Medicine by Alexandros G. Sfakianakis,Anapafseos 5 Agios Nikolaos 72100 Crete Greece,00302841026182,00306932607174,alsfakia@gmail.com,
Αρχειοθήκη ιστολογίου
-
►
2023
(272)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (141)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (131)
-
►
2022
(2066)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (80)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (170)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (190)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (203)
-
►
2021
(7399)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (186)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (472)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (851)
-
►
2020
(2517)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (792)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (21)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (28)
-
▼
2019
(12076)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (19)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (54)
-
▼
Φεβρουαρίου
(4765)
-
▼
Φεβ 01
(191)
- Impact of Lower Extremity Dysmorphia on Lymphedema...
- Expanding the use of the perforator free flap in b...
- In Defense of Evidence-Based Medicine in Plastic S...
- Breast implant weight vs volume: Reappraising brea...
- Browning of Human Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue afte...
- Refining Post-Orthognathic Surgery Facial Contour ...
- Reply to the letter: “Reply to: Enhancement of Pro...
- Reply to: ‘Enhancement of Progenitor Cells by Two-...
- Re: Use of hyaluronic acid fillers for acquired co...
- RESPONSE: A simple way to reduce surgical-site inf...
- A simple way to reduce surgical-site infections in...
- “Response to: Refining Post-Orthognathic Surgery F...
- Reply: Impact of Lower Extremity Dysmorphia on Lym...
- Public attitudes toward urban water sustainability...
- Retraction Note: Endocrine disruptors induce pertu...
- Surface tension, rheology and hydrophobicity of rh...
- Seasonal changes in water sources used by woody sp...
- Hospital Infection Prevention: How Much Can We Pre...
- High incidence of MTHFR, CBS, and MTRR polymorphis...
- A pilot prospective study of 577-nm yellow subthre...
- The photocytotoxicity effect of cationic sulfonate...
- [ASAP] Ribosomal Synthesis of Backbone-Cyclic Pept...
- [ASAP] Chiroptical Activity Enhancement via Struct...
- ‘Druggable Target’ for Treating Alzheimer’s Discov...
- The Top 9 Augmented Reality Companies in Healthcare
- Cell culture made easy with new 24-channel pipetti...
- Does information and communication technologies im...
- Experimental investigation of diesel engine perfor...
- Synthesis and characterization of magnetic Fe 3 O ...
- Preparation of various thiol-functionalized carbon...
- The application of forward osmosis for simulated s...
- Dehydration and insulinopenia are necessary and su...
- Smart scanning for low-illumination and fast RESOL...
- Magnetization reversal driven by low dimensional c...
- The coevolution of lifespan and reversible plasticity
- Satb1 regulates the effector program of encephalit...
- Noisy defects in the high-Tc superconductor Bi2Sr2...
- A number-based inventory of size-resolved black ca...
- Patterns of genetic differentiation and the footpr...
- The LACSEMS: what radiologists need to know
- Imaging post-stereotactic body radiation therapy r...
- [ASAP] Crystal Structure of the Transcription Regu...
- [ASAP] Rational Design via Synergistic Combination...
- Working Scientist podcast: How to beat research fu...
- Macedonia name change paves way for science cooper...
- UC Berkeley bans new research funding from Huawei
- Management of Australia’s Murray–Darling basin dee...
- Watch a levitating droplet pinball around its cont...
- French research chief: grants are up, bureaucracy ...
- Michael F. Atiyah (1929–2019)
- 3D printing with light
- In vivo comparison of the proangiogenic properties...
- Biocompatibility and biodistribution of surface-mo...
- 4-Methyl-5-Pentylbenzene-1,3-Diol Regulates Chemot...
- Dehydration and insulinopenia are necessary and su...
- Smart scanning for low-illumination and fast RESOL...
- Magnetization reversal driven by low dimensional c...
- The coevolution of lifespan and reversible plasticity
- Satb1 regulates the effector program of encephalit...
- Noisy defects in the high-Tc superconductor Bi2Sr2...
- A number-based inventory of size-resolved black ca...
- Patterns of genetic differentiation and the footpr...
- French research chief: grants are up, bureaucracy ...
- [ASAP] Aza-Rubottom Oxidation: Synthetic Access to...
- [ASAP] Zirconium-Based Metal–Organic Frameworks fo...
- [ASAP] High-Throughput “FP-Tag” Assay for the Iden...
- [ASAP] Rapid Room-Temperature Synthesis of a Metas...
- [ASAP] Regioselective Carbonylation of 2,2-Disubst...
- [ASAP] Rate–Driving Force Relationships in the Mul...
- [ASAP] Elucidating the Nuclear Quantum Dynamics of...
- [ASAP] Enantioselective Allylation Using Allene, a...
- Genome Analysis of Carbaryl-Degrading Strain Pseud...
- UC Berkeley bans new research funding from Huawei
- Medical-grade polycaprolactone scaffolds made by m...
- Structural and biomechanical changes to dentin ext...
- Driving Policy Change to Improve Micronutrient Sta...
- Evaluating the Whoops Proof S.C . Campaign: A Pair...
- Environmental risk appraisement of disinfection by...
- Mutual relationships of biochar and soil pH, CEC, ...
- Rapid liquid-phase microextraction of analytes fro...
- Poly(ionic liquid) embedded particles as efficient...
- Rapid assessment of total MCPD esters in palm-base...
- KEV: a free software for calculating the equilibri...
- An ultrasensitive electrochemical aptasensor for e...
- 😴😴😴Sleep Medicine🕵🕵️♀️
- Michael F. Atiyah (1929–2019)
- Macedonia name change paves way for science cooper...
- Livestock and Carnivores: Economic and Ecological ...
- 🤓🧘 Dangerous non-food products🧛♂️🤦🤦♀️
- Molecular Systems Biology
- Mammakarzinom: Molekulare Diagnostik und Erkenntni...
- Protein engineering comes of age
- The conserved theme of ribosome hibernation: from ...
