Mechanophores

from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2BV9kPt
[ASAP] Drastically Reduced Ion Mobility in a Nanopore Due to Enhanced Pairing and Collisions between Dehydrated Ions

from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2Ue5Qio
[ASAP] Self-Assembling Micelles Based on an Intrinsically Disordered Protein Domain

from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2U9IVoh
[ASAP] Correction to “Intrinsic Reactivity of Diatomic 3d Transition-Metal Carbides in the Thermal Activation of Methane: Striking Electronic Structure Effects”
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2BUf4ZH
[ASAP] Solution NMR Analysis of Ligand Environment in Quaternary Ammonium-Terminated Self-Assembled Monolayers on Gold Nanoparticles: The Effect of Surface Curvature and Ligand Structure

from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2BUx2LQ
[ASAP] Porosity Dependence of Compression and Lattice Rigidity in Metal–Organic Framework Series

from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2U77emE
[ASAP] Pickering Emulsion-Derived Liquid–Solid Hybrid Catalyst for Bridging Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Catalysis

from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2U9xyg3
[ASAP] Regioselective Hydrogenation of a 60-Carbon Nanographene Molecule toward a Circumbiphenyl Core

from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2Uc6Ovm
[ASAP] Substrate-Driven Transient Self-Assembly and Spontaneous Disassembly Directed by Chemical Reaction with Product Release

from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2BOuTRR
[ASAP] Correction to “Graphene Nanoribbons Derived from Zigzag Edge-Encased Poly(-2,9-dibenzo[,]coronenylene) Polymer Chains”
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2U4VbGx
High-profile subscription journals critique Plan S
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2INfAim
US adopts science-based guidance for chemical-attack response
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2NwmhUr
Renal Epithelioid Angiomyolipoma Undergoing Aggressive Clinical Outcome: The MDM2 Expression in Tumor Cells of Two Cases.
| Related Articles |
Renal Epithelioid Angiomyolipoma Undergoing Aggressive Clinical Outcome: The MDM2 Expression in Tumor Cells of Two Cases.
Tohoku J Exp Med. 2019;247(2):119-127
Authors: Inoue C, Saito R, Nakanishi W, Kumata H, Eba S, Fujishima F, Watanabe M, Sasano H
Abstract
Epithelioid angiomyolipoma (EAML) has been known as a potentially malignant tumor which occasionally recur and/or metastasize to other organs, and clinically and pathologically recognized as distinct entity. However, the mechanisms of recurrence and/or metastasis (recurrence/metastasis) has still remained unknown. Here, we report two cases of renal EAML associated with recurrence/metastasis, and three cases of EAML in kidney or liver without recurrence/metastasis. According to the previous histological predictive models of EAML, the primary tumor was classified as low risk group in one of the cases with recurrence/metastasis in spite of its malignant behavior. Therefore, we considered that further investigation about the mechanisms of recurrence/metastasis in EAML is required for a malignancy prediction. We focused on some cell-cycle modulators, including mouse double minute 2 homolog (MDM2), which is ubiquitin ligase well-known to promote malignant behaviors by p53 ubiquitination and degradation, and also other cellular processes including genomic instability and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in p53-independent manners in various human malignancies. Immunohistochemical evaluation revealed that MDM2 protein expression increased stepwise throughout every steps of metastasis/recurrence in both cases, although it was negative in primary tumors. In conclusion, this is the first study demonstrating that MDM2 could play an important role in the molecular mechanisms of recurrence/metastasis of EAML. Further analyses focusing on MDM2 pathway could contribute to the identification of novel prognostic factors and/or therapeutic targets in EAML patients.
PMID: 30799331 [PubMed - in process]
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2GMN5zq
The 10-Min Holistic Self-Care for Patients with Breast Cancer-Related Lymphedema: Pilot Randomized Controlled Study.
| Related Articles |
The 10-Min Holistic Self-Care for Patients with Breast Cancer-Related Lymphedema: Pilot Randomized Controlled Study.
Tohoku J Exp Med. 2019;247(2):139-147
Authors: Arinaga Y, Piller N, Sato F, Ishida T, Ohtake T, Kikuchi K, Sato-Tadano A, Tada H, Miyashita M
Abstract
About 20% of patients with breast cancer are likely to develop breast cancer-related lymphedema (BCRL) following an axillary clearance, and BCRL can be refractory or irreversible to treatment. The aim of this pilot randomized controlled study was to evaluate the effectiveness of a 10-min holistic self-care program for patients with BCRL in Japan. The intervention group (n = 22) practiced the BCRL self-care program including 1) modified Japanese Radio Taiso (Rajio Taiso, national calisthenics in Japan), 2) gentle arm exercises combined with deep breathing, 3) central lymphatic drainage, and 4) skin care using a traditional lymphatic drainage technique daily for 6 months, while the control group (n = 21) received usual care from their hospitals. There was significant group*time interaction in the relative edema volume and relative volume change of the hand, with the intervention group having the better outcome. The intervention group showed significant improvement in transepidermal water loss as well as the mental health component summary score of the SF-8, most of BCRL-related symptoms, self-care time and score, frequencies of exercise, self-lymphatic drainage and skin care, and perceived adherence and effectiveness to self-care, although we were unable to exclude the possibility of the Hawthorne effect. Notably, even in the control group, the self-care was similarly increased, but the significant improvements were detected only in transepidermal water loss on the forearm and upper arm, pain and coldness. In conclusion, the patients who practiced the holistic BCRL self-care for 6 months have shown greater improvement.
PMID: 30799328 [PubMed - in process]
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2NvErFY
Relation of High Social Capital to Preferable Emotional Response to News Media Broadcasting of Natural Disasters: A Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study in Japan.
| Related Articles |
Relation of High Social Capital to Preferable Emotional Response to News Media Broadcasting of Natural Disasters: A Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study in Japan.
Tohoku J Exp Med. 2019;247(2):129-137
Authors: Horiuchi S, Ozaki A, Inoue M, Aida J, Yamaoka K
Abstract
Media coverage of disasters potentially damages mental health. Moreover, its effects may differ as recipients may have different emotional responses toward media. The present study examined whether social capital, known to be protective against mental problems, influences a recipient's emotional response toward news media broadcasting of natural disasters via newspapers, television and internet in Japan. Three social capital components, social participation, social support and cognitive social capital, were considered in the present study as each component reportedly had different effect on mental health. This nationwide cross-sectional survey was undertaken in 2015 among 1,200 Japanese citizens aged 15 to 79 years who were selected using the multi-stage sampling procedure. Data were collected via the drop-off pick-up method using a printed structured questionnaire. Negative and positive emotions were classified based on recipients' responses against news media. Among 1,190 participants who reported emotions toward news media, 30.9% (368) had experienced any natural disasters, 37.4% (445) belonged to at least one formal or informal organization (social participation), 40.2% (478) had high social support, and 68.8% (819) had high cognitive social capital. High social support was associated with both reduced negative emotional response (OR 0.66, 95% Confidence Interval (CI) 0.47-0.93) and increased positive emotional response (OR 1.48, 95% CI 1.04-2.12) in multivariate analyses, while high cognitive social capital was only associated with increased positive emotional response (OR 1.62, 95% CI 1.11-2.37). These results suggest protective effects of social support and cognitive social capital against news media coverage of natural disasters.
PMID: 30799327 [PubMed - in process]
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2GMK4Po
Multimodality imaging of small bowel neoplasms
Abstract
Although the small intestine accounts for over 90% of the surface area of the alimentary tract, tumors of the small intestine represent less than 5% of all gastrointestinal tract neoplasms. Common small bowel tumors typically are well evaluated with cross-sectional imaging modalities such as CT and MR, but accurate identification and differentiation can be challenging. Differentiating normal bowel from abnormal tumor depends on imaging modality and the particular technique. While endoscopic evaluation is typically more sensitive for the detection of intraluminal tumors that can be reached, CT and MR, as well as select nuclear medicine studies, remain superior for evaluating extraluminal neoplasms. Understanding the imaging characteristics of typical benign and malignant small bowel tumors is critical, because of overlapping features and associated secondary complications.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2NsclLC
Nutrient removal in an algal membrane photobioreactor: effects of wastewater composition and light/dark cycle
Abstract
Graesiella emersonii was cultivated in an osmotic membrane photobioreactor (OMPBR) for nutrients removal from synthetic wastewater in continuous mode. At 1.5 days of hydraulic retention time and under continuous illumination, the microalgae removed nitrogen (N) completely at influent NH4+-N concentrations of 4–16 mg/L, with removal rates of 3.03–12.1 mg/L-day. Phosphorus (P) removal in the OMPBR was through biological assimilation as well as membrane rejection, but PO43−-P assimilation by microalgae could be improved at higher NH4+-N concentrations. Microalgae biomass composition was affected by N/P ratio in wastewater, and a higher N/P ratio resulted in higher P accumulation in the biomass. The OMPBR accumulated about 0.35 g/L biomass after 12 days of operation under continuous illumination. However, OMPBR operation under 12 h light/12 h dark cycle lowered biomass productivity by 60%, which resulted in 20% decrease in NH4+-N removal and nearly threefold increase in PO43−-P accumulation in the OMPBR. Prolonged dark phase also affected carbohydrate accumulation in biomass, although its effects on lipid and protein accumulation were negligible. The microalgae also exhibited high tendency to aggregate and settle, which could be attributed to reduction in cell surface charge and enrichment of soluble algal products in the OMPBR. Due to a relatively shorter operating period, membrane biofouling and salt accumulation did not influence the permeate flux significantly. These results improve the understanding of the effects of N/P ratio and light/dark cycle on biomass accumulation and nutrients removal in the OMPBR.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2XpKRuL
Evaluation of underground hydraulic fracturing using transient electromagnetic method
Abstract
The effective area of hydraulic fracturing is the core index to evaluate its effects. Through conducting transient electromagnetic tests, this paper deals with the influential range of the underground hydraulic fracturing as well as water-cut detection and gas extraction in the fracturing area. The resistivity response law of the coal seam in hydraulic fracturing process is explored, and the water-bearing area is determined. The obtained results from the tests show that the water-cut areas of the coal seam, measured by anti-interference transient electromagnetic instrument after fracturing, are commonly placed in the low-resistance area of the transient test. Further, the variations of amplitude of the low-resistance area in various directions of the test line are different. According to the variation law of the apparent resistivity of the coal seam before and after fracturing, the effective influential area of the hydraulic fracturing is defined, and the influence range is evaluated to be 35 m. The water cut and the gas extraction tests of the coal seam before and after fracturing are performed. The results reveal that the growth of water content in the coal seam is inversely proportional to the distance from the hydraulic fracturing borehole. The effective fracturing zone with the increment of the water content reaching 0.2% is the effective fracturing zone, and the effective fracturing zone of #9 and #10 is 38 m. After hydraulic fracturing, the gas extraction concentration would be in the range of 25.4–75.4%, with the average of 70.22%, which is 21.22% higher than that of the original coal body. The net amount of the gas extraction after fracturing is about eight times of that before fracturing. The effective fracturing range, which is determined by transient electromagnetic, is verified successfully. Exploring the effective fracturing regions of the hydraulic fracturing process would be very helpful in improving the evaluation system of the hydraulic fracturing effect.
from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2NtAfq8
Temporomandibular pain in adolescents with a history of preterm birth
Abstract
Aim
To evaluate the frequency of TMD pain among adolescents with a history of preterm birth compared to a matched control group.
Methods
A group of 192 preterm‐born adolescents was followed up at the age of 17–19 years and compared to matched controls. Self‐report questionnaires included screening questions about TMD pain, chronic diseases, general health, depression, anxiety, anger, antisocial behavior, and self‐concept. TMD pain was defined as answering 'yes' to one or both of the following questions: "Do you have pain in the temple, face, temporomandibular joint, or jaws once a week or more?" and "Do you have pain when you open your mouth wide or chew once a week or more often?" Data analysis was performed using chi‐square test and logistic regression model with likelihood ratio test.
Results
A TMD pain frequency of 23% of preterm‐born adolescents and 26% among the controls was found, with no significant differences between the groups. Neither were there differences regarding anxiety, depression, anger, or self‐confidence. Within the preterm group, adolescents with TMD pain registered tension and pain in the body, trouble sleeping, stomach pain, and feelings of hopelessness about the future. The controls with TMD pain, more reported having a bad life, feeling like a failure, and having bodily pain. Among tested background variables only TMJ locking or intermittent locking once a week or more was found to explain TMD pain in adolescents.
Conclusion
A high frequency of TMD pain was found in both groups, one possible explanation could be TMJ dysfunction.
This article is protected by copyright. All rights reserved.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2GRLhoX
Acute Stress Facilitates LTD Induction at Glutamatergic Synapses in the Hippocampal CA1 Region by Activating μ-Opioid Receptors on GABAergic Neurons.
| Related Articles |
Acute Stress Facilitates LTD Induction at Glutamatergic Synapses in the Hippocampal CA1 Region by Activating μ-Opioid Receptors on GABAergic Neurons.
Front Neurosci. 2019;13:71
Authors: Fan KM, Qiu LJ, Ma N, Du YN, Qian ZQ, Wei CL, Han J, Ren W, Shi MM, Liu ZQ
Abstract
Acute stress impairs recall memory through the facilitation of long-term depression (LTD) of hippocampal synaptic transmission. The endogenous opioid system (EOS) plays essential roles in stress-related emotional and physiological responses. Specifically, behavioral studies have shown that the impairment of memory retrieval induced by stressful events involves the activation of opioid receptors. However, it is unclear whether signaling mediated by μ-opioid receptors (μRs), one of the three major opioid receptors, participates in acute stress-related hippocampal LTD facilitation. Here, we examined the effects of a single elevated platform (EP) stress exposure on excitatory synaptic transmission and plasticity at the Schaffer collateral-commissural (SC) to CA1 synapses by recording electrically evoked field excitatory postsynaptic potentials and population spikes of hippocampal pyramidal neurons in anesthetized adult mice. EP stress exposure attenuated GABAergic feedforward and feedback inhibition of CA1 pyramidal neurons and facilitated low-frequency stimulation (LFS)-induced long-term depression (LTD) at SC-CA1 glutamatergic synapses. These effects were reproduced by exogenously activating μRs in unstressed mice. The specific deletion of μRs on GABAergic neurons (μRGABA) not only prevented the EP stress-induced memory impairment but also reversed the EP stress-induced attenuation of GABAergic inhibition and facilitation of LFS-LTD. Our results suggest that acute stress endogenously activates μRGABA to attenuate hippocampal GABAergic signaling, thereby facilitating LTD induction at excitatory synapses and eliciting memory impairments.