- Editorial Board
- Ablation of NMDA receptors in dopamine neurons dis...
- DNA methylation of the Tacr2 gene in a CUMS model ...
- Management of Australia’s Murray–Darling basin dee...
- 3D printing with light
- Systemic thrombolysis for acute submassive pulmona...
- A case of aggressive giant dermatofibrosarcoma pro...
-
▼
Φεβ 01
(191)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (5155)
-
►
2018
(3144)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (3144)
Ετικέτες
Πληροφορίες
Παρασκευή 1 Φεβρουαρίου 2019
Public attitudes toward urban water sustainability transitions: a multi-city survey in the western United States
Abstract
This article presents an integrated theoretical model, drawing from sustainability transition research and attitude theory, to explain public perceptions of urban water sustainability transitions and public support for transformational water-management strategies. We test the model with empirical data from a random-sample residential survey in three cities in the western United States dependent on Colorado River water: Phoenix, Arizona, Denver, Colorado, and Las Vegas, Nevada. As one of the most heavily managed and over-allocated transboundary river systems in the world, sustainable water management of the Colorado River is critical to the future of the region. Cities face increasing pressure on water resources as population, development, and uncertainty about the future increase. While a growing number of scholars focus on sustainability transitions, a few studies focus explicitly on the role of the public as fundamental actors. This is despite the acknowledgement that public support may constrain or enable transitions and that major societal changes will affect the public in numerous and critical ways. We hypothesize that environmental orientation, procedural knowledge, perceived personal responsibility, trust in government, and socio-economic resources predict public perceptions of the need for transitions and public support for transformational water-management strategies. We use ANOVA to identify differences between cities, and confirmatory factor analysis and structural equation modeling to evaluate the conceptual model. Results provide partial support for the hypothesized model and the findings replicate across cities. The findings suggest several policy implications for basin-wide and city-scale water management in the Colorado River basin.
from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2DOYOuD
Retraction Note: Endocrine disruptors induce perturbations in endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria of human pluripotent stem cell derivatives
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2t2TopA
Surface tension, rheology and hydrophobicity of rhizodeposits and seed mucilage influence soil water retention and hysteresis
Abstract
Aims
Rhizodeposits collected from hydroponic solutions with roots of maize and barley, and seed mucilage washed from chia, were added to soil to measure their impact on water retention and hysteresis in a sandy loam soil at a range of concentrations. We test the hypothesis that the effect of plant exudates and mucilages on hydraulic properties of soils depends on their physicochemical characteristics and origin.
Methods
Surface tension and viscosity of the exudate solutions were measured using the Du Noüy ring method and a cone-plate rheometer, respectively. The contact angle of water on exudate treated soil was measured with the sessile drop method. Water retention and hysteresis were measured by equilibrating soil samples, treated with exudates and mucilages at 0.46 and 4.6 mg g−1 concentration, on dialysis tubing filled with polyethylene glycol (PEG) solution of known osmotic potential.
Results
Surface tension decreased and viscosity increased with increasing concentration of the exudates and mucilage in solutions. Change in surface tension and viscosity was greatest for chia seed exudate and least for barley root exudate. Contact angle increased with increasing maize root and chia seed exudate concentration in soil, but not barley root. Chia seed mucilage and maize root rhizodeposits enhanced soil water retention and increased hysteresis index, whereas barley root rhizodeposits decreased soil water retention and the hysteresis effect. The impact of exudates and mucilages on soil water retention almost ceased when approaching wilting point at −1500 kPa matric potential.
Conclusions
Barley rhizodeposits behaved as surfactants, drying the rhizosphere at smaller suctions. Chia seed mucilage and maize root rhizodeposits behaved as hydrogels that hold more water in the rhizosphere, but with slower rewetting and greater hysteresis.
from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2SpsoyI
Seasonal changes in water sources used by woody species in a tropical coastal dune forest
Abstract
Aims
Our aim was to investigate the water sources used by woody species under contrasting water availability and the extent of water-sources-use differentiation among dominant woody species in a tropical coastal dune forest.
Methods
We sampled 15 woody species in a Brazilian restinga forest and, through Bayesian isotope mixing models, we estimated the proportion of water sources used. We tested whether water-sources-use was (i) different between contrasting water availability conditions; (ii) dependent on growth form, plant size or crown illumination; and (iii) influenced by stand density, evenness or biomass.
Results
We found a seasonal variation in water-sources-use, but no vertical soil-water partitioning among woody species. In wetter periods, plants used mainly water from top-soil, as a shallow water table limited water uptake to top-soil layers recharged with rainwater. Contrastingly, during drier periods, with the absence of rain and a deeper water table, plants generally relied on deeper (50 cm) soil layers. Only under less-wet conditions, a greater evenness and density implied higher water-uptake depth heterogeneity among plants. However, changes in the main water-sources used by plants were neither evoked in more dense or diverse plots, nor induced by plant size.
Conclusions
Our study shows that restinga species have dynamic shifts in water-uptake depth caused by seasonal water availability changes, influenced by the combined effect of insufficient moisture at shallow soil layers and water-table lowering in drier periods. These temporal shifts are common among species, implying that restinga woody community has a homogeneous strategy of water-resources acquisition. This study enhances our understanding of the effects that water variations can have on water-resource use in restinga forests.
from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2Gi1HFK
Hospital Infection Prevention: How Much Can We Prevent and How Hard Should We Try?
Abstract
Purpose of Review
To summarize the extent to which hospital-acquired infections (HAIs) are preventable and to assess expectations, challenges, and barriers to improve patient outcomes.
Recent Findings
HAIs cause significant morbidity and mortality. Getting to zero HAIs is a commonly stated goal yet leads to unrealistic expectations. The extent to which all HAIs can be prevented remains debatable and is subject to multiple considerations and barriers. Current infection prevention science is inexact and evolving. Evidence-based infection prevention practices are often incompletely implemented and at times controversial. Highly sensitive surveillance results in overdiagnosis, calling into question the real incidence of HAIs. Perceived reductions in HAIs by gaming the system lead to false conclusions about preventability and may cause harm. Successful HAI reduction programs require executive oversight yet keeping hospital leaders engaged in infection prevention is a challenge given competing priorities. Medicine is not a physical science with precisely defined laws; thus, infection prevention interventions are subject to variable outcomes.