PMID: 30800053 [PubMed]
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2U6WNQ0
Glutamine synthetase is necessary for sarcoma adaptation to glutamine deprivation and tumor growth

from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2BU4EJI
The Role of NMDA Receptors in Alzheimer's Disease.
| Related Articles |
The Role of NMDA Receptors in Alzheimer's Disease.
Front Neurosci. 2019;13:43
Authors: Liu J, Chang L, Song Y, Li H, Wu Y
Abstract
In Alzheimer's disease (AD), early synaptic dysfunction is associated with the increased oligomeric amyloid-beta peptide, which causes NMDAR-dependent synaptic depression and spine elimination. Memantine, low-affinity NMDAR channel blocker, has been used in the treatment of moderate to severe AD. However, clear evidence is still deficient in demonstrating the underlying mechanisms and a relationship between NMDARs dysfunction and AD. This review focuses on not only changes in expression of different NMDAR subunits, but also some unconventional modes of NMDAR action.
PMID: 30800052 [PubMed]
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2BWmrzQ
Improved Wavelet Threshold for Image De-noising.
| Related Articles |
Improved Wavelet Threshold for Image De-noising.
Front Neurosci. 2019;13:39
Authors: Zhang Y, Ding W, Pan Z, Qin J
Abstract
With the development of communication technology and network technology, as well as the rising popularity of digital electronic products, an image has become an important carrier of access to outside information. However, images are vulnerable to noise interference during collection, transmission and storage, thereby decreasing image quality. Therefore, image noise reduction processing is necessary to obtain higher-quality images. For the characteristics of its multi-analysis, relativity removal, low entropy, and flexible bases, the wavelet transform has become a powerful tool in the field of image de-noising. The wavelet transform in application mathematics has a rapid development. De-noising methods based on wavelet transform is proposed and achieved with good results, but shortcomings still remain. Traditional threshold functions have some deficiencies in image de-noising. A hard threshold function is discontinuous, whereas a soft threshold function causes constant deviation. To address these shortcomings, a method for removing image noise is proposed in this paper. First, the method decomposes the noise image to determine the wavelet coefficients. Second, the wavelet coefficient is applied on the high-frequency part of the threshold processing by using the improved threshold function. Finally, the de-noised images are obtained to rebuild the images in accordance with the estimation in the wavelet-based conditions. Experiment results show that this method, discussed in this paper, is better than traditional hard threshold de-noising and soft threshold de-noising methods, in terms of objective effects and subjective visual effects.
PMID: 30800051 [PubMed]
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2UasJD9
Novel Terpolymers from Borane Initiated Copolymerization of Triphenyl Arsonium and Sulfoxonium Ylides: An Unexpected Light Emission
We report the first synthesis of well‐defined poly[(phenylmethylene‐co‐methylpropenylene)‐b‐methylene, [(C1‐co‐C3)‐b‐C1], terpolymers via one‐pot borane initiated random copolymerization of ω‐methylallyl (C3 units, chain is growing by three carbon atoms at a time) and benzyltriphenylarsonium (C1 units, chain is growing by one carbon atom at a time) ylides, followed by polymerization of sulfoxonium methylide (C1 units). The synthesized terpolymers possess a predictable molecular weight and monomodal low polydispersity (Mn, NMR=1.83‐9.68×103 g /mol, Đ =1.09‐1.22). Other substituted arsonium ylides, such as prenyltriphenyl, propyltriphenyl and (4‐fluorobenzyl)triphenyl can also be used instead of benzyltriphenylarsonium ylide, affording well‐defined terpolymers too (Mn, NMR=4.3‐9.1×103 g/mol, Đ=1.16–1.22). An unexpected light emission phenomenon was discovered in these non‐conjugated terpolymers, as demonstrated by fluorescence and NMR spectroscopy. This phenomenon can be attributed to the formation of conjugated small blocks along the allylic monomeric units as the result of isomerization of the double bonds (isomerization‐induced light emission).
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2T10Z7j
Biochemical profiles of two thermostable and organic solvent–tolerant esterases derived from a compost metagenome
Abstract
Owing to the functional versatility and potential applications in industry, interest in lipolytic enzymes tolerant to organic solvents is increasing. In this study, functional screening of a compost soil metagenome resulted in identification of two lipolytic genes, est1 and est2, encoding 270 and 389 amino acids, respectively. The two genes were heterologously expressed and characterized. Est1 and Est2 are thermostable enzymes with optimal enzyme activities at 80 and 70 °C, respectively. A second-order rotatable design, which allows establishing the relationship between multiple variables with the obtained responses, was used to explore the combined effects of temperature and pH on esterase stability. The response curve indicated that Est1, and particularly Est2, retained high stability within a broad range of temperature and pH values. Furthermore, the effects of organic solvents on Est1 and Est2 activities and stabilities were assessed. Notably, Est2 activity was significantly enhanced (two- to tenfold) in the presence of ethanol, methanol, isopropanol, and 1-propanol over a concentration range between 6 and 30% (v/v). For the short-term stability (2 h of incubation), Est2 exhibited high tolerance against 60% (v/v) of ethanol, methanol, isopropanol, DMSO, and acetone, while Est1 activity resisted these solvents only at lower concentrations (below 30%, v/v). Est2 also displayed high stability towards some water-immiscible organic solvents, such as ethyl acetate, diethyl ether, and toluene. With respect to long-term stability, Est2 retained most of its activity after 26 days of incubation in the presence of 30% (v/v) ethanol, methanol, isopropanol, DMSO, or acetone. All of these features indicate that Est1 and Est2 possess application potential.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2EcDkXu
Interplay of lncRNA H19/miR-675 and lncRNA NEAT1/miR-204 in breast cancer.
| Related Articles |
Interplay of lncRNA H19/miR-675 and lncRNA NEAT1/miR-204 in breast cancer.