Summary
Perhaps up to 55–70% of HAIs are potentially preventable. This is subject to a law of diminishing returns as the preventable proportion of HAIs may reduce over time with improvements in patient safety. As the principle tenet of medicine is first do no harm, infection prevention programs should relentlessly pursue reliable, sustainable, and practical strategies for heightened patient safety.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2HNDJEV
High incidence of MTHFR, CBS, and MTRR polymorphisms in vitiligo patients. Preliminary report in a retrospective study
OBJECTIVE: Vitiligo is a multifactorial polygenic disorder with a complex pathogenesis. It is related to both genetic and no genetic factors. The role of genetics is currently studied with several analytical approaches, such as genetic linkage, candidate gene association studies, genome-wide association studies (GWAS), deep DNA re-sequencing and gene expression studies. To date, there are no genetic traits directly related to vitiligo pathogenesis.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: 43 cases of vitiligo patients and 30 healthy donors recruited as control, were screened by assaying the biochemical molecules involved in the self-cells cytotoxicity (haptoglobin and homocysteine) and candidate genes involved in the regulatory process of the re-methylation cycles and transsulfuration. Candidate genes and their polymorphisms screened are methylene-tetrahydrofolate-reductase (MTHFR) C677T and A1298C; cystathionine-beta-synthase enzyme (CBS) I278T and Ins68bp; and methionine-synthase-reductase (MTRR) A66G.
RESULTS: A peculiar genetic profile in vitiligo patients are defined: 11.6% of vitiligo patients shown polymorphic variant MTHFR 677TT vs. 3.3% of healthy donor MTHFR 677CC profile (p=0.0017); 14.0% of vitiligo patients shown CBS polymorphic variant 278TT vs. 3.3% of healthy donor 278II profile (p=0.0012); and 11.6% of vitiligo patients shown MTRR 66GG vs. 3.3% of healthy donor MTRR 677AA profile (p>0.0001).
CONCLUSIONS: This is the first study reporting the correlation between the polymorphic status of MTHFR C677T, CBS I278T, and MTRR A66G and vitiligo. The genetic screening of these polymorphisms could be useful for early detection of the inheritance risk factor in a subject carrying relatives with vitiligo. Although these data could suggest a kind of dysregulation, genetically based, of thiols production mechanisms. Based on these results, we have not been able to get hypothesis about the putative pathogenesis of vitiligo, and the precise cause remains unclear.
L'articolo High incidence of MTHFR, CBS, and MTRR polymorphisms in vitiligo patients. Preliminary report in a retrospective study sembra essere il primo su European Review.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2UtlxSo
A pilot prospective study of 577-nm yellow subthreshold micropulse laser treatment with two different power settings for acute central serous chorioretinopathy
Abstract
To compare the efficacy of 50% threshold power with 25% threshold power of 577-nm subthreshold micropulse laser (SMPL) for acute central serous chorioretinopathy (CSC). Prospective, interventional, non-randomized, comparative case series. A total of 54 patients (54 eyes) with acute CSC were enrolled. Twenty-four eyes received 25% threshold power and 30 eyes received 50% threshold power of 577-nm SMPL. Best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA), central macular thickness (CMT), and complete absorption of subretinal fluid (SRF) were evaluated at 1 month and 3 months. The complete absorption rate of SRF in the 50% power group was significantly greater than that in the 25% power group at 1 month (70.0% vs 25.0%, p < 0.001) and at 3 months (83.3% vs 54.2%, p < 0.001). Mean BCVA improved from 0.34 ± 0.20 LogMAR to 0.02 ± 0.13 LogMAR in the 50% power group and from 0.27 ± 0.15 LogMAR to 0.14 ± 0.21 LogMAR in the 25% power group with a significant difference between the two groups after 3 months (p = 0.027). In the 50% power group, the CMT decreased from 491.6 ± 154.8 μm at baseline to 231.3 ± 92.3 μm at 1 month and 228.2 ± 88.1 μm at 3 months, and in the 25% power group, the CMT decreased from 444.9 ± 164.1 to 306.8 ± 102.6 μm at 1 month and 254.5 ± 101.7 μm at 3 months. There was statistical difference of CMT at 1 month (p = 0.009) but no significant difference at 3 months between the two groups (p = 0.232). SMPL with 50% threshold power may be more effective than 25% threshold power for acute CSC.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2MMDBEy
The photocytotoxicity effect of cationic sulfonated corrole towards lung cancer cells: in vitro and in vivo study
Abstract
Corrole is a kind of new and promising photosensitizer (PS) in cancer photodynamic therapy (PDT). However, the protein molecular mechanism of PDT activity for corrole under light irradiation is still not clear. In this paper, water-soluble cationic sulfonated corrole (1) and its metal complexes (1-Fe, 1-Mn, and 1-Cu) were prepared, and the photodynamic anti-cancer activity against various tumor cells was investigated by MTT assay. The potential molecular mechanism of PDT activity was elucidated by fluorescence microscope, flow cytometry, molecular docking, and western blotting analysis. Besides, the potential PDT anti-tumor effect of 1 in vivo was assessed in human tumor xenografts in mice. Quantitative analysis revealed that 1's phototoxicity triggered a significant generation of reactive oxygen species, causing disruption of mitochondrial membrane potential. The results of western blotting (WB) assay shown in 1's phototoxicity could induce cell apoptosis via ROS-mediated mitochondrial caspase apoptosis pathway, in which SIRT1 protein degradation played a key role. PTD activity in vivo shown in 1 could significantly reduce the growth of A549 xenografted tumor, without obvious loss of mice body weight. We clearly found that cationic sulfonated corrole is a potential candidate of PS in vitro and in vivo. The phototoxicity of 1 could induce A549 cell apoptosis by inducing ROS production increase, further to activate the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway. We concluded that SIRT1 protein is a more appropriate target in this progress.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2DQ04NW
[ASAP] Ribosomal Synthesis of Backbone-Cyclic Peptides Compatible with In Vitro Display

from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2DP6L2E
[ASAP] Chiroptical Activity Enhancement via Structural Control: The Chiral Synthesis and Reversible Interconversion of Two Intrinsically Chiral Gold Nanoclusters

from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2MKkMBQ
‘Druggable Target’ for Treating Alzheimer’s Discovered
To date, results have been mixed. In a new paper, published in Cell Stem Cell, researchers at the University of California San Diego School of Medicine, in collaboration with colleagues in San Diego and The Netherlands, focused on the alternative therapeutic target: tau. Using induced pluripotent stem cell-derived (iPSC) neurons from AD patients, the researchers report that cholesteryl esters (CE)— the storage product for excess cholesterol within cells— act as regulators of tau. Import...
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2Wy6Lvq
The Top 9 Augmented Reality Companies in Healthcare
Augmented Reality Vs. Virtual Reality Augmented reality (AR) has shown an amazing development curve since Boeing researcher, Thomas Caudell coined the term "augmented reality" in 1990. The technology changed how an NFL football game is perceived through television. Emmy award-winning Sportvision introduced the yellow first down line painted on the field in 1998, and the game has never been the same. Yet, AR does not only have a transformative impact on sports broadcasting but also on navigat...
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2RBN0Q8
Cell culture made easy with new 24-channel pipetting heads for VIAFLO 96/384
Two versions of the 24-channel heads are available to accommodate the need for different volumes – a 10 to 300 µl option for cell or reagent addition, and a larger 50 to 1,250 µl version for media and buffer transfers – allowing the user to fill a 24-well plate in seconds. Both options use INTEGRA's proprietary GripTip system, which ensures perfect alignment and eliminates the risk of pipette tips leaking or falling off. As with existing 96- and 384-channel options, all of INTEGRA's pipett...
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2WD9yDQ
Does information and communication technologies improve environmental quality in the era of globalization? An empirical analysis
Abstract
This study intends to examine the impact of ICTs (i.e., internet usage and mobile cellular subscriptions), globalization, electricity consumption, financial development, and economic growth on environmental quality by using 1994–2014 panel data of BRICS economies. This study employed a second-generation panel unit root test accounting for the presence of cross-sectional dependence and indicated that carbon dioxide emissions, electricity consumption, financial development, internet usage, mobile usage, globalization, and economic growth have integration of order one. The results from Westerlund panel co-integration test confirms that the variables are co-integrated and revealed that ICT-finance-globalization-electricity-GDP-CO2 nexus has long-run equilibrium relationship. The results from dynamic seemingly unrelated regression (DSUR) indicate that internet usage and mobile cellular subscriptions (ICTs) have significant, adverse impact on carbon dioxide emissions. To put it simply, ICT positively contributes towards environmental quality. Similarly, economic growth also has an adverse effect on carbon dioxide emissions. On the other hand, electricity consumption, globalization, and financial development have a significant positive effect on carbon emissions. In addition, Granger causality test results show the presence of a bidirectional causal relationship between internet usage and environmental quality, financial development and electricity consumption, ICT and financial development, mobile cellular subscription and globalization, economic growth and environmental quality, and internet usage and economic growth. A unidirectional causal link is detected running from mobile cellular subscriptions towards environmental quality, ICT towards electricity consumption, financial development towards environmental quality, globalization towards environmental quality, and globalization towards economic growth. Moreover, time series analysis has also been done in this study to analyze the findings for each of BRICS countries which are directed towards important policy implications. For instance, ICT policy can play an integral part in improving environmental quality policy.
from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2S4g9Iv
Experimental investigation of diesel engine performance fuelled with the blends of Jatropha curcas , ethanol, and diesel
Abstract
Nonrenewable fossil fuels show increased demand and with fossil fuels at a rapid depleting stage, there seems to be an increase in requirement for alternative fuels too. Biofuels and blended fossil fuels are one of a kind. Nonedible jatropha (Jatropha curcas) oil-based methyl ester was produced and mixed with ethanol and blended with conventional diesel in various compositions. Jatropha biodiesel is used because of its great blending capacity with diesel. Sodium hydroxide is used as a catalyst which allows miscibility between ethanol and diesel. In present epoch, the paucity of fossil fuels and its adverse impact have driven researchers to focus on alternative fuels. Biodiesel is one of the most favorable and promising alternatives in the application of automobiles, boilers, gas turbines, etc. This study targets at finding the engine performance and emission characteristics under various load conditions on Kirloskar single-cylinder VCR research engine by blending both jatropha biodiesel and ethanol with base diesel at various compositions. Both jatropha biodiesel and ethanol have high calorific value which is a most important factor for engine power production. The performance analysis showed that the biodiesel blend of 98% diesel with 1.5% jatropha biodiesel and 0.5% (D98J1.5E0.5) of ethanol had a significant improvement in the engine performance than the conventional diesel.