Mol Oncol. 2019 Feb 25;:
Authors: Müller V, Ferrer LO, Steinbach B, Pantel K, Schwarzenbach H
Abstract
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are frequently precursor RNAs of microRNAs (miRNAs) or act as competing endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs) to interact with miRNAs. To better understand the shared impact of lncRNAs and miRNAs in the regulatory post-transcriptional network, we focused here on the relationships between (i) lncRNA H19 and miR-675, (ii) NEAT1 and miR-204, and (iii) HOTAIR and miR-331 in plasma of early breast cancer (BC) patients. We quantified each RNA in plasma samples of 63 BC patients and 10 healthy women by quantitative real-time PCR. In cell culture experiments, the influence of these non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) on proliferation and apoptosis of BC cell line MCF-7 was examined. Plasma levels of H19 (p=0.030), NEAT1 (p=0.030) and miR-331 (p=0.012) were deregulated in BC patients compared with healthy women. In both cohorts, the concentrations of H19 correlated with those of miR-675 (p=0.0001). Higher H19 (p=0.001) along with lower miR-675 (p=0.007) levels, and higher miR-204 (p=0.017) along with lower NEAT1 (p=0.030) levels were detected in plasma of HER2-positive patients compared with the other BC subgroups. Whereas the expression of HOTAIR was below the detection level, miR-331 levels correlated with nodal status (p=0.002), and recurrence (p=0.012). In cell culture experiments, a competitive impact on cell proliferation and apoptosis by these ncRNAs was also documented. Our findings describe a relationship of the plasma levels of H19/miR-675 and NEAT1/miR-204 in the different BC subtypes; in addition, they reveal interplay between these lncRNAs and miRNAs in the regulatory network in MCF-7 cells, which should also be considered in the search for new diagnostic and therapeutic markers.
PMID: 30803129 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher]
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2Eieeql
Aptamer functionalized curcumin-loaded human serum albumin (HSA) nanoparticles for targeted delivery to HER-2 positive breast cancer cells.
| Related Articles |
Aptamer functionalized curcumin-loaded human serum albumin (HSA) nanoparticles for targeted delivery to HER-2 positive breast cancer cells.
Int J Biol Macromol. 2019 Feb 22;:
Authors: Saleh T, Soudi T, Shojaosadati SA
Abstract
In this study, an HER2 aptamer-decorated curcumin-loaded human serum albumin nanoparticle (Apt-HSA/CCM NP) was developed and characterized as a new anticancer formulation for targeted delivery to human epithelial growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) overexpressing breast cancer cells. Conjugation of HER2 Apt to the surface of HSA NPs was confirmed by gel electrophoresis and FTIR analysis. The obtained NPs have the hydrodynamic diameter of 281.1 ± 11.1 nm and zeta potential of -33.3 ± 2.5 mV. The data demonstrated that encapsulation of curcumin in HSA NPs by desolvation method has increased water solubility by 400 folds. Fluorescent microscopy image demonstrated remarkable cytoplasmic uptake of Apt-HSA/CCM NPs in HER2-overexpressing SK-BR-3 cells compared to unconjugated counterparts. Cytotoxicity experiments demonstrated no significant difference between cytotoxic effect of free curcumin and non-targeted HSA/CCM NPs in both HER2 positive and HER2 negative cell lines. However, the toxicity of Apt-HSA/CCM NPs was significantly higher and cell viability reached 36% after 72 h in SK-BR3 cell line. These results suggest that this targeted delivery system has the potential to be considered as a promising candidate for the treatment of HER2 positive cancer cells.
PMID: 30802519 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher]
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2T0Z96p
Management of HER2-Positive Early Breast Cancer.
| Related Articles |
Management of HER2-Positive Early Breast Cancer.
Breast Care (Basel). 2018 Dec;13(6):453-455
Authors: Steger G, Lüftner D, Stöger H, Thürlimann B, Untch M
PMID: 30800041 [PubMed]
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2EfDsFA
Comparison of 4 FDA-approved mechanical thrombectomy devices for acute ischemic stroke: a network meta-analysis.
| Related Articles |
Comparison of 4 FDA-approved mechanical thrombectomy devices for acute ischemic stroke: a network meta-analysis.
World Neurosurg. 2019 Feb 22;:
Authors: Deng L, Qiu S, Wang L, Li Y, Wang D, Liu M
Abstract
BACKGROUND: The use of mechanical thrombectomy for the treatment of acute ischemic stroke (AIS) is rapidly growing. However there are limited data on the comparative effects of the various devices approved by the FDA for the treatment of AIS. We aimed to perform a network meta-analysis to assess the relative efficacy and safety of 4 thrombectomy devices.
METHODS: We searched PubMed, the Cochrane Library Central Register of Controlled Trials, Embase for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and parallel group observational studies which assessed thrombectomy devices in patients with AIS. Primary efficacy outcomes included functional independence (90-day modified Rankin Scale [mRS] score) and recanalization rate (thrombolysis in cerebral infarction [TICI score]). Safety outcomes included incidence of symptomatic intracranial hemorrhages (sICH) and 90-day mortality.
RESULTS: 5 RCTs and 5 observational studies, including 1659 participants were included. According to GRADE, most of the studies are of moderate evidence quality. Compared with Penumbra, Solitaire and Trevo were associated with higher rates of functional independence (3.75[1.44, 7.66]; 4.68[1.42,11.50], respectively). For revascularization, Solitaire and Trevo had higher rates of successful recanalization than Merci (2.99[1.15,6.53]; 3.34[1.20,8.01], respectively). In terms of safety outcomes (sHT and mortality), there was no significant difference between any comparators.
CONCLUSIONS: We concluded that stent-retriever devices were superior to non-stent retriever devices in functional outcomes and recanalization without significant increases in death or symptomatic hemorrhage. We found no evidence for a differential therapy effect by stent type. Further high-quality RCTs assessing efficacy difference between these two stent-retrievers are justified.
PMID: 30802552 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher]
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2TlBixG
Radiation exposure and operation time in percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy using fluoroscopy-based navigation system.
| Related Articles |
Radiation exposure and operation time in percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy using fluoroscopy-based navigation system.
World Neurosurg. 2019 Feb 22;:
Authors: Qin H, Huang S, Xu L, Wei P, Jiang J, Xie Z, Luo X, Tan H, Huang W
Abstract
OBJECTIVE: This study evaluated radiation exposure and operation time of percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy (PELD) by using fluoroscopy-based navigation system for access and localization.
METHODS: 86 PELD cases performed by a single surgeon were retrospectively analyzed. Patients were separated into two groups: Group A (using a 3D-printed navigation instrument and fluoroscopy-based navigation system) and Group B (with conventional fluoroscopy and standard instrumentation) . The operation, fluoroscopy, and total access time were collected, as well as fluoroscopy and access times.
RESULTS: The operative time for Group A was 59 minutes (standard deviation (stdev), 6 minutes) and 106 minutes (stdev, 15 minutes) in Group B (p<0.001). In Group A, fluoroscopy was used an average of 5 times (stdev, 0.7) and 29 times (stdev, 8) in Group B (p<0.001). The fluoroscopy time was 9 minutes (stdev, 2 minutes) in Group A and 40 minutes (stdev, 8 minutes) in Group B (p<0.001). The number of times access attempts were 1.3 (stdev, 0.5) in Group A and 8 times (stdev, 2 times) in Group B (p<0.001). The total access time was 11 minutes (stdev, 2 minutes) in Group A and 28 minutes (stdev, 5 minutes) in Group B (p<0.001).