from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2UBglMu
Synthesis and characterization of magnetic Fe 3 O 4 @CaSiO 3 composites and evaluation of their adsorption characteristics for heavy metal ions
Abstract
A two-component material (Fe3O4@CaSiO3) with an Fe3O4 magnetite core and layered porous CaSiO3 shell from calcium nitrate and sodium silicate was synthesized by precipitation. The structure, morphology, magnetic properties, and composition of the Fe3O4@CaSiO3 composite were characterized in detail, and its adsorption performance, adsorption kinetics, and recyclability for Cu2+, Ni2+, and Cr3+ adsorption were studied. The Fe3O4@CaSiO3 composite has a 2D core–layer architecture with a cotton-like morphology, specific surface area of 41.56 m2/g, pore size of 16 nm, and pore volume of 0.25 cm3/g. The measured magnetization saturation values of the magnetic composite were 57.1 emu/g. Data of the adsorption of Cu2+, Ni2+, and Cr3+ by Fe3O4@CaSiO3 fitted the Redlich–Peterson and pseudo-second-order models well, and all adsorption processes reached equilibrium within 150 min. The maximum adsorption capacities of Fe3O4@CaSiO3 toward Cu2+, Ni2+, and Cr3+ were 427.10, 391.59, and 371.39 mg/g at an initial concentration of 225 mg/L and a temperature of 293 K according to the fitted curve with the Redlich–Peterson model, respectively. All adsorption were spontaneous endothermic processes featuring an entropy increase, including physisorption, chemisorption, and ion exchange; among these process, chemisorption was the primary mechanism. Fe3O4@CaSiO3 exhibited excellent adsorption, regeneration, and magnetic separation performance, thereby demonstrating its potential applicability to removing heavy metal ions.
from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2MJDUzO
Preparation of various thiol-functionalized carbon-based materials for enhanced removal of mercury from aqueous solution
Abstract
In this work, biochar (BC), activated carbon (AC), and graphene oxide (GO) were thiol-functionalized using 3-mercaptopropyltrimethoxysilane (3-MPTS) (named as BCS, ACS, and GOS, respectively). BCS, ACS, and GOS were synthesized mainly via the interaction between hydrolyzed 3-MPTS and surface oxygen-containing functional groups (e.g., –OH, O–C=O, and C=O) and π-π interaction. The materials before and after modification were characterized and tested for mercury removal, including sorption kinetics and isotherms, the effects of adsorbent dosage, initial pH, and ionic strength. Pseudo-second-order sorption kinetic model (R2 = 0.992~1.000) and Langmuir sorption isotherm model (R2 = 0.964~0.998) fitted well with the sorption data of mercury. GOS had the most –SH groups with the largest adsorption capacity for Hg2+ and CH3Hg+ (449.6 and 127.5 mg/g), followed by ACS (235.7 and 86.7 mg/g) and BCS (175.6 and 30.3 mg/g), which were much larger than GO (96.7 and 4.9 mg/g), AC (81.1 and 24.6 mg/g), and BC (95.6 and 9.4 mg/g). GOS and ACS showed stable mercury adsorption properties at a wide pH range (2~9) and ionic strength (0.01~0.1 mol/L). Mercury maybe removed by ligand exchange, surface complexation, and electrostatic attraction.
from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2DOZBf6
The application of forward osmosis for simulated surface water treatment by using trisodium citrate as draw solute
Abstract
In this study, trisodium citrate was used as draw solute in forward osmosis (FO) due to its biodegradability and easy reuse after FO dilution. The effect of operating conditions on FO performance was investigated. The study focused on the long-term flux performance and membrane fouling when surface water was used as feed solution. A water flux of 9.8 LMH was observed using 0.5 M trisodium citrate as draw solution in PRO mode. In the long-term FO process, trisodium citrate showed a slight decrease in total flux loss (13.06%) after 20 h of operation. The membrane fouling was significantly reduced after a two-step physical cleaning. A considerable flux recovery (> 95%) of the fouled membrane was finally obtained. Therefore, this study proves the superiority of trisodium citrate as draw solution and paves a new way in applying FO directly for surface water reclamation.
from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2MJDSba
Dehydration and insulinopenia are necessary and sufficient for euglycemic ketoacidosis in SGLT2 inhibitor-treated rats
Dehydration and insulinopenia are necessary and sufficient for euglycemic ketoacidosis in SGLT2 inhibitor-treated rats
Dehydration and insulinopenia are necessary and sufficient for euglycemic ketoacidosis in SGLT2 inhibitor-treated rats, Published online: 01 February 2019; doi:10.1038/s41467-019-08466-w
The use of sodium-glucose transport protein 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors for the treatment of diabetes has been associated with euglycemic ketoacidosis and increased glucose production and glucagon secretion. Here Perry et al. show that these effects rely on both insulinopenia and dehydration, and thus suggest ways to manage the side effects associated with the use of SGLT2 inhibitors.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2Gi8zTB
Smart scanning for low-illumination and fast RESOLFT nanoscopy in vivo
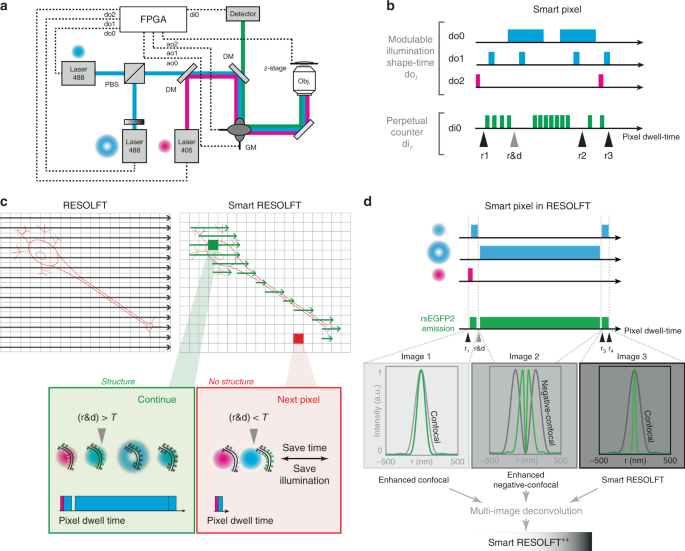
Smart scanning for low-illumination and fast RESOLFT nanoscopy in vivo
Smart scanning for low-illumination and fast RESOLFT nanoscopy in vivo, Published online: 01 February 2019; doi:10.1038/s41467-019-08442-4
Long acquisition time and high illumination intensities needed in super-resolution imaging often generate photobleaching and phototoxicity. Here the authors develop a non-deterministic scanning approach based on a real-time feedback system that enables faster acquisition with lower light doses for in vivo imaging.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2HLjacf
Magnetization reversal driven by low dimensional chaos in a nanoscale ferromagnet
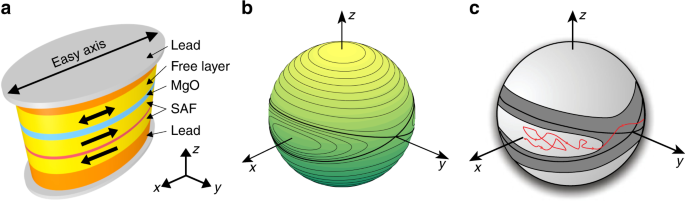