CONCLUSIONS: PELD using fluoroscopy-based navigation system showed lower operative, fluoroscopy, and access time compared to conventional techniques. In addition, fewer fluoroscopy images and access attempts were made in the navigation group. These data suggest that this novel technique reduces fluoroscopy, operation time and may reduce risks of repeated surgical access attempts.
PMID: 30802551 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher]
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2IEt4gf
Future Oncology; +23 new citations
23 new pubmed citations were retrieved for your search. Click on the search hyperlink below to display the complete search results:
These pubmed results were generated on 2019/02/26
PubMed comprises more than millions of citations for biomedical literature from MEDLINE, life science journals, and online books. Citations may include links to full-text content from PubMed Central and publisher web sites.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2IO1fBU
Daily briefing: Clinical trial will target Alzheimer’s disease with gene therapy
Daily briefing: Clinical trial will target Alzheimer's disease with gene therapy
Daily briefing: Clinical trial will target Alzheimer's disease with gene therapy, Published online: 25 February 2019; doi:10.1038/d41586-019-00712-x
Plan to "bathe the brain" with lower-risk gene variants, cooling cloud banks could vanish in a warmer world andfrom A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2Eyjyab
Cell division cycle associated 5 promotes colorectal cancer progression by activating the ERK signaling pathway
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2EzzgCa
Integrated phenotypic screening and activity-based protein profiling to reveal potential therapy targets of pancreatic cancer.
 | Related Articles |
Integrated phenotypic screening and activity-based protein profiling to reveal potential therapy targets of pancreatic cancer.
Chem Commun (Camb). 2019 Jan 31;55(11):1596-1599
Authors: Liu W, Zhang Z, Zhang ZM, Hao P, Ding K, Li Z
Abstract
Pancreatic cancer has been defined as one of the most complex and challenging cancers to treat, but very few valid therapeutic targets have been identified to date. To address this issue, a 61-compound library was readily created by Ugi reaction followed by phenotypic screening, leading to the discovery of two most potent inhibitors, P21 and P26, which significantly impair BxPC-3 pancreatic cancer cell survival. A series of interacting protein hits, such as GSTO1, FAM213A, RAB6A/6B/39A and USMG5, were subsequently identified by quantitative chemoproteomics studies. The main cellular target, GSTO1, was further validated as a novel pancreatic cancer therapeutic target.
PMID: 30656306 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2SZBFin
Accessory right V6 behind the bronchus intermedius during VATS right upper lobectomy.
| Related Articles |
Accessory right V6 behind the bronchus intermedius during VATS right upper lobectomy.
Int J Surg Case Rep. 2019 Feb 19;56:17-19
Authors: Amore D, Molino A, Caterino U, Bergaminelli C, Casazza D, Palma A, Imitazione P, Curcio C
Abstract
INTRODUCTION: The anatomical abnormalities in pulmonary veins can have a serious impact on pulmonary resections.
PRESENTATION OF CASE: We report the case of a 70-year-old woman undergoing VATS right upper lobectomy for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. During subcarinal dissection, an anomalous vein draining from the superior segment of the right lower lobe into the left atrium and passing behind the bronchus intermedius was incidentally discovered. The patient had, in addition to the inferior pulmonary vein formed by the confluence of superior and common basal veins, a supernumerary vessel identified as: accessory right V6. Retrospective review of preoperative enhanced chest computed tomography confirmed the pulmonary vascular anomaly.
DISCUSSION/CONCLUSION: A careful dissection during pulmonary resections can help to recognize variations of the pulmonary veins, avoiding unexpected intraoperative complications.
PMID: 30802760 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher]
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2H8X01k
CDKL1 promotes the chemoresistance of human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells to hydroxycamptothecin.
| Related Articles |
CDKL1 promotes the chemoresistance of human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells to hydroxycamptothecin.
Mol Cell Probes. 2019 Feb 22;:
Authors: Li K, Meng Z, Jiang L, Xia C, Xu K, Yuan D, Chen H, Zhang B, Liu S
Abstract
CDKL1 is a cyclin-dependent kinase-like kinase that is highly expressed in diverse types of cancer cells. However, the role of CDKL1 in the chemoresistance of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) remains largely undefined. Here, we explored the role of CDKL1 in the chemoresistance of the human OSCC cell line CAL27 to hydroxycamptothecin (HCPT). Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction and western blotting revealed that exposure of CAL27 cells to HCPT led to a marked increase in the expression of CDKL1 at the mRNA and protein levels. Knockdown of CDKL1 significantly suppressed cell proliferation and induced cell cycle G0/G1 phase arrest in CAL27 cells based on the results of MTT and flow cytometry assays, respectively. CAL27 cells displayed attenuated biological activity of the cell population. After treatment with HCPT, whereas CDKL1 overexpression increased the resistance to HCPT of the remaining cells. Moreover, the western blot showed that the expression of cleaved-caspase 3 and phosphorylated ataxia telangiectasia mutated proteins was upregulated by HCPT treatment in CAL27 cells. Furthermore, CDKL1 overexpression partially reversed the inhibitory effects of HCPT in CAL27 cells. These results suggest that CDKL1 overexpression decreased the chemosensitivity of OSCC cells to HCPT, indicating a potential strategic approach for reversing the HCPT resistance in human OSCC.
PMID: 30802495 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher]
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2EjdLEm
In vitro activity and mode of action of phenolic compounds on Leishmania donovani.
| Related Articles |
In vitro activity and mode of action of phenolic compounds on Leishmania donovani.
PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019 Feb 25;13(2):e0007206
Authors: Antwi CA, Amisigo CM, Adjimani JP, Gwira TM
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Leishmaniasis is a disease caused by the protozoan parasite, Leishmania. The disease remains a global threat to public health requiring effective chemotherapy for control and treatment. In this study, the effect of some selected phenolic compounds on Leishmania donovani was investigated. The compounds were screened for their anti-leishmanial activities against promastigote and intracellular amastigote forms of Leishmania donovani.
METHODOLOGY/PRINCIPAL FINDINGS: The dose dependent effect and cytotoxicity of the compounds were determined by the MTT assay. Flow cytometry was used to determine the effect of the compounds on the cell cycle. Parasite morphological analysis was done by microscopy and growth kinetic studies were conducted by culturing cells and counting at 24 hours intervals over 120 hours. The cellular levels of iron in promastigotes treated with compounds was determined by atomic absorption spectroscopy and the effect of compounds on the expression of iron dependent enzymes was investigated using RT-qPCR. The IC50 of the compounds ranged from 16.34 μM to 124 μM compared to amphotericin B and deferoxamine controls. Rosmarinic acid and apigenin were the most effective against the promastigote and the intracellular amastigote forms. Selectivity indexes (SI) of rosmarinic acid and apigenin were 15.03 and 10.45 respectively for promastigotes while the SI of 12.78 and 5.20 respectively was obtained for intracellular amastigotes. Morphologically, 70% of rosmarinic acid treated promastigotes showed rounded morphology similar to the deferoxamine control. About 30% of cells treated with apigenin showed distorted cell membrane. Rosmarinic acid and apigenin induced cell arrest in the G0/G1 phase in promastigotes. Elevated intracellular iron levels were observed in promastigotes when parasites were treated with rosmarinic acid and this correlated with the level of expression of iron dependent genes.