Magnetization reversal driven by low dimensional chaos in a nanoscale ferromagnet
Magnetization reversal driven by low dimensional chaos in a nanoscale ferromagnet, Published online: 01 February 2019; doi:10.1038/s41467-019-08444-2
Energy-efficient manipulation of spins at the nanoscale can advance magnetic storage and computing technologies. Here the authors show that low-dimensional chaos generated by alternating spin torque can induce magnetic switching in a nanoscale ferromagnet.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2HM8hqt
The coevolution of lifespan and reversible plasticity
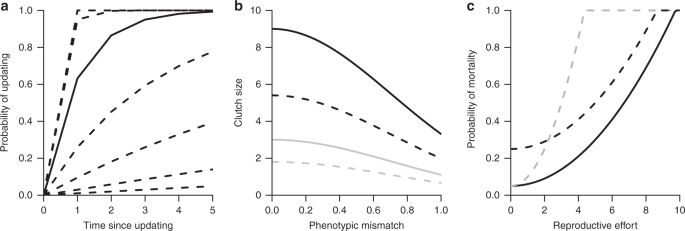
The coevolution of lifespan and reversible plasticity
The coevolution of lifespan and reversible plasticity, Published online: 01 February 2019; doi:10.1038/s41467-019-08502-9
Reversible phenotypic plasticity is expected to be favoured by long lifespan, as this increases the environmental variation individuals experience. Here, the authors develop a model showing how phenotypic plasticity can drive selection on lifespan, leading to coevolution of these traits.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2S4r05t
Satb1 regulates the effector program of encephalitogenic tissue Th17 cells in chronic inflammation
Satb1 regulates the effector program of encephalitogenic tissue Th17 cells in chronic inflammation
Satb1 regulates the effector program of encephalitogenic tissue Th17 cells in chronic inflammation, Published online: 01 February 2019; doi:10.1038/s41467-019-08404-w
A chromatin remodelling factor Satb1 is essential for T cell lineage development in the thymus. Here the authors show that while Satb1 is dispensable for the differentiation of Th17 cells and their response to gut commensals, it plays a critical role in pathogenic Th17 effector function in EAE by directly activating Bhlhe40 and modulating PD-1.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2HLjcRp
Noisy defects in the high-Tc superconductor Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8+x
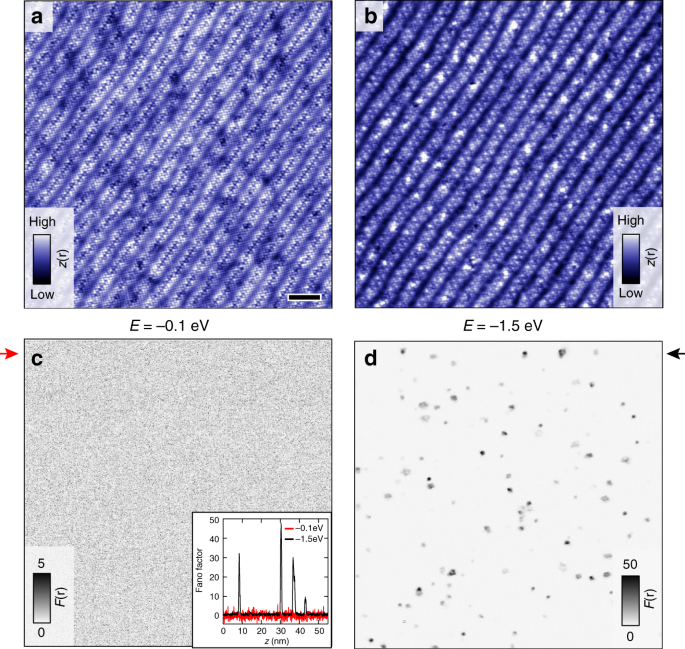
Noisy defects in the high-Tc superconductor Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8+x
Noisy defects in the high-<i>T</i><sub>c</sub> superconductor Bi<sub>2</sub>Sr<sub>2</sub>CaCu<sub>2</sub>O<sub>8+x</sub>, Published online: 01 February 2019; doi:10.1038/s41467-019-08518-1
The effects of dopants in high-temperature superconductors on the surrounding electronic structure give insights into their unconventional microscopic behaviour. Here the authors find a new class of defects that they identify as oxygen dopants whose ionization and local environment induce unusual atomic-scale charge dynamics.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2t0et47
A number-based inventory of size-resolved black carbon particle emissions by global civil aviation
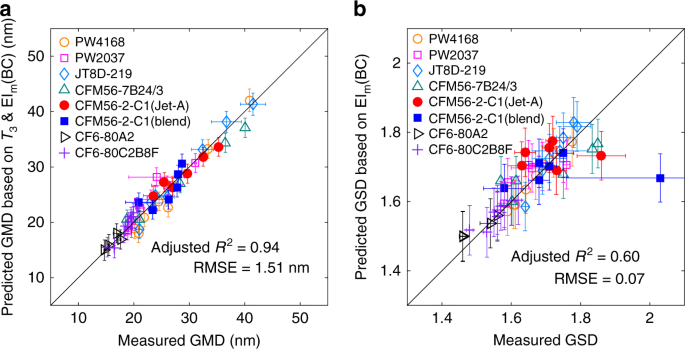
A number-based inventory of size-resolved black carbon particle emissions by global civil aviation
A number-based inventory of size-resolved black carbon particle emissions by global civil aviation, Published online: 01 February 2019; doi:10.1038/s41467-019-08491-9
Size-resolved Black Carbon (BC) particle number emission inventory is not available for global civil aviation. Here the authors converted BC mass emission inventory into number emission inventory and found that aviation BC number emission contributes to 1.3% of total ground anthropogenic emissions and 3.6% on global average.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2Usa4m6
Patterns of genetic differentiation and the footprints of historical migrations in the Iberian Peninsula
Patterns of genetic differentiation and the footprints of historical migrations in the Iberian Peninsula
Patterns of genetic differentiation and the footprints of historical migrations in the Iberian Peninsula, Published online: 01 February 2019; doi:10.1038/s41467-018-08272-w
The Iberian Peninsula has a complex history. Here, the authors analyse the genetic structure of the modern Iberian population at fine scale, revealing historical population movements associated with the time of Muslim rule.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2CZej1n
The LACSEMS: what radiologists need to know
Abstract
Endoscopic drainage is increasingly used in lieu of percutaneous or surgical drainage of pancreatitis-related fluid collections. The lumen-apposing, covered, self-expanding, metallic stent (LACSEMS) is a newly produced stent for the transmural drainage of such fluid collections. The use of LACSEMS devices requires close coordination between knowledgeable radiologic and gastrointestinal providers. We review pancreatitis-related fluid collections and show examples from our experience with LACSEMS and the appropriate case selection, planning, deployment, and follow-up for this novel device.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2G856I2
Imaging post-stereotactic body radiation therapy responses for hepatocellular carcinoma: typical imaging patterns and pitfalls
Abstract
Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) has increased utility in the management of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) ranging from local therapy in early-stage HCC not suitable for other focal therapies to end-stage HCC. As the indications for the use of SBRT in HCC expand, diagnostic imaging is being increasingly used to assess response to treatment. The imaging features of tumor response do not parallel those of other focal therapies such as radiofrequency ablation or trans-arterial chemoembolization that immediately devascularize the tumor. The tumor response to SBRT on imaging takes much longer and often shows gradual changes including the reduction of enhancement and size over several months. It is essential to recognize the typical imaging patterns of response, as well as the appearance of focal liver reaction in the non-target liver that can confound image interpretation. The timing of treatment response assessment imaging is fundamental to minimize the potential for false negative response. The purpose of this article is to review the variable post-SBRT imaging features of HCC and adjacent liver parenchyma and discuss the potential pitfalls of imaging evaluation after SBRT for HCC.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2Uzm7hs