CONCLUSIONS/SIGNIFICANCE: The data suggests that rosmarinic acid exerts its anti-leishmanial effect via iron chelation resulting in variable morphological changes and cell cycle arrest.
PMID: 30802252 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher]
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2T3E4s2
Male reprotoxicity associated with Sophora japonica treatment: evaluation of cellular and molecular events in vitro.
| Related Articles |
Male reprotoxicity associated with Sophora japonica treatment: evaluation of cellular and molecular events in vitro.
J Physiol Pharmacol. 2018 Dec;69(6):
Authors: Solek P, Shemedyuk N, Gorka A, Bilska-Kos A, Shemedyuk A, Koziorowski M
Abstract
Toxicological studies are urgently needed to confirm the safety of Sophora japonica extracts for clinical use. In particular, in addition to pharmacy and pharmacology, phytotherapy, herbal medication, Sophora japonica extracts are widely used as biologically active supplements. Scientfic data suggests that some of Sophora japonica extract components have very comprehensive biological effects. In the present study, our hypothesis assumed the potential reprotoxicity of Sophora japonica extract in respect to mouse germ cells (GC-1 spg, GC-2 spd) in vitro. Specifically, we were interested in the high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) identification of extract components and its stress-related effects on cellular and biochemical features, such as mitochondrial metabolism, cell cycle progression, oxidative stress balance and micronuclei formation. The results indicate that Sophora japonica extract induces oxidative/nitrosative stress-mediated impairment of the mechanism for free radicals scavenging, which may provoke genotoxic events in germ cells, by cell cycle arrest and micronuclei formation. Therefore, the interplay between reactive oxygen species (ROS)/reactive nitrogen species (RNS) and antioxidant system is critical for normal testicular function maintenance in the their environment. The specific pathways and mechanisms involved in the reprotoxicity of Sophora japonica need to be further investigated.
PMID: 30802219 [PubMed - in process]
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2EenR9f
Astaxanthin Combine With Human Serum Albumin To Abrogate Cell Proliferation, Migration, And Drug-Resistant In Human Ovarian Carcinoma SKOV3 Cells.
| Related Articles |
Astaxanthin Combine With Human Serum Albumin To Abrogate Cell Proliferation, Migration, And Drug-Resistant In Human Ovarian Carcinoma SKOV3 Cells.
Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2019 Feb 25;:
Authors: Su XZ, Chen R, Wang CB, Ouyang XL, Jiang Y, Zhu MY
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Astaxanthin (AST) shows a large range of beneficial effects together with anti-cancer and antioxidation properties. Human serum albumin (HSA) is the most abundant protein in blood plasma which plays the role of depot and transport protein for many exogenous compounds. However, whether HSA could enhance AST-induced cytotoxic effects in human ovarian cancer cells has not been examined to date.
OBJECTIVE: This study aims to explore the anticancer effect and the molecular mechanism of AST combine with HSA induced cytotoxicity in ovarian cancer SKOV3 cells.
METHOD: The ovarian cancer SKOV3 cells were treated by AST combined with HSA to study the effects of cell proliferation, cell morphology, cell cycle arrest, related protein expression, nuclear transfer, cell migration, and drug-resistant.
RESULTS: Our data confirmed that AST+HSA treatment enhanced the anticancer effects of AST, arrested G1 phase cell cycle and induced apoptosis in SKOV3 cells. AST+HSA induced apoptosis via mitochondrial apoptotic pathways was related to the increased ratio of Bcl-2/Bax and activation of caspase-3. Besides, exposure of cells to AST+HSA triggered the inactivation of NF-κB and activation p53 and MAPKs signaling pathways. Furthermore, AST+HSA significantly overcome the drug-resistant and inhibited the migration of SKOV3 cells.
CONCLUSION: AST combined treatment with HSA considerably inhibited NF-κB expression and translocation to nucleus, thereby improving the AST-induced cytotoxic effect on SKOV3 cells. These findings may provide rationale to combine AST with HSA for the treatment of ovarian cancer.
PMID: 30799797 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher]
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2T4807u
Silencing the PIK3CA Gene Enhances the Sensitivity of Childhood Leukemia Cells to Chemotherapy Drugs by Suppressing the Phosphorylation of Akt.
  | Related Articles |
Silencing the PIK3CA Gene Enhances the Sensitivity of Childhood Leukemia Cells to Chemotherapy Drugs by Suppressing the Phosphorylation of Akt.
Yonsei Med J. 2019 Feb;60(2):182-190
Authors: Liang X, Xin X, Qi D, Fu C, Ding M
Abstract
PURPOSE: This study aimed to investigate the effects of PIK3CA on the sensitivity of acute B lymphocytic leukemia cells (Nalm-6 cells) to chemotherapy drugs.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: Children's normal B lymphocytes and Nalm-6 cells were cultured. Nalm-6 cells were transfected with PIK3CA siRNA (siPIK3CA group) or its negative control (PIK3CA-Control group). Normal Nalm-6 cells were named Mock group. Nalm-6 cells transfected by PIK3CA siRNA were treated with Akt inhibitor (siPIK3CA+Akti-1/2 group). mRNA and protein expression was detected by qRT-PCR and Western blot. Proliferation and sensitivity to chemotherapeutic drugs was detected by MTT assay. Cell cycle and apoptosis was explored by low cytometry. Transwell assay was performed to test invasion.
RESULTS: PIK3CA mRNA (p=0.008) and protein (p=0.006) expression was higher in Nalm-6 cells than that in normal B lymphocytes. Compared with the Mock group and PIK3CA-Control group, Nalm-6 cells of the siPIK3CA group had lower OD495 values (all p<0.05) and invasion cell numbers (p=0.03 and p=0.025), as well as a higher proportion of G0/G1 phase cells (p=0.020 and p=0.022), percentage of apoptosis (p=0.016 and p=0.022), and inhibition rate (all p<0.05). pAkt expression in the siPIK3CA group (p=0.026 and p=0.031) and siPIK3CA+Akti-1/2 group (p=0.019 and p=0.023) was lower than that in the Mock group.
CONCLUSION: PIK3CA silencing inhibited Nalm-6 cell proliferation and invasion, and promoted their apoptosis and sensitivity to chemotherapeutic drugs, potentially through regulation of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.
PMID: 30666840 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2EgSdrA
Anticancer effect of pan-PI3K inhibitor on multiple myeloma cells: Shedding new light on the mechanisms involved in BKM120 resistance.
 | Related Articles |
Anticancer effect of pan-PI3K inhibitor on multiple myeloma cells: Shedding new light on the mechanisms involved in BKM120 resistance.