[ASAP] Crystal Structure of the Transcription Regulator RsrR Reveals a [2Fe–2S] Cluster Coordinated by Cys, Glu, and His Residues

from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2S6YxMb
[ASAP] Rational Design via Synergistic Combination Leads to an Outstanding Deep-Ultraviolet Birefringent Li2Na2B2O5 Material with an Unvalued B2O5 Functional Gene

from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2UAGXwZ
Working Scientist podcast: How to beat research funding's boom and bust cycle
Working Scientist podcast: How to beat research funding's boom and bust cycle
Working Scientist podcast: How to beat research funding's boom and bust cycle, Published online: 01 February 2019; doi:10.1038/d41586-019-00403-7
How governments decide when to boost basic research funding, and when to scale back support.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2FZCnVX
Macedonia name change paves way for science cooperation with Greece
Macedonia name change paves way for science cooperation with Greece
Macedonia name change paves way for science cooperation with Greece, Published online: 01 February 2019; doi:10.1038/d41586-019-00346-z
Science features in a deal that ends almost 30 years of hostilities over a shared name.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2GgsPVI
UC Berkeley bans new research funding from Huawei
UC Berkeley bans new research funding from Huawei
UC Berkeley bans new research funding from Huawei, Published online: 01 February 2019; doi:10.1038/d41586-019-00451-z
Moratorium comes after the US justice department charged the Chinese company with stealing trade secrets.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2GgBg3e
Management of Australia’s Murray–Darling basin deemed ‘negligent’
Management of Australia's Murray–Darling basin deemed 'negligent'
Management of Australia's Murray–Darling basin deemed 'negligent', Published online: 01 February 2019; doi:10.1038/d41586-019-00438-w
An independent review offers a scathing assessment of water-sharing policies for the country's largest river system.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2WA0sYj
Watch a levitating droplet pinball around its container
Watch a levitating droplet pinball around its container
Watch a levitating droplet pinball around its container, Published online: 01 February 2019; doi:10.1038/d41586-019-00334-3
A bead of alcohol stars in a playful variation on a centuries-old physics demonstration.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2D9vH3J
French research chief: grants are up, bureaucracy is down
French research chief: grants are up, bureaucracy is down
French research chief: grants are up, bureaucracy is down, Published online: 01 February 2019; doi:10.1038/d41586-019-00157-2
Thierry Damerval speaks to Nature about his first year at the helm of the French National Research Agency, the nation's main competitive funder.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2UxdG6c
Michael F. Atiyah (1929–2019)
Michael F. Atiyah (1929–2019)
Michael F. Atiyah (1929–2019), Published online: 01 February 2019; doi:10.1038/d41586-019-00358-9
Mathematician who transformed the fields he brought together.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2TxVER6
3D printing with light
3D printing with light
3D printing with light, Published online: 31 January 2019; doi:10.1038/d41586-019-00410-8
Researchers develop new type of 3D printer - 'the replicator'.from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2HJyHZP
In vivo comparison of the proangiogenic properties of chlordecone and three of its dechlorinated derivatives formed by in situ chemical reduction
Abstract
In situ chemical reduction (ISCR) has been identified as a possible way for the remediation of soils contaminated by chlordecone (CLD). Evidences provided by the literature indicate an association between the development of prostate cancer and CLD exposure (Multigner et al. 2010). In a previous in vitro study, we demonstrated that the two main dechlorinated CLD derivatives formed by ISCR, CLD-1Cl, and CLD-3Cl have lower cytotoxicity and proangiogenic properties than CLD itself (Legeay et al. 2017). By contrast, nothing is known on the in vivo proangiogenic effect of these dechlorinated derivatives. Based on in vitro data, the aims of this study were therefore to evaluate the in vivo influence of CLD and three of its dechlorinated metabolites in the control of neovascularization in a mice model of prostate cancer. The proangiogenic effect of CLD and three of its dechlorinated derivatives, CLD-1Cl, CLD-3Cl, and CLD-4Cl, was evaluated on a murine model of human prostate tumor (PC-3) treated, at two exposure levels: 33 μg/kg and 1.7 μg/kg respectively reflecting acute and chronic toxic exposure in human. The results of serum measurements show that, for the same ingested dose, the three metabolite concentrations were significantly lower than that of CLD. Dechlorination of CLD lead therefore to molecules that are biologically absorbed or metabolized, or both, faster than the parent molecule. Prostate tumor growth was lower in the groups treated by the three metabolites compared to the one treated by CLD. The vascularization measured on the tumor sections was inversely proportional to the rate of dechlorination, the treatment with CLD-4Cl showing no difference with control animals treated with only the vehicle oil used for all substances tested. We can therefore conclude that the proangiogenic effect of CLD is significantly decreased following the ISCR-resulting dechlorination. Further investigations are needed to elucidate the molecular mechanisms by which dechlorination of CLD reduces proangiogenic effects in prostate tumor.
from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2S1RdkZ
Biocompatibility and biodistribution of surface-modified yttrium oxide nanoparticles for potential theranostic applications
Abstract
The surface of ultrafine yttrium oxide nanoparticles (NPs) with mean size of 7–8 nm was modified with a functional polymer layer to improve their dispersion and impart fluorescent properties for imaging purposes. Surface functionalization was achieved by silanization of yttrium oxide NPs with 3-trimethoxysilylpropyl methacrylate followed by grafting of a co-polymer made of acrylic acid (AA) and ethylene glycol methacrylate phosphate (EGMP). The polymer shell decreases the surface energy of NPs, enhances their polarity, and, as a result, improves their colloidal stability. The synthesized NPs are capable of scavenging free radicals and for this reason have therapeutic potential that warrants further investigations. Furthermore, these stabilized core–shell NPs showed a very low cytotoxicity, confirming that the polymer shell sensibly improves the biocompatibility of bare yttrium oxide NPs, which are otherwise toxic on their own. Poly-EGMP yttrium NPs proved to be safe up to 0.1 mg/g body weight in 1 month old Sprague–Dawley rats, showing also the ability to cross the blood–brain barrier short time after tail injection. The surface modification of yttrium NPs here described allows these NPs to be potentially used in theranostics to reduce neurodegenerative damage due to the heat stress.
from Energy Ecology Environment Ambio via Terpsi Hori on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2UwAYJx
4-Methyl-5-Pentylbenzene-1,3-Diol Regulates Chemotactic Cell Aggregation and Spore Maturation Via Different Mechanisms in Dictyostelium discoideum
Abstract
4-Methyl-5-pentylbenzene-1,3-diol (MPBD), a product of the polyketide synthase SteelyA, is a signaling molecule that regulates Dictyostelium discoideum development. During early development, MPBD controls chemotactic cell aggregation by regulating the expression of genes in the cAMP signaling pathway; however, during culmination at late development, it induces spore maturation. In the present study, we analyzed the effects of MPBD, its derivatives, and a putative MPBD-derived metabolite on developmental defects in the MPBD-less stlA null mutant. Using structure–activity relationship studies, it was observed that in MPBD, the functional groups that were essential for induction of spore maturation were different from those essential for induction of cell aggregation. Dictyoquinone, a putative MPBD metabolite rescued the aggregation defect in stlA null mutant in early development, but not the spore maturation defect at the later stage. Our data suggest that MPBD regulates chemotactic cell aggregation and spore maturation via different mechanisms.
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2Bg1Zd3
Dehydration and insulinopenia are necessary and sufficient for euglycemic ketoacidosis in SGLT2 inhibitor-treated rats
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2S4ABt0
Smart scanning for low-illumination and fast RESOLFT nanoscopy in vivo

from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2UAJiIq
Magnetization reversal driven by low dimensional chaos in a nanoscale ferromagnet

from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2S4AuxA
The coevolution of lifespan and reversible plasticity

from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2UDfCud
Satb1 regulates the effector program of encephalitogenic tissue Th17 cells in chronic inflammation
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2S4s7lo
Noisy defects in the high-Tc superconductor Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8+x

from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2UDfvih
A number-based inventory of size-resolved black carbon particle emissions by global civil aviation

from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2S4AcH0
Patterns of genetic differentiation and the footprints of historical migrations in the Iberian Peninsula
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2UDfoTT
French research chief: grants are up, bureaucracy is down
from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://go.nature.com/2WzeRnz
[ASAP] Aza-Rubottom Oxidation: Synthetic Access to Primary a-Aminoketones

from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2UCaYN1
[ASAP] Zirconium-Based Metal–Organic Frameworks for the Removal of Protein-Bound Uremic Toxin from Human Serum Albumin

from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2UsIV2i
[ASAP] High-Throughput “FP-Tag” Assay for the Identification of Glycosyltransferase Inhibitors

from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2S6uPH9
[ASAP] Rapid Room-Temperature Synthesis of a Metastable Ordered Intermetallic Electrocatalyst

from A via a.sfakia on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2UCb4nR
Αναζήτηση αυτού του ιστολογίου
! # Ola via Alexandros G.Sfakianakis on Inoreader
-
Correction to: SEOM Clinical Guideline for treatment of muscle-invasive and metastatic urothelial bladder cancer (2016) Due to a technical i...
-
Abstract The Gram-negative pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa is found ubiquitously within the environment and is recognised as an opportuni...