Eur J Pharmacol. 2019 Jan 05;842:89-98
Authors: Safaroghli-Azar A, Bashash D, Kazemi A, Pourbagheri-Sigaroodi A, Momeny M
Abstract
The correlation between the Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) axis and crucial mechanisms involved in the maintenance of the neoplastic nature of multiple myeloma (MM) has recently evolved a general agreement that PI3K inhibition-based therapies could construct an exciting perspective for the future treatment strategies. Our results outlined that abrogation of PI3K using pan-PI3K inhibitor BKM120 decreased survival of MM cells through induction of a caspase-3-dependent apoptosis coupled with SIRT1-mediated G2/M arrest in both KMM-1 and RPMI 8226 cell lines; however, the cell responses to the inhibitor was quite different, introducing wild-type PTEN-expressing RPMI 8226 as less sensitive cells. By investigating the sensitivity extent of a panel of hematological cell lines to BKM120, we found no significant association with respect to PTEN status. As far as we are aware, the results of the present study propose for the first time that the inhibitory effect of BKM120 was overshadowed, at least partially, through over-expression of either c-Myc or nuclear factor (NF)-κB in less sensitive MM cells. While there was no significant effect of the inhibitor on the expression of c-Myc in RPMI 8226, we found an enhanced cytotoxic effect when BKM120 was used in combination with a small molecule inhibitor of c-Myc. Noteworthy, the results of the synergistic experiments also revealed that BKM120 could produce a synergistic anti-cancer effect with carfilzomib (CFZ) and provided an enhanced therapeutic efficacy in MM cells, highlighting that PI3K inhibition might be a befitting approach in MM both in mono and combined therapy.
PMID: 30401630 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2EcG2ft
The new 6q27 tumor suppressor DACT2, frequently silenced by CpG methylation, sensitizes nasopharyngeal cancer cells to paclitaxel and 5-FU toxicity via β-catenin/Cdc25c signaling and G2/M arrest.
  | Related Articles |
The new 6q27 tumor suppressor DACT2, frequently silenced by CpG methylation, sensitizes nasopharyngeal cancer cells to paclitaxel and 5-FU toxicity via β-catenin/Cdc25c signaling and G2/M arrest.
Clin Epigenetics. 2018 02 27;10(1):26
Authors: Zhang Y, Fan J, Fan Y, Li L, He X, Xiang Q, Mu J, Zhou D, Sun X, Yang Y, Ren G, Tao Q, Xiang T
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is prevalent in South China, including Hong Kong and Southeast Asia, constantly associated with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection. Epigenetic etiology attributed to EBV plays a critical role in NPC pathogenesis. Through previous CpG methylome study, we identified Disheveled-associated binding antagonist of beta-catenin 2 (DACT2) as a methylated target in NPC. Although DACT2 was shown to regulate Wnt signaling in some carcinomas, its functions in NPC pathogenesis remain unclear.
METHODS: RT-PCR, qPCR, MSP, and BGS were applied to measure expression levels and promoter methylation of DACT2 in NPC. Transwell, flow cytometric analysis, colony formation, and BrdU-ELISA assay were used to assess different biological functions affected by DACT2. Immunofluorescence, Western blot, and dual-luciferase reporter assay were used to explore the mechanisms of DACT2 functions. Chemosensitivity assay was used to measure the impact of DACT2 on chemotherapy drugs.
RESULTS: We found that DACT2 is readily expressed in multiple normal adult tissues including upper respiratory tissues. However, it is frequently downregulated in NPC and correlated with promoter methylation. DNA methyltransferase inhibitor 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine restored its expression in NPC cells. DACT2 methylation was further detected in 29/32 (91%) NPC tumors but not in any (0/8) normal nasopharyngeal tissue samples. Ectopic expression of DACT2 in NPC cells suppressed their proliferation, migration, and invasion through downregulating matrix metalloproteinases. DACT2 expression also induced G2/M arrest in NPC cells through directly suppressing β-catenin/Cdc25c signaling, which sensitized NPC cells to paclitaxel and 5-FU, but not cisplatin.
CONCLUSION: Our results demonstrate that DACT2 is frequently inactivated epigenetically by CpG methylation in NPC, while it inhibits NPC cell proliferation and metastasis via suppressing β-catenin/Cdc25c signaling. Our study suggests that DACT2 promoter methylation is a potential epigenetic biomarker for the detection and chemotherapy guidance of NPC.
PMID: 30359298 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2T10biX
[Toxicity of immune checkpoints inhibitors].
 | Related Articles |
[Toxicity of immune checkpoints inhibitors].
Rev Mal Respir. 2018 Dec;35(10):1028-1038
Authors: Delaunay M, Caron P, Sibaud V, Godillot C, Collot S, Milia J, Prévot G, Mazières J
Abstract
INTRODUCTION: Anti-tumoral immunotherapy is currently the basis of a profound modification of therapeutic concepts in oncology, in particular since the arrival of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI). In addition to their efficacy profile, these immune-targeted agents also generate adverse events. With the increasing use of ICI for a growing number of tumor types, awareness of immunotherapy-related adverse events is essential to ensure prompt diagnosis and effective management of these potentially serious adverse events.
BACKGROUND: Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA4) and programmed cell death protein 1 (PD1) are two co-inhibitory receptors that are expressed on activated T cells against which therapeutic blocking antibodies have reached routine clinical use. Immune checkpoint blockade can induce inflammatory adverse effects, termed immune-related adverse events (irAEs), which resemble autoimmune disease. Though severe irAEs remain rare, they can be fatal if not diagnosed and treated in an appropriate manner.
OUTLOOK AND CONCLUSION: Additional studies are needed to better understand the clinical characteristics and chronology of these adverse effects and to clarify their pathophysiological mechanisms.
PMID: 30213624 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2Edq7xD
Noncoding RNA-nucleated heterochromatin spreading is intrinsically labile and requires accessory elements for epigenetic stability.
  | Related Articles |
Noncoding RNA-nucleated heterochromatin spreading is intrinsically labile and requires accessory elements for epigenetic stability.
Elife. 2018 07 18;7:
Authors: Greenstein RA, Jones SK, Spivey EC, Rybarski JR, Finkelstein IJ, Al-Sady B
Abstract
The heterochromatin spreading reaction is a central contributor to the formation of gene-repressive structures, which are re-established with high positional precision, or fidelity, following replication. How the spreading reaction contributes to this fidelity is not clear. To resolve the origins of stable inheritance of repression, we probed the intrinsic character of spreading events in fission yeast using a system that quantitatively describes the spreading reaction in live single cells. We show that spreading triggered by noncoding RNA-nucleated elements is stochastic, multimodal, and fluctuates dynamically across time. This lack of stability correlates with high histone turnover. At the mating type locus, this unstable behavior is restrained by an accessory cis-acting element REIII, which represses histone turnover. Further, REIII safeguards epigenetic memory against environmental perturbations. Our results suggest that the most prevalent type of spreading, driven by noncoding RNA-nucleators, is epigenetically unstable and requires collaboration with accessory elements to achieve high fidelity.
PMID: 30020075 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2JE46Zp
Clinical Practice Guideline: Tonsillectomy in Children (Update).
| Related Articles |
Clinical Practice Guideline: Tonsillectomy in Children (Update).
Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2019 Feb;160(1_suppl):S1-S42
Authors: Mitchell RB, Archer SM, Ishman SL, Rosenfeld RM, Coles S, Finestone SA, Friedman NR, Giordano T, Hildrew DM, Kim TW, Lloyd RM, Parikh SR, Shulman ST, Walner DL, Walsh SA, Nnacheta LC
Abstract
OBJECTIVE: This update of a 2011 guideline developed by the American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery Foundation provides evidence-based recommendations on the pre-, intra-, and postoperative care and management of children 1 to 18 years of age under consideration for tonsillectomy. Tonsillectomy is defined as a surgical procedure performed with or without adenoidectomy that completely removes the tonsil, including its capsule, by dissecting the peritonsillar space between the tonsil capsule and the muscular wall. Tonsillectomy is one of the most common surgical procedures in the United States, with 289,000 ambulatory procedures performed annually in children <15 years of age based on the most recent published data. This guideline is intended for all clinicians in any setting who interact with children who may be candidates for tonsillectomy.
PURPOSE: The purpose of this multidisciplinary guideline is to identify quality improvement opportunities in managing children under consideration for tonsillectomy and to create explicit and actionable recommendations to implement these opportunities in clinical practice. Specifically, the goals are to educate clinicians, patients, and/or caregivers regarding the indications for tonsillectomy and the natural history of recurrent throat infections. Additional goals include the following: optimizing the perioperative management of children undergoing tonsillectomy, emphasizing the need for evaluation and intervention in special populations, improving the counseling and education of families who are considering tonsillectomy for their children, highlighting the management options for patients with modifying factors, and reducing inappropriate or unnecessary variations in care. Children aged 1 to 18 years under consideration for tonsillectomy are the target patient for the guideline. For this guideline update, the American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery Foundation selected a panel representing the fields of nursing, anesthesiology, consumers, family medicine, infectious disease, otolaryngology-head and neck surgery, pediatrics, and sleep medicine.
KEY ACTION STATEMENTS: The guideline update group made strong recommendations for the following key action statements (KASs): (1) Clinicians should recommend watchful waiting for recurrent throat infection if there have been <7 episodes in the past year, <5 episodes per year in the past 2 years, or <3 episodes per year in the past 3 years. (2) Clinicians should administer a single intraoperative dose of intravenous dexamethasone to children undergoing tonsillectomy. (3) Clinicians should recommend ibuprofen, acetaminophen, or both for pain control after tonsillectomy. The guideline update group made recommendations for the following KASs: (1) Clinicians should assess the child with recurrent throat infection who does not meet criteria in KAS 2 for modifying factors that may nonetheless favor tonsillectomy, which may include but are not limited to multiple antibiotic allergies/intolerance, PFAPA (periodic fever, aphthous stomatitis, pharyngitis, and adenitis), or history of >1 peritonsillar abscess. (2) Clinicians should ask caregivers of children with obstructive sleep-disordered breathing and tonsillar hypertrophy about comorbid conditions that may improve after tonsillectomy, including growth retardation, poor school performance, enuresis, asthma, and behavioral problems. (3) Before performing tonsillectomy, the clinician should refer children with obstructive sleep-disordered breathing for polysomnography if they are <2 years of age or if they exhibit any of the following: obesity, Down syndrome, craniofacial abnormalities, neuromuscular disorders, sickle cell disease, or mucopolysaccharidoses. (4) The clinician should advocate for polysomnography prior to tonsillectomy for obstructive sleep-disordered breathing in children without any of the comorbidities listed in KAS 5 for whom the need for tonsillectomy is uncertain or when there is discordance between the physical examination and the reported severity of oSDB. (5) Clinicians should recommend tonsillectomy for children with obstructive sleep apnea documented by overnight polysomnography. (6) Clinicians should counsel patients and caregivers and explain that obstructive sleep-disordered breathing may persist or recur after tonsillectomy and may require further management. (7) The clinician should counsel patients and caregivers regarding the importance of managing posttonsillectomy pain as part of the perioperative education process and should reinforce this counseling at the time of surgery with reminders about the need to anticipate, reassess, and adequately treat pain after surgery. (8) Clinicians should arrange for overnight, inpatient monitoring of children after tonsillectomy if they are <3 years old or have severe obstructive sleep apnea (apnea-hypopnea index ≥10 obstructive events/hour, oxygen saturation nadir <80%, or both). (9) Clinicians should follow up with patients and/or caregivers after tonsillectomy and document in the medical record the presence or absence of bleeding within 24 hours of surgery (primary bleeding) and bleeding occurring later than 24 hours after surgery (secondary bleeding). (10) Clinicians should determine their rate of primary and secondary posttonsillectomy bleeding at least annually. The guideline update group made a strong recommendation against 2 actions: (1) Clinicians should not administer or prescribe perioperative antibiotics to children undergoing tonsillectomy. (2) Clinicians must not administer or prescribe codeine, or any medication containing codeine, after tonsillectomy in children younger than 12 years. The policy level for the recommendation about documenting recurrent throat infection was an option: (1) Clinicians may recommend tonsillectomy for recurrent throat infection with a frequency of at least 7 episodes in the past year, at least 5 episodes per year for 2 years, or at least 3 episodes per year for 3 years with documentation in the medical record for each episode of sore throat and ≥1 of the following: temperature >38.3°C (101°F), cervical adenopathy, tonsillar exudate, or positive test for group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus.
DIFFERENCES FROM PRIOR GUIDELINE: (1) Incorporating new evidence profiles to include the role of patient preferences, confidence in the evidence, differences of opinion, quality improvement opportunities, and any exclusion to which the action statement does not apply. (2) There were 1 new clinical practice guideline, 26 new systematic reviews, and 13 new randomized controlled trials included in the current guideline update. (3) Inclusion of 2 consumer advocates on the guideline update group. (4) Changes to 5 KASs from the original guideline: KAS 1 (Watchful waiting for recurrent throat infection), KAS 3 (Tonsillectomy for recurrent infection with modifying factors), KAS 4 (Tonsillectomy for obstructive sleep-disordered breathing), KAS 9 (Perioperative pain counseling), and KAS 10 (Perioperative antibiotics). (5) Seven new KASs: KAS 5 (Indications for polysomnography), KAS 6 (Additional recommendations for polysomnography), KAS 7 (Tonsillectomy for obstructive sleep apnea), KAS 12 (Inpatient monitoring for children after tonsillectomy), KAS 13 (Postoperative ibuprofen and acetaminophen), KAS 14 (Postoperative codeine), and KAS 15a (Outcome assessment for bleeding). (6) Addition of an algorithm outlining KASs. (7) Enhanced emphasis on patient and/or caregiver education and shared decision making.
PMID: 30798778 [PubMed - in process]
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2EcyPwa
Αναζήτηση αυτού του ιστολογίου
! # Ola via Alexandros G.Sfakianakis on Inoreader
-
Correction to: SEOM Clinical Guideline for treatment of muscle-invasive and metastatic urothelial bladder cancer (2016) Due to a technical i...
-
Abstract The Gram-negative pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa is found ubiquitously within the environment and is recognised as an opportuni...
